| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
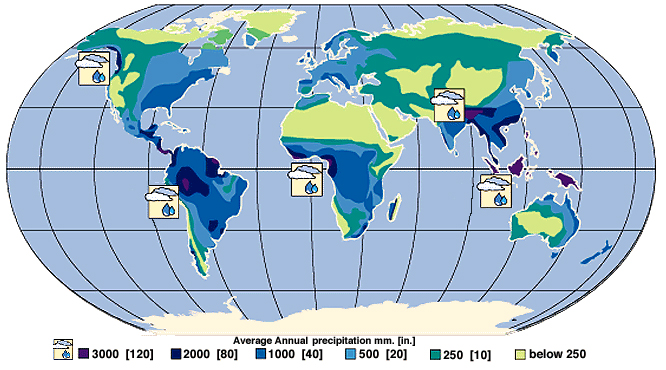
Precipitation is a major control of fresh water availability, and it is unevenly distributed around the globe (see [link] ). More precipitation falls near the equator, and landmasses there are characterized by a tropical rainforest climate. Less precipitation tends to fall near 20–30° north and south latitude, where the world’s largest deserts are located. These rainfall and climate patterns are related to global wind circulation cells. The intense sunlight at the equator heats air, causing it to rise and cool, which decreases the ability of the air mass to hold water vapor and results in frequent rainstorms. Around 30° north and south latitude, descending air conditions produce warmer air, which increases its ability to hold water vapor and results in dry conditions. Both the dry air conditions and the warm temperatures of these latitude belts favor evaporation. Global precipitation and climate patterns are also affected by the size of continents, major ocean currents, and mountains.
Flowing water from rain and melted snow on land enters river channels by surface runoff (see [link] ) and groundwater seepage (see [link] ). River discharge describes the volume of water moving through a river channel over time (see [link] ). The relative contributions of surface runoff vs. groundwater seepage to river discharge depend on precipitation patterns, vegetation, topography, land use, and soil characteristics. Soon after a heavy rainstorm, river discharge increases due to surface runoff. The steady normal flow of river water is mainly from groundwater that discharges into the river. Gravity pulls river water downhill toward the ocean. Along the way the moving water of a river can erode soil particles and dissolve minerals, creating the river’s load of moving sediment grains and dissolved ions. Groundwater also contributes a large amount of the dissolved ions in river water. The geographic area drained by a river and its tributaries is called a drainage basin . The Mississippi River drainage basin includes approximately 40% of the U.S., a measure that includes the smaller drainage basins (also called watersheds), such as the Ohio River and Missouri River that help to comprise it. Rivers are an important water resource for irrigation and many cities around the world. Some of the world’s rivers that have had international disputes over water supply include the Colorado (Mexico, southwest U.S.), Nile (Egypt, Ethiopia, Sudan), Euphrates (Iraq, Syria, Turkey), Ganges (Bangladesh, India), and Jordan (Israel, Jordan, Syria).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Bi 101 for lbcc ilearn campus' conversation and receive update notifications?