| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

Enzyme-linked receptors are cell-surface receptors with intracellular domains that are associated with an enzyme. In some cases, the intracellular domain of the receptor itself is an enzyme. Other enzyme-linked receptors have a small intracellular domain that interacts directly with an enzyme. The enzyme-linked receptors normally have large extracellular and intracellular domains, but the membrane-spanning region consists of a single alpha-helical region of the peptide strand. When a ligand binds to the extracellular domain, a signal is transferred through the membrane, activating the enzyme. Activation of the enzyme sets off a chain of events within the cell that eventually leads to a response. One example of this type of enzyme-linked receptor is the tyrosine kinase receptor ( [link] ). A kinase is an enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from ATP to another protein. The tyrosine kinase receptor transfers phosphate groups to tyrosine molecules (tyrosine residues). First, signaling molecules bind to the extracellular domain of two nearby tyrosine kinase receptors. The two neighboring receptors then bond together, or dimerize. Phosphates are then added to tyrosine residues on the intracellular domain of the receptors (phosphorylation). The phosphorylated residues can then transmit the signal to the next messenger within the cytoplasm.
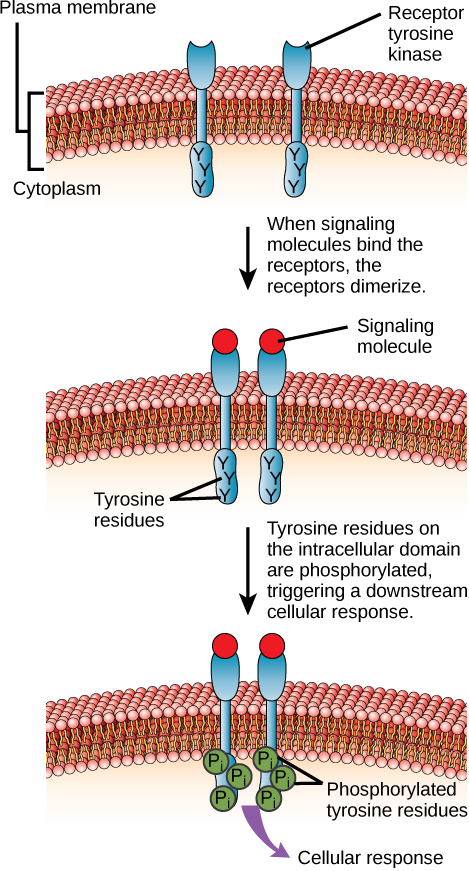
HER2 is a receptor tyrosine kinase. In 30 percent of human breast cancers, HER2 is permanently activated, resulting in unregulated cell division. Lapatinib, a drug used to treat breast cancer, inhibits HER2 receptor tyrosine kinase autophosphorylation (the process by which the receptor adds phosphates onto itself), thus reducing tumor growth by 50 percent. Besides autophosphorylation, which of the following steps would be inhibited by Lapatinib?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Cell biology' conversation and receive update notifications?