| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Show that the alternating series does not converge. What hypothesis of the alternating series test is not met?
The formula will be derived in the next chapter. Use the remainder to find a bound for the error in estimating by the fifth partial sum for and
For one has When When When
The formula will be derived in the next chapter. Use the remainder to find a bound for the error in estimating by the fifth partial sum for and
How many terms in are needed to approximate accurate to an error of at most
Let Then when or and whereas
How many terms in are needed to approximate accurate to an error of at most
Sometimes the alternating series converges to a certain fraction of an absolutely convergent series at a faster rate. Given that find Which of the series and gives a better estimation of using terms?
Let Then so
The alternating series is more accurate for terms.
The following alternating series converge to given multiples of Find the value of predicted by the remainder estimate such that the partial sum of the series accurately approximates the left-hand side to within the given error. Find the minimum for which the error bound holds, and give the desired approximate value in each case. Up to decimals places,
[T] error
[T] The series plays an important role in signal processing. Show that converges whenever ( Hint: Use the formula for the sine of a sum of angles.)
[T] If what is
The partial sum is the same as that for the alternating harmonic series.
[T] Plot the series for Explain why diverges when How does the series behave for other
[T] Plot the series for and comment on its behavior
The series jumps rapidly near the endpoints. For
away from the endpoints, the graph looks like
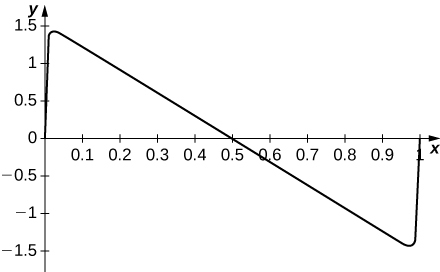
[T] Plot the series for and describe its graph.
[T] The alternating harmonic series converges because of cancellation among its terms. Its sum is known because the cancellation can be described explicitly. A random harmonic series is one of the form where is a randomly generated sequence of in which the values are equally likely to occur. Use a random number generator to produce random and plot the partial sums of your random harmonic sequence for to Compare to a plot of the first partial sums of the harmonic series.
Here is a typical result. The top curve consists of partial sums of the harmonic series. The bottom curve plots partial sums of a random harmonic series.

[T] Estimates of can be accelerated by writing its partial sums as and recalling that converges to one as Compare the estimate of using the sums with the estimate using
[T] The Euler transform rewrites as For the alternating harmonic series, it takes the form Compute partial sums of until they approximate accurate to within How many terms are needed? Compare this answer to the number of terms of the alternating harmonic series are needed to estimate
By the alternating series test, so one needs terms of the alternating harmonic series to estimate to within The first partial sums of the series are (up to four decimals) and the tenth partial sum is within of
[T] In the text it was stated that a conditionally convergent series can be rearranged to converge to any number. Here is a slightly simpler, but similar, fact. If is such that as but diverges, then, given any number there is a sequence of such that Show this for as follows.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?