| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Determine the normal boiling point (in kelvin) of dichloroethane, CH 2 Cl 2 . Find the actual boiling point using the Internet or some other source, and calculate the percent error in the temperature. Explain the differences, if any, between the two values.
Under what conditions is spontaneous?
The reaction will be spontaneous at temperatures greater than 287 K.
At room temperature, the equilibrium constant ( K w ) for the self-ionization of water is 1.00 10 −14 . Using this information, calculate the standard free energy change for the aqueous reaction of hydrogen ion with hydroxide ion to produce water. (Hint: The reaction is the reverse of the self-ionization reaction.)
Hydrogen sulfide is a pollutant found in natural gas. Following its removal, it is converted to sulfur by the reaction What is the equilibrium constant for this reaction? Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic?
K = 5.35
10
15
The process is exothermic.
Consider the decomposition of CaCO 3 ( s ) into CaO( s ) and CO 2 ( g ). What is the equilibrium partial pressure of CO 2 at room temperature?
In the laboratory, hydrogen chloride (HCl( g )) and ammonia (NH 3 ( g )) often escape from bottles of their solutions and react to form the ammonium chloride (NH 4 Cl( s )), the white glaze often seen on glassware. Assuming that the number of moles of each gas that escapes into the room is the same, what is the maximum partial pressure of HCl and NH 3 in the laboratory at room temperature? (Hint: The partial pressures will be equal and are at their maximum value when at equilibrium.)
1.0 10 −8 atm. This is the maximum pressure of the gases under the stated conditions.
Benzene can be prepared from acetylene. Determine the equilibrium constant at 25 °C and at 850 °C. Is the reaction spontaneous at either of these temperatures? Why is all acetylene not found as benzene?
Carbon dioxide decomposes into CO and O 2 at elevated temperatures. What is the equilibrium partial pressure of oxygen in a sample at 1000 °C for which the initial pressure of CO 2 was 1.15 atm?
Carbon tetrachloride, an important industrial solvent, is prepared by the chlorination of methane at 850 K.
What is the equilibrium constant for the reaction at 850 K? Would the reaction vessel need to be heated or cooled to keep the temperature of the reaction constant?
Acetic acid, CH
3 CO
2 H, can form a dimer, (CH
3 CO
2 H)
2 , in the gas phase.
The dimer is held together by two hydrogen bonds with a total strength of 66.5 kJ per mole of dimer.
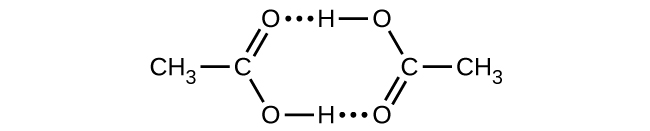
At 25 °C, the equilibrium constant for the dimerization is 1.3 10 3 (pressure in atm). What is Δ S ° for the reaction?
−0.16 kJ
Nitric acid, HNO
3 , can be prepared by the following sequence of reactions:
How much heat is evolved when 1 mol of NH 3 ( g ) is converted to HNO 3 ( l )? Assume standard states at 25 °C.
Determine Δ G for the following reactions.
(a) Antimony pentachloride decomposes at 448 °C. The reaction is:
An equilibrium mixture in a 5.00 L flask at 448 °C contains 3.85 g of SbCl 5 , 9.14 g of SbCl 3 , and 2.84 g of Cl 2 .
(b) Chlorine molecules dissociate according to this reaction:
1.00% of Cl 2 molecules dissociate at 975 K and a pressure of 1.00 atm.
(a) −22.1 kJ;
(b) 61.6 kJ/mol

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ut austin - principles of chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?