| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The following equations are not in slope-intercept form:
The following equation are in slope-intercept form. In each case, specify the slope and .
When the equation of a line is written in slope-intercept form, two important properties of the line can be seen: the slope and the intercept . Let's look at these two properties by graphing several lines and observing them carefully.
Graph the line .
| 0 | ||
| 4 | 1 | |
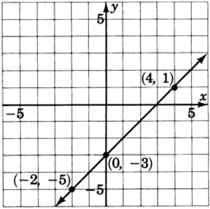
Looking carefully at this line, answer the following two questions.
At what number does this line cross the ? Do you see this number in the equation?
The line crosses the at .
Place your pencil at any point on the line. Move your pencil exactly one unit horizontally to the right. Now, how many units straight up or down must you move your pencil to get back on the line? Do you see this number in the equation?
After moving horizontally one unit to the right, we must move exactly one vertical unit up. This number is the coefficient of .
Graph the line .
| 0 | 1 | |
| 3 | 3 | |
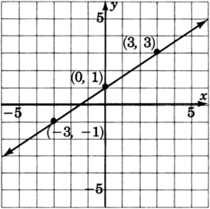
Looking carefully at this line, answer the following two questions.
At what number does this line cross the ? Do you see this number in the equation?
The line crosses the at .
Place your pencil at any point on the line. Move your pencil exactly one unit horizontally to the right. Now, how many units straight up or down must you move your pencil to get back on the line? Do you see this number in the equation?
After moving horizontally one unit to the right, we must move exactly unit upward. This number is the coefficient of .
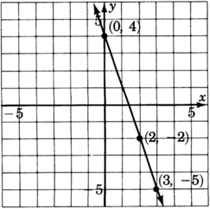
Graph the line .
| 0 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 2 |
Looking carefully at this line, answer the following two questions.
At what number does the line cross the ? Do you see this number in the equation?
The line crosses the at . After moving horizontally 1 unit to the right, we must move exactly 3 units downward.
Place your pencil at any point on the line. Move your pencil exactly one unit horizontally to the right. Now, how many units straight up or down must you move your pencil to get back on the line? Do you see this number in the equation?
In the graphs constructed in Sample Set B and Practice Set B, each equation had the form . We can answer the same questions by using this form of the equation (shown in the diagram).
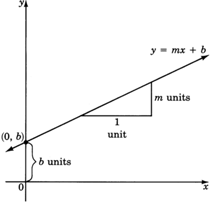
At what number does the line cross the ? Do you see this number in the equation?
In each case, the line crosses the at the constant . The number is the number at which the line crosses the , and it is called the . The ordered pair corresponding to the is
Place your pencil at any point on the line. Move your pencil exactly one unit horizontally to the right. Now, how many units straight up or down must you move your pencil to get back on the line? Do you see this number in the equation?
To get back on the line, we must move our pencil exactly vertical units.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Algebra i for the community college' conversation and receive update notifications?