| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
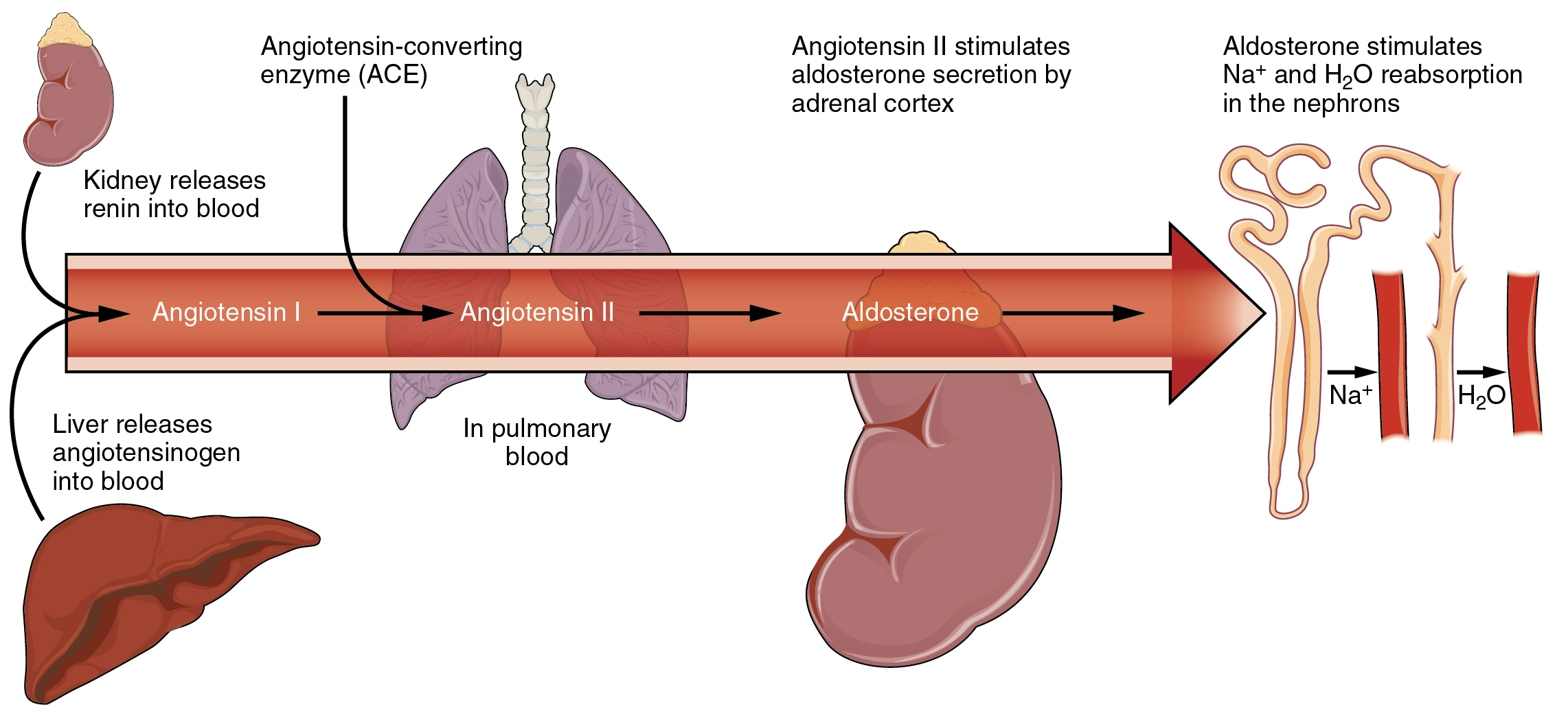
Sodium is reabsorbed from the renal filtrate, and potassium is excreted into the filtrate in the renal collecting tubule. The control of this exchange is governed principally by two hormones—aldosterone and angiotensin II.
