| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The heat needed to change the temperature of a given substance (with no change in phase) is: q = m c Δ T (see previous chapter on thermochemistry). The heat needed to induce a given change in phase is given by q = n Δ H .
Using these equations with the appropriate values for specific heat of ice, water, and steam, and enthalpies of fusion and vaporization, we have:
Converting the quantities in J to kJ permits them to be summed, yielding the total heat required:
40.5 kJ
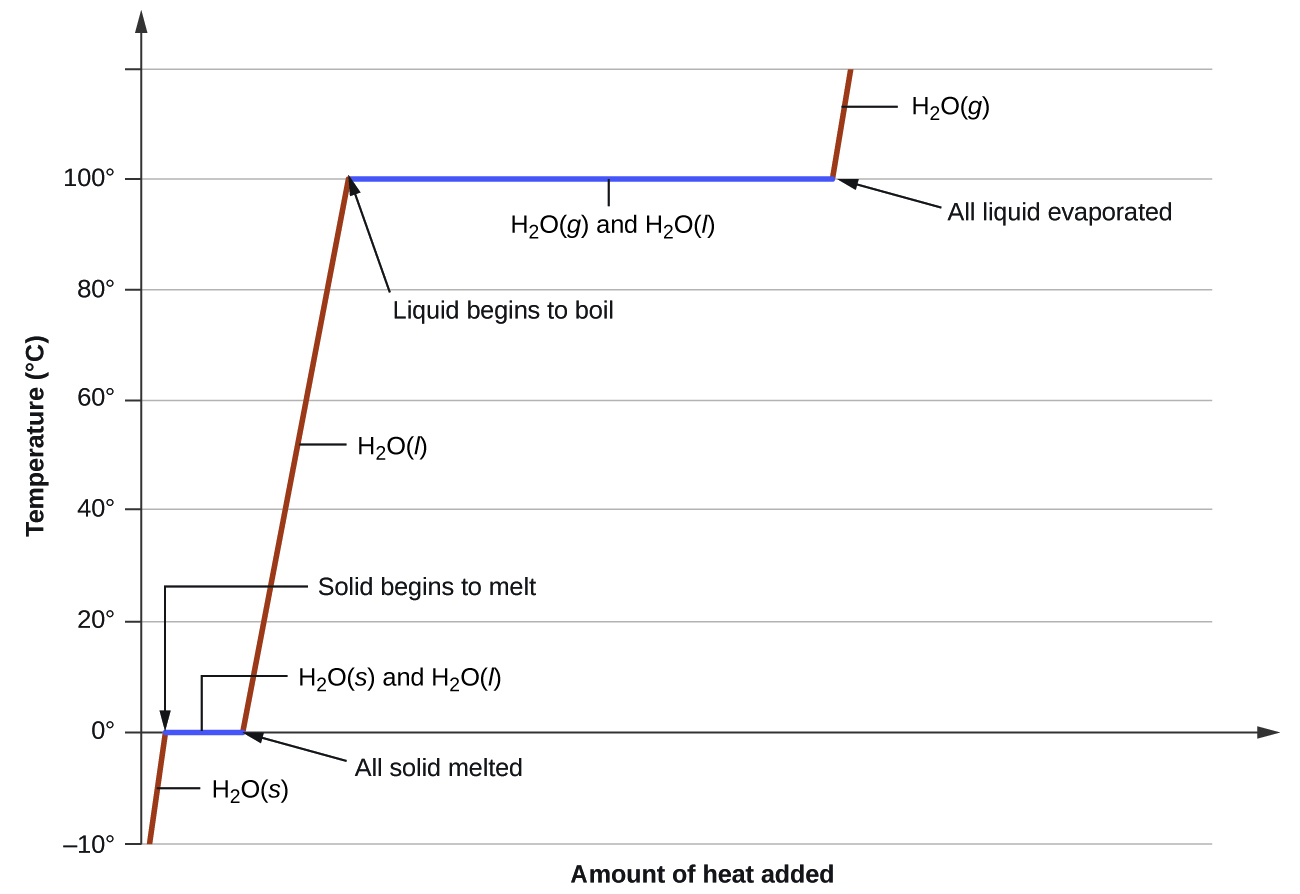
Phase transitions are processes that convert matter from one physical state into another. There are six phase transitions between the three phases of matter. Melting, vaporization, and sublimation are all endothermic processes, requiring an input of heat to overcome intermolecular attractions. The reciprocal transitions of freezing, condensation, and deposition are all exothermic processes, involving heat as intermolecular attractive forces are established or strengthened. The temperatures at which phase transitions occur are determined by the relative strengths of intermolecular attractions and are, therefore, dependent on the chemical identity of the substance.
Heat is added to boiling water. Explain why the temperature of the boiling water does not change. What does change?
Heat is added to ice at 0 °C. Explain why the temperature of the ice does not change. What does change?
The heat is absorbed by the ice, providing the energy required to partially overcome intermolecular attractive forces in the solid and causing a phase transition to liquid water. The solution remains at 0 °C until all the ice is melted. Only the amount of water existing as ice changes until the ice disappears. Then the temperature of the water can rise.
What feature characterizes the dynamic equilibrium between a liquid and its vapor in a closed container?
Identify two common observations indicating some liquids have sufficient vapor pressures to noticeably evaporate?
We can see the amount of liquid in an open container decrease and we can smell the vapor of some liquids.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ut austin - principles of chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?