| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Earl is building a doghouse, whose front is in the shape of a square topped with a triangle. There will be a rectangular door through which the dog can enter and exit the house. Earl wants to find the area of the front of the doghouse so that he can purchase the correct amount of paint. Using the measurements of the front of the house, shown in [link] , we can create an expression that combines several variable terms, allowing us to solve this problem and others like it.
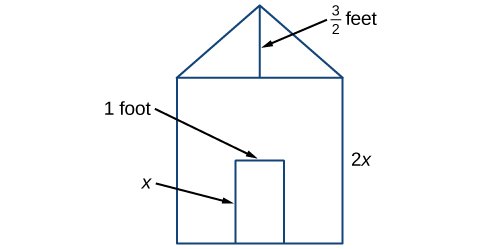
First find the area of the square in square feet.
Then find the area of the triangle in square feet.
Next find the area of the rectangular door in square feet.
The area of the front of the doghouse can be found by adding the areas of the square and the triangle, and then subtracting the area of the rectangle. When we do this, we get or ft 2 .
In this section, we will examine expressions such as this one, which combine several variable terms.
The formula just found is an example of a polynomial , which is a sum of or difference of terms, each consisting of a variable raised to a nonnegative integer power. A number multiplied by a variable raised to an exponent, such as is known as a coefficient . Coefficients can be positive, negative, or zero, and can be whole numbers, decimals, or fractions. Each product such as is a term of a polynomial . If a term does not contain a variable, it is called a constant .
A polynomial containing only one term, such as is called a monomial . A polynomial containing two terms, such as is called a binomial . A polynomial containing three terms, such as is called a trinomial .
We can find the degree of a polynomial by identifying the highest power of the variable that occurs in the polynomial. The term with the highest degree is called the leading term because it is usually written first. The coefficient of the leading term is called the leading coefficient . When a polynomial is written so that the powers are descending, we say that it is in standard form.
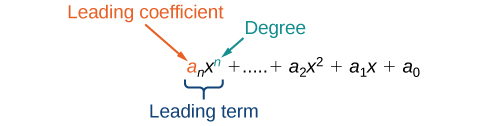
A polynomial is an expression that can be written in the form
Each real number a i is called a coefficient . The number that is not multiplied by a variable is called a constant . Each product is a term of a polynomial . The highest power of the variable that occurs in the polynomial is called the degree of a polynomial. The leading term is the term with the highest power, and its coefficient is called the leading coefficient .
Given a polynomial expression, identify the degree and leading coefficient .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Selected topics in algebra' conversation and receive update notifications?