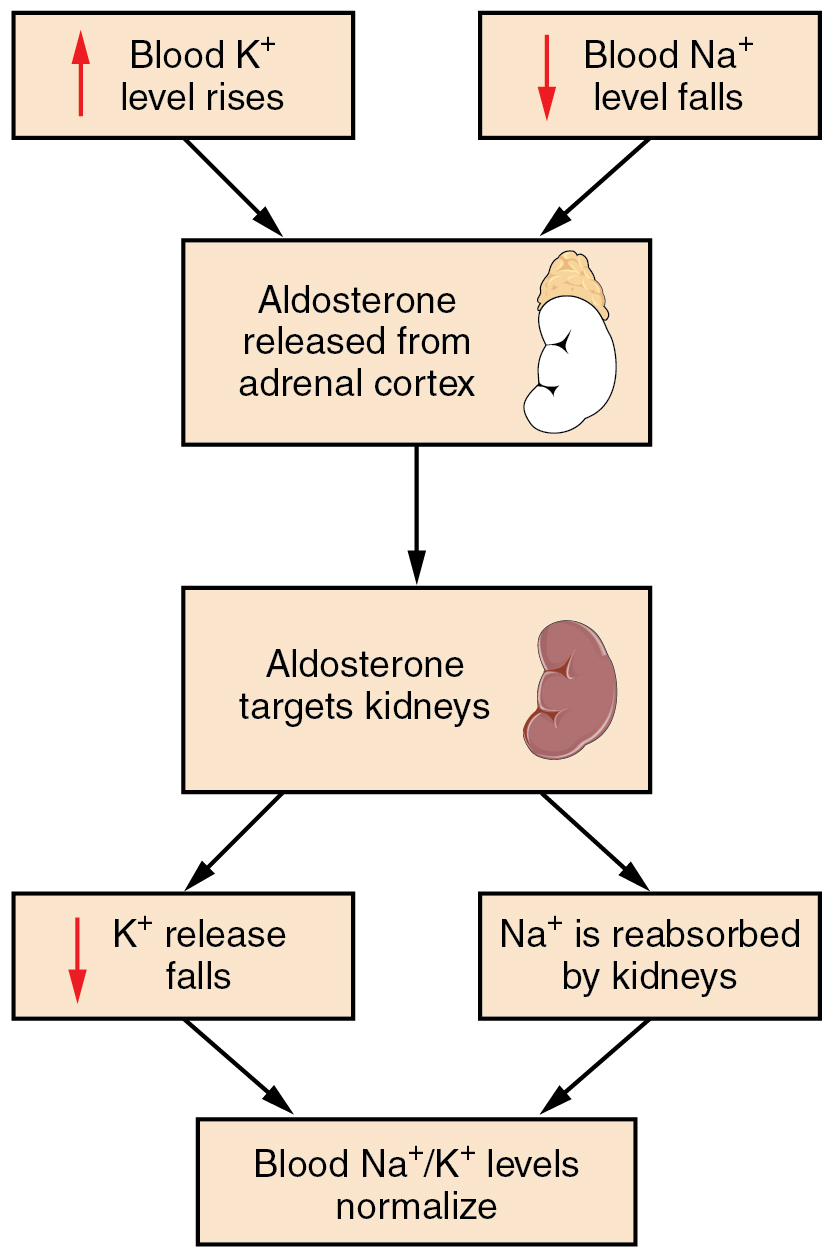
Recall that aldosterone increases the excretion of potassium and the reabsorption of sodium in the distal tubule. Aldosterone is released if blood levels of potassium increase, if blood levels of sodium severely decrease, or if blood pressure decreases. Its net effect is to conserve and increase water levels in the plasma by reducing the excretion of sodium, and thus water, from the kidneys. In a negative feedback loop, increased osmolality of the ECF (which follows aldosterone-stimulated sodium absorption) inhibits the release of the hormone ( [link] ).
Angiotensin II causes vasoconstriction and an increase in systemic blood pressure. This action increases the glomerular filtration rate, resulting in more material filtered out of the glomerular capillaries and into Bowman’s capsule. Angiotensin II also signals an increase in the release of aldosterone from the adrenal cortex.
In the distal convoluted tubules and collecting ducts of the kidneys, aldosterone stimulates the synthesis and activation of the sodium-potassium pump ( [link] ). Sodium passes from the filtrate, into and through the cells of the tubules and ducts, into the ECF and then into capillaries. Water follows the sodium due to osmosis. Thus, aldosterone causes an increase in blood sodium levels and blood volume. Aldosterone’s effect on potassium is the reverse of that of sodium; under its influence, excess potassium is pumped into the renal filtrate for excretion from the body.
Calcium and phosphate are both regulated through the actions of three hormones: parathyroid hormone (PTH), dihydroxyvitamin D (calcitriol), and calcitonin. All three are released or synthesized in response to the blood levels of calcium.
PTH is released from the parathyroid gland in response to a decrease in the concentration of blood calcium. The hormone activates osteoclasts to break down bone matrix and release inorganic calcium-phosphate salts. PTH also increases the gastrointestinal absorption of dietary calcium by converting vitamin D into dihydroxyvitamin D (calcitriol), an active form of vitamin D that intestinal epithelial cells require to absorb calcium.
PTH raises blood calcium levels by inhibiting the loss of calcium through the kidneys. PTH also increases the loss of phosphate through the kidneys.
Calcitonin is released from the thyroid gland in response to elevated blood levels of calcium. The hormone increases the activity of osteoblasts, which remove calcium from the blood and incorporate calcium into the bony matrix.
Electrolytes serve various purposes, such as helping to conduct electrical impulses along cell membranes in neurons and muscles, stabilizing enzyme structures, and releasing hormones from endocrine glands. The ions in plasma also contribute to the osmotic balance that controls the movement of water between cells and their environment. Imbalances of these ions can result in various problems in the body, and their concentrations are tightly regulated. Aldosterone and angiotensin II control the exchange of sodium and potassium between the renal filtrate and the renal collecting tubule. Calcium and phosphate are regulated by PTH, calcitrol, and calcitonin.
Watch this video to see an explanation of the effect of seawater on humans. What effect does drinking seawater have on the body?
Drinking seawater dehydrates the body as the body must pass sodium through the kidneys, and water follows.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology: energy, maintenance and environmental exchange' conversation and receive update notifications?