| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We witness and utilize changes of physical state, or phase transitions, in a great number of ways. As one example of global significance, consider the evaporation, condensation, freezing, and melting of water. These changes of state are essential aspects of our earth’s water cycle as well as many other natural phenomena and technological processes of central importance to our lives. In this module, the essential aspects of phase transitions are explored.
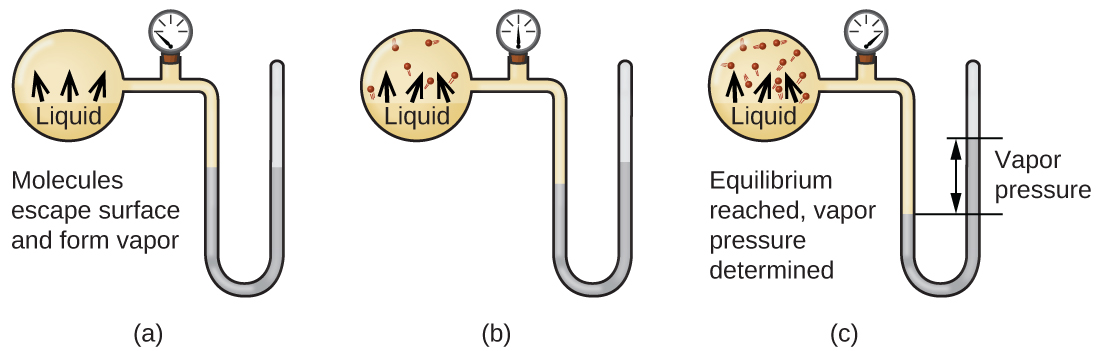
When a liquid vaporizes in a closed container, gas molecules cannot escape. As these gas phase molecules move randomly about, they will occasionally collide with the surface of the condensed phase, and in some cases, these collisions will result in the molecules re-entering the condensed phase. The change from the gas phase to the liquid is called condensation . When the rate of condensation becomes equal to the rate of vaporization , neither the amount of the liquid nor the amount of the vapor in the container changes. The vapor in the container is then said to be in equilibrium with the liquid. Keep in mind that this is not a static situation, as molecules are continually exchanged between the condensed and gaseous phases. Such is an example of a dynamic equilibrium , the status of a system in which reciprocal processes (for example, vaporization and condensation) occur at equal rates. The pressure exerted by the vapor in equilibrium with a liquid in a closed container at a given temperature is called the liquid’s vapor pressure (or equilibrium vapor pressure). The area of the surface of the liquid in contact with a vapor and the size of the vessel have no effect on the vapor pressure, although they do affect the time required for the equilibrium to be reached. We can measure the vapor pressure of a liquid by placing a sample in a closed container, like that illustrated in [link] , and using a manometer to measure the increase in pressure that is due to the vapor in equilibrium with the condensed phase.
The chemical identities of the molecules in a liquid determine the types (and strengths) of intermolecular attractions possible; consequently, different substances will exhibit different equilibrium vapor pressures. Relatively strong intermolecular attractive forces will serve to impede vaporization as well as favoring “recapture” of gas-phase molecules when they collide with the liquid surface, resulting in a relatively low vapor pressure. Weak intermolecular attractions present less of a barrier to vaporization, and a reduced likelihood of gas recapture, yielding relatively high vapor pressures. The following example illustrates this dependence of vapor pressure on intermolecular attractive forces.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ut austin - principles of chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?