This module is from Fundamentals of Mathematics by Denny Burzynski and Wade Ellis, Jr. This module discusses how to read and write decimals. By the end of the module students should understand the meaning of digits occurring to the right of the ones position, be familiar with the meaning of decimal fractions and be able to read and write a decimal fraction.
Section overview
- Digits to the Right of the Ones Position
- Decimal Fractions
- Reading Decimal Fractions
- Writing Decimal Fractions
Digits to the right of the ones position
We began our study of arithmetic (
[link] ) by noting that our number system is called a positional number system with base ten. We also noted that each position has a particular value. We observed that each position has ten times the value of the position to its right.
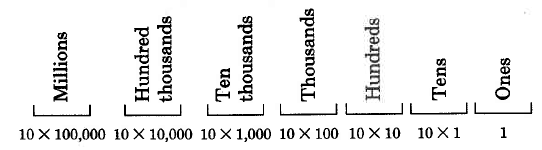
This means that each position has
the value of the position to its left.
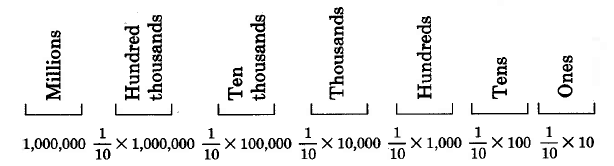
Thus, a digit written to the right of the units position must have a value of
of 1. Recalling that the word "of" translates to multiplication
, we can see that the value of the
first position to the right of the units digit is
of 1, or
The value of the
second position to the right of the units digit is
of
, or
The value of the third position to the right of the units digit is
of
, or
This pattern continues.
We can now see that if we were to write digits in positions to the right of the units positions, those positions have values that are fractions. Not only do the positions have fractional values, but the fractional values are all powers of 10
.
Decimal fractions
Decimal point, decimal
If we are to write numbers with digits appearing to the right of the units digit, we must have a way of denoting where the whole number part ends and the fractional part begins. Mathematicians denote the separation point of the units digit and the tenths digit by writing a
decimal point . The word
decimal comes from the Latin prefix "deci" which means ten, and we use it because we use a base ten number system. Numbers written in this form are called
decimal fractions , or more simply,
decimals .
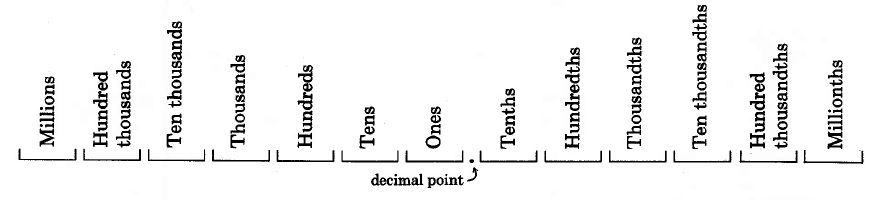
Notice that decimal numbers have the suffix "th."
Decimal fraction
A
decimal fraction is a fraction in which the denominator is a power of 10.
The following numbers are examples of decimals.
- 42.6
The 6 is in the tenths position.
- 9.8014
The 8 is in the tenths position.
The 0 is in the hundredths position.
The 1 is in the thousandths position.
The 4 is in the ten thousandths position.
- 0.93
The 9 is in the tenths position.
The 3 is in the hundredths position.
Quite often a zero is inserted in front of a decimal point (in the units position) of a decimal fraction that has a value less than one. This zero helps keep us from overlooking the decimal point.
- 0.7
The 7 is in the tenths position.
We can insert zeros to the right of the right-most digit in a decimal fraction without changing the value of the number.
Reading decimal fractions
Reading a decimal fraction
To read a decimal fraction,
- Read the whole number part as usual. (If the whole number is less than 1, omit steps 1 and 2.)
- Read the decimal point as the word "and."
- Read the number to the right of the decimal point as if it were a whole number.
- Say the name of the position of the last digit.



