| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
At a fibrous joint, the adjacent bones are directly connected to each other by fibrous connective tissue, and thus the bones do not have a joint cavity between them ( [link] ). The gap between the bones may be narrow or wide. There are three types of fibrous joints. A suture is the narrow fibrous joint found between most bones of the skull. At a syndesmosis joint, the bones are more widely separated but are held together by a narrow band of fibrous connective tissue called a ligament or a wide sheet of connective tissue called an interosseous membrane. This type of fibrous joint is found between the shaft regions of the long bones in the forearm and in the leg. Lastly, a gomphosis is the narrow fibrous joint between the roots of a tooth and the bony socket in the jaw into which the tooth fits.
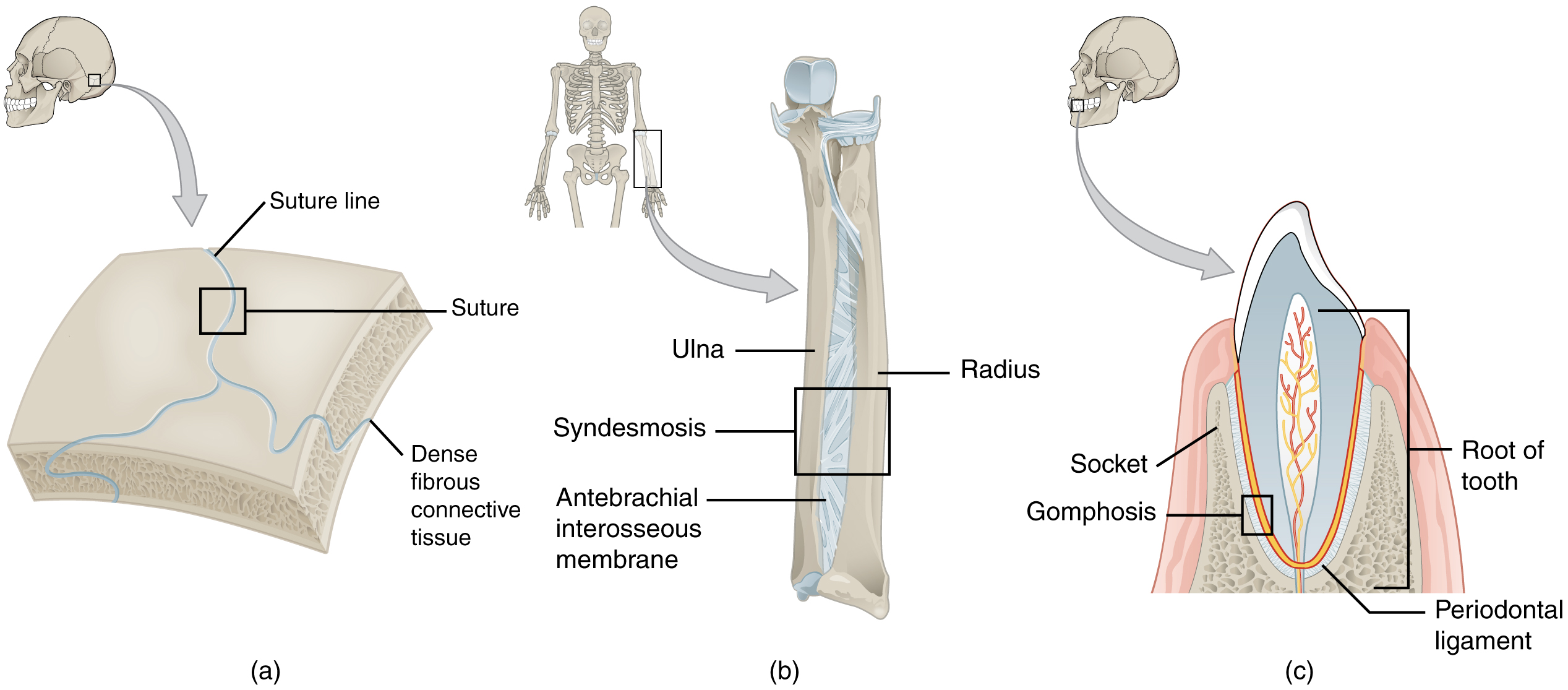
All the bones of the skull, except for the mandible, are joined to each other by a fibrous joint called a suture . The fibrous connective tissue found at a suture (“to bind or sew”) strongly unites the adjacent skull bones and thus helps to protect the brain and form the face. In adults, the skull bones are closely opposed and fibrous connective tissue fills the narrow gap between the bones. The suture is frequently convoluted, forming a tight union that prevents most movement between the bones. (See [link] a .) Thus, skull sutures are functionally classified as a synarthrosis, although some sutures may allow for slight movements between the cranial bones.
In newborns and infants, the areas of connective tissue between the bones are much wider, especially in those areas on the top and sides of the skull that will become the sagittal, coronal, squamous, and lambdoid sutures. These broad areas of connective tissue are called fontanelles ( [link] ). During birth, the fontanelles provide flexibility to the skull, allowing the bones to push closer together or to overlap slightly, thus aiding movement of the infant’s head through the birth canal. After birth, these expanded regions of connective tissue allow for rapid growth of the skull and enlargement of the brain. The fontanelles greatly decrease in width during the first year after birth as the skull bones enlarge. When the connective tissue between the adjacent bones is reduced to a narrow layer, these fibrous joints are now called sutures. At some sutures, the connective tissue will ossify and be converted into bone, causing the adjacent bones to fuse to each other. This fusion between bones is called a synostosis (“joined by bone”). Examples of synostosis fusions between cranial bones are found both early and late in life. At the time of birth, the frontal and maxillary bones consist of right and left halves joined together by sutures, which disappear by the eighth year as the halves fuse together to form a single bone. Late in life, the sagittal, coronal, and lambdoid sutures of the skull will begin to ossify and fuse, causing the suture line to gradually disappear.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology: support and movement' conversation and receive update notifications?