| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
so When the series diverges by the divergence test. The interval of convergence is
so When the series is an absolutely convergent p -series. The interval of convergence is
In the following exercises, find the radius of convergence of each series.
In the following exercises, use the ratio test to determine the radius of convergence of each series.
In the following exercises, given that with convergence in find the power series for each function with the given center a , and identify its interval of convergence.
Use the next exercise to find the radius of convergence of the given series in the subsequent exercises.
Explain why, if then whenever and, therefore, the radius of convergence of is
as and when Therefore, converges when by the n th root test.
Suppose that such that if n is even. Explain why
Suppose that such that if n is odd. Explain why
We can rewrite and since
Suppose that converges on Find the interval of convergence of
Suppose that converges on Find the interval of convergence of
If then so converges.
In the following exercises, suppose that satisfies where for each n . State whether each series converges on the full interval or if there is not enough information to draw a conclusion. Use the comparison test when appropriate.
( Hint: Let if for some n , otherwise
Consider the series where if and otherwise. Then and so the series converges on by the comparison test.
Suppose that is a polynomial of degree N . Find the radius and interval of convergence of
[T] Plot the graphs of and of the partial sums for on the interval Comment on the approximation of by near and near as N increases.
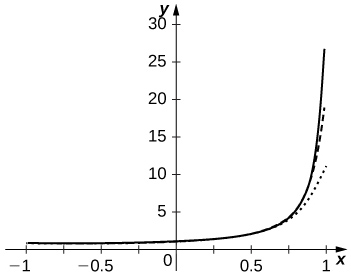
The approximation is more accurate near
The partial sums follow
more closely as
N increases but are never accurate near
since the series diverges there.
[T] Plot the graphs of and of the partial sums for on the interval Comment on the behavior of the sums near and near as N increases.
[T] Plot the graphs of the partial sums for on the interval Comment on the behavior of the sums near and near as N increases.
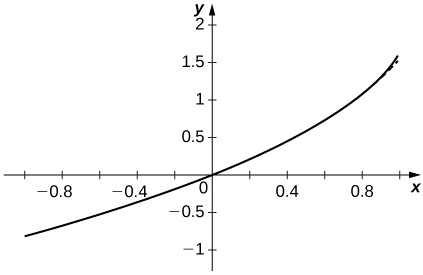
The approximation appears to stabilize quickly near both
[T] Plot the graphs of the partial sums for on the interval Comment on the behavior of the sums near and near as N increases.
[T] Plot the graphs of the partial sums for on the interval Comment on how these plots approximate as N increases.
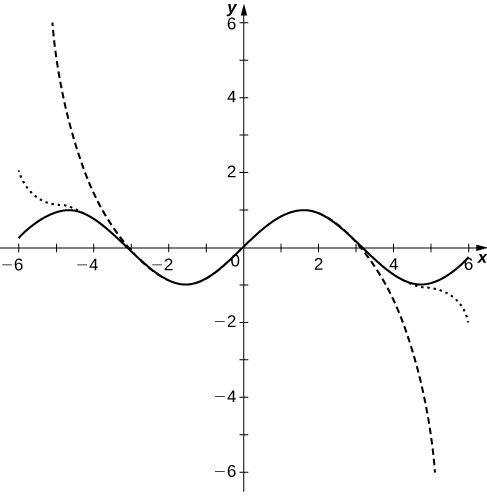
The polynomial curves have roots close to those of
up to their degree and then the polynomials diverge from
[T] Plot the graphs of the partial sums for on the interval Comment on how these plots approximate as N increases.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?