| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Rather than start with urine formation, this section will start with urine excretion. Urine is a fluid of variable composition that requires specialized structures to remove it from the body safely and efficiently. Blood is filtered, and the filtrate is transformed into urine at a relatively constant rate throughout the day. This processed liquid is stored until a convenient time for excretion. All structures involved in the transport and storage of the urine are large enough to be visible to the naked eye. This transport and storage system not only stores the waste, but it protects the tissues from damage due to the wide range of pH and osmolarity of the urine, prevents infection by foreign organisms, and for the male, provides reproductive functions.
The urethra transports urine from the bladder to the outside of the body for disposal. The urethra is the only urologic organ that shows any significant anatomic difference between males and females; all other urine transport structures are identical ( [link] ).
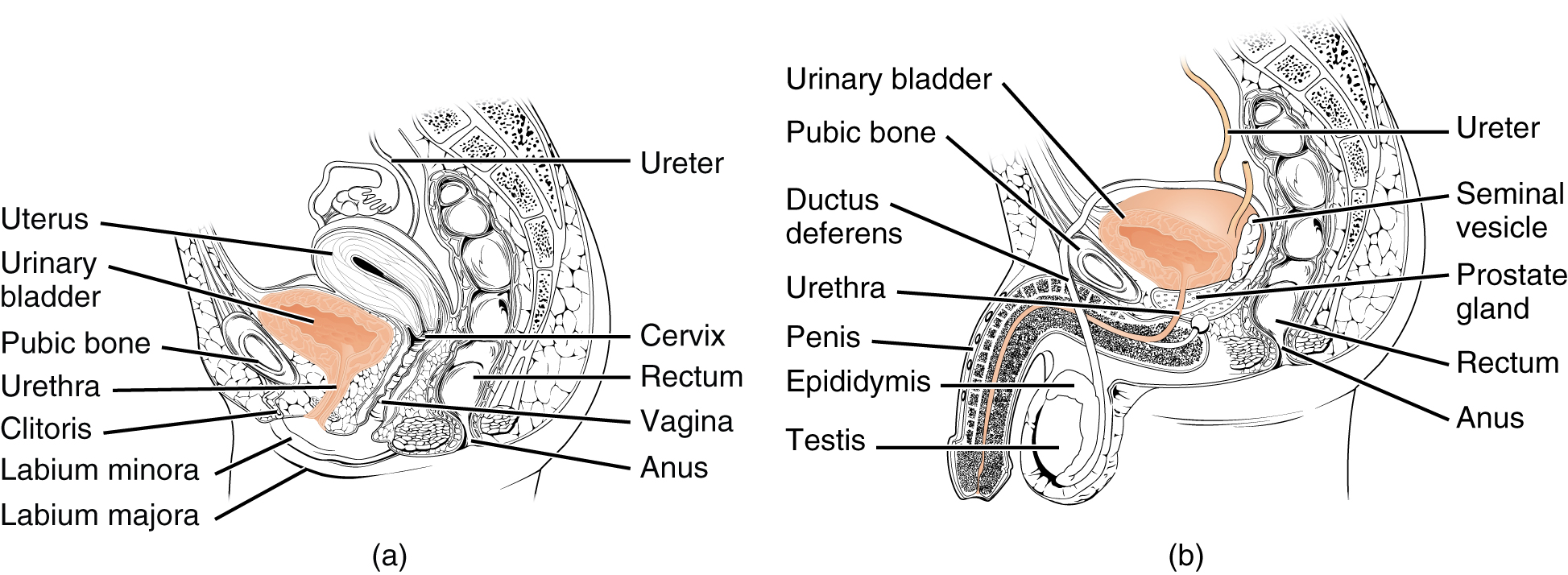
The urethra in both males and females begins inferior and central to the two ureteral openings forming the three points of a triangular-shaped area at the base of the bladder called the trigone (Greek tri- = “triangle” and the root of the word “trigonometry”). The urethra tracks posterior and inferior to the pubic symphysis (see [link] a ). In both males and females, the proximal urethra is lined by transitional epithelium, whereas the terminal portion is a nonkeratinized, stratified squamous epithelium. In the male, pseudostratified columnar epithelium lines the urethra between these two cell types. Voiding is regulated by an involuntary autonomic nervous system-controlled internal urinary sphincter , consisting of smooth muscle and voluntary skeletal muscle that forms the external urinary sphincter below it.
The external urethral orifice is embedded in the anterior vaginal wall inferior to the clitoris, superior to the vaginal opening (introitus), and medial to the labia minora. Its short length, about 4 cm, is less of a barrier to fecal bacteria than the longer male urethra and the best explanation for the greater incidence of UTI in women. Voluntary control of the external urethral sphincter is a function of the pudendal nerve. It arises in the sacral region of the spinal cord, traveling via the S2–S4 nerves of the sacral plexus.
The male urethra passes through the prostate gland immediately inferior to the bladder before passing below the pubic symphysis (see [link] b ). The length of the male urethra varies between men but averages 20 cm in length. It is divided into four regions: the preprostatic urethra, the prostatic urethra, the membranous urethra, and the spongy or penile urethra. The preprostatic urethra is very short and incorporated into the bladder wall. The prostatic urethra passes through the prostate gland. During sexual intercourse, it receives sperm via the ejaculatory ducts and secretions from the seminal vesicles. Paired Cowper’s glands (bulbourethral glands) produce and secrete mucus into the urethra to buffer urethral pH during sexual stimulation. The mucus neutralizes the usually acidic environment and lubricates the urethra, decreasing the resistance to ejaculation. The membranous urethra passes through the deep muscles of the perineum, where it is invested by the overlying urethral sphincters. The spongy urethra exits at the tip (external urethral orifice) of the penis after passing through the corpus spongiosum. Mucous glands are found along much of the length of the urethra and protect the urethra from extremes of urine pH. Innervation is the same in both males and females.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the '101-321-va - vertebrate form and function ii' conversation and receive update notifications?