| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Unique for its role in human reproduction, a gamete is a specialized sex cell carrying 23 chromosomes—one half the number in body cells. At fertilization, the chromosomes in one male gamete, called a sperm (or spermatozoon), combine with the chromosomes in one female gamete, called an oocyte. The function of the male reproductive system ( [link] ) is to produce sperm and transfer them to the female reproductive tract. The paired testes are a crucial component in this process, as they produce both sperm and androgens, the hormones that support male reproductive physiology. In humans, the most important male androgen is testosterone. Several accessory organs and ducts aid the process of sperm maturation and transport the sperm and other seminal components to the penis, which delivers sperm to the female reproductive tract. In this section, we examine each of these different structures, and discuss the process of sperm production and transport.
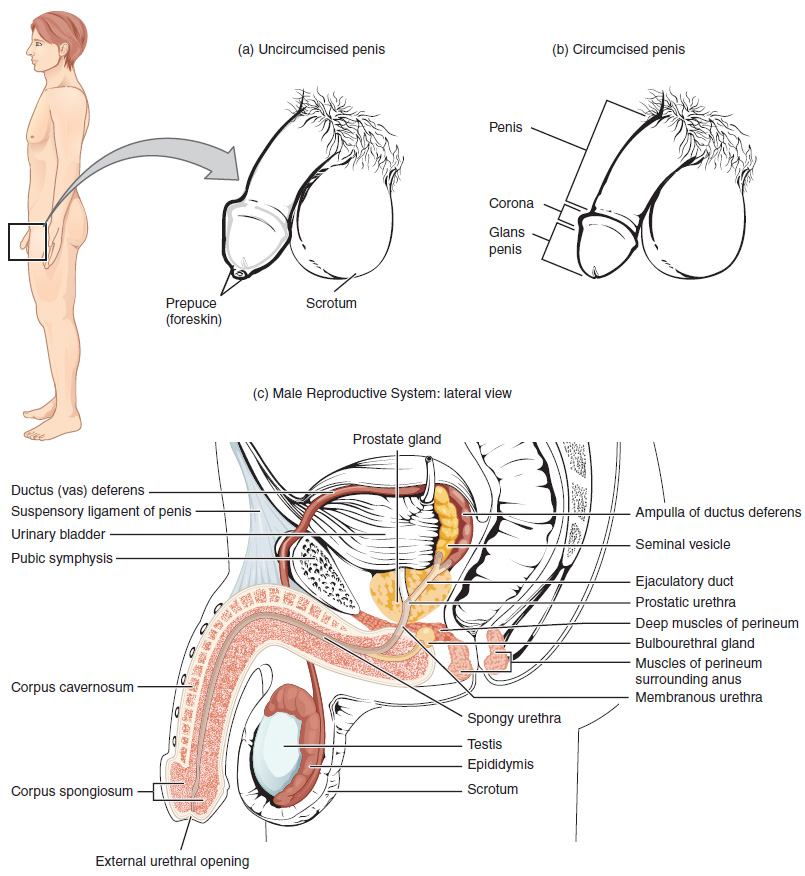
The testes are located in a skin-covered, highly pigmented, muscular sack called the scrotum that extends from the body behind the penis (see [link] ). This location is important in sperm production, which occurs within the testes, and proceeds more efficiently when the testes are kept 2 to 4°C below core body temperature.
The dartos muscle makes up the subcutaneous muscle layer of the scrotum ( [link] ). It continues internally to make up the scrotal septum, a wall that divides the scrotum into two compartments, each housing one testis. Descending from the internal oblique muscle of the abdominal wall are the two cremaster muscles, which cover each testis like a muscular net. By contracting simultaneously, the dartos and cremaster muscles can elevate the testes in cold weather (or water), moving the testes closer to the body and decreasing the surface area of the scrotum to retain heat. Alternatively, as the environmental temperature increases, the scrotum relaxes, moving the testes farther from the body core and increasing scrotal surface area, which promotes heat loss. Externally, the scrotum has a raised medial thickening on the surface called the raphae.
The testes (singular = testis) are the male gonads —that is, the male reproductive organs. They produce both sperm and androgens, such as testosterone, and are active throughout the reproductive lifespan of the male.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the '101-321-va - vertebrate form and function ii' conversation and receive update notifications?