| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The characteristic sound of a motorcycle buzzing by is an example of the Doppler effect . The high-pitch scream shifts dramatically to a lower-pitch roar as the motorcycle passes by a stationary observer. The closer the motorcycle brushes by, the more abrupt the shift. The faster the motorcycle moves, the greater the shift. We also hear this characteristic shift in frequency for passing race cars, airplanes, and trains. It is so familiar that it is used to imply motion and children often mimic it in play.
The Doppler effect is an alteration in the observed frequency of a sound due to motion of either the source or the observer. Although less familiar, this effect is easily noticed for a stationary source and moving observer. For example, if you ride a train past a stationary warning bell, you will hear the bell’s frequency shift from high to low as you pass by. The actual change in frequency due to relative motion of source and observer is called a Doppler shift . The Doppler effect and Doppler shift are named for the Austrian physicist and mathematician Christian Johann Doppler (1803–1853), who did experiments with both moving sources and moving observers. Doppler, for example, had musicians play on a moving open train car and also play standing next to the train tracks as a train passed by. Their music was observed both on and off the train, and changes in frequency were measured.
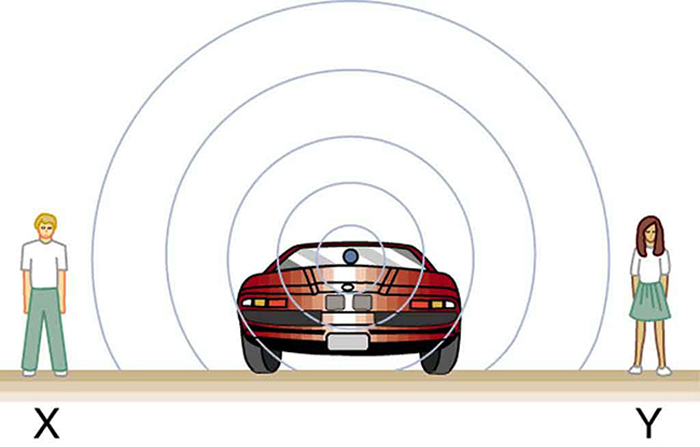
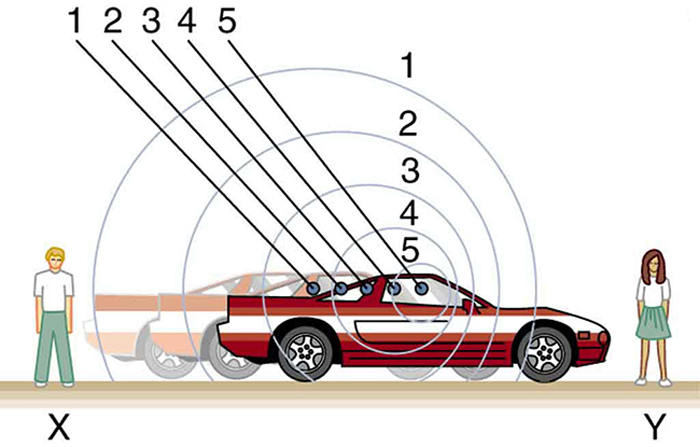
What causes the Doppler shift? [link] , [link] , and [link] compare sound waves emitted by stationary and moving sources in a stationary air mass. Each disturbance spreads out spherically from the point where the sound was emitted. If the source is stationary, then all of the spheres representing the air compressions in the sound wave centered on the same point, and the stationary observers on either side see the same wavelength and frequency as emitted by the source, as in [link] . If the source is moving, as in [link] , then the situation is different. Each compression of the air moves out in a sphere from the point where it was emitted, but the point of emission moves. This moving emission point causes the air compressions to be closer together on one side and farther apart on the other. Thus, the wavelength is shorter in the direction the source is moving (on the right in [link] ), and longer in the opposite direction (on the left in [link] ). Finally, if the observers move, as in [link] , the frequency at which they receive the compressions changes. The observer moving toward the source receives them at a higher frequency, and the person moving away from the source receives them at a lower frequency.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics for the modern world' conversation and receive update notifications?