| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
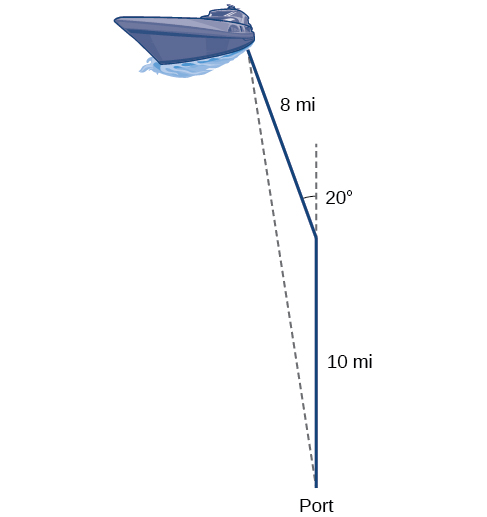
Suppose a boat leaves port, travels 10 miles, turns 20 degrees, and travels another 8 miles as shown in [link] . How far from port is the boat?
Unfortunately, while the Law of Sines enables us to address many non-right triangle cases, it does not help us with triangles where the known angle is between two known sides, a SAS (side-angle-side) triangle , or when all three sides are known, but no angles are known, a SSS (side-side-side) triangle . In this section, we will investigate another tool for solving oblique triangles described by these last two cases.
The tool we need to solve the problem of the boat’s distance from the port is the Law of Cosines , which defines the relationship among angle measurements and side lengths in oblique triangles. Three formulas make up the Law of Cosines. At first glance, the formulas may appear complicated because they include many variables. However, once the pattern is understood, the Law of Cosines is easier to work with than most formulas at this mathematical level.
Understanding how the Law of Cosines is derived will be helpful in using the formulas. The derivation begins with the Generalized Pythagorean Theorem , which is an extension of the Pythagorean Theorem to non-right triangles. Here is how it works: An arbitrary non-right triangle is placed in the coordinate plane with vertex at the origin, side drawn along the x -axis, and vertex located at some point in the plane, as illustrated in [link] . Generally, triangles exist anywhere in the plane, but for this explanation we will place the triangle as noted.
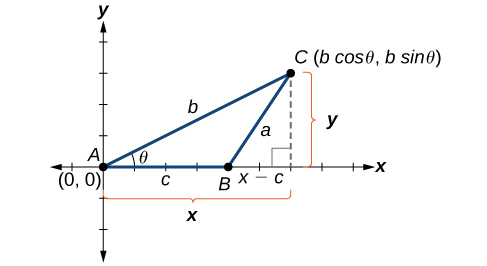
We can drop a perpendicular from to the x- axis (this is the altitude or height). Recalling the basic trigonometric identities , we know that
In terms of and The point located at has coordinates Using the side as one leg of a right triangle and as the second leg, we can find the length of hypotenuse using the Pythagorean Theorem. Thus,
The formula derived is one of the three equations of the Law of Cosines. The other equations are found in a similar fashion.
Keep in mind that it is always helpful to sketch the triangle when solving for angles or sides. In a real-world scenario, try to draw a diagram of the situation. As more information emerges, the diagram may have to be altered. Make those alterations to the diagram and, in the end, the problem will be easier to solve.
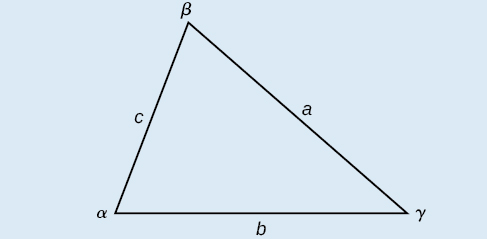
The Law of Cosines states that the square of any side of a triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides minus twice the product of the other two sides and the cosine of the included angle. For triangles labeled as in [link] , with angles and and opposite corresponding sides and respectively, the Law of Cosines is given as three equations.
To solve for a missing side measurement, the corresponding opposite angle measure is needed.
When solving for an angle, the corresponding opposite side measure is needed. We can use another version of the Law of Cosines to solve for an angle.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Contemporary math applications' conversation and receive update notifications?