| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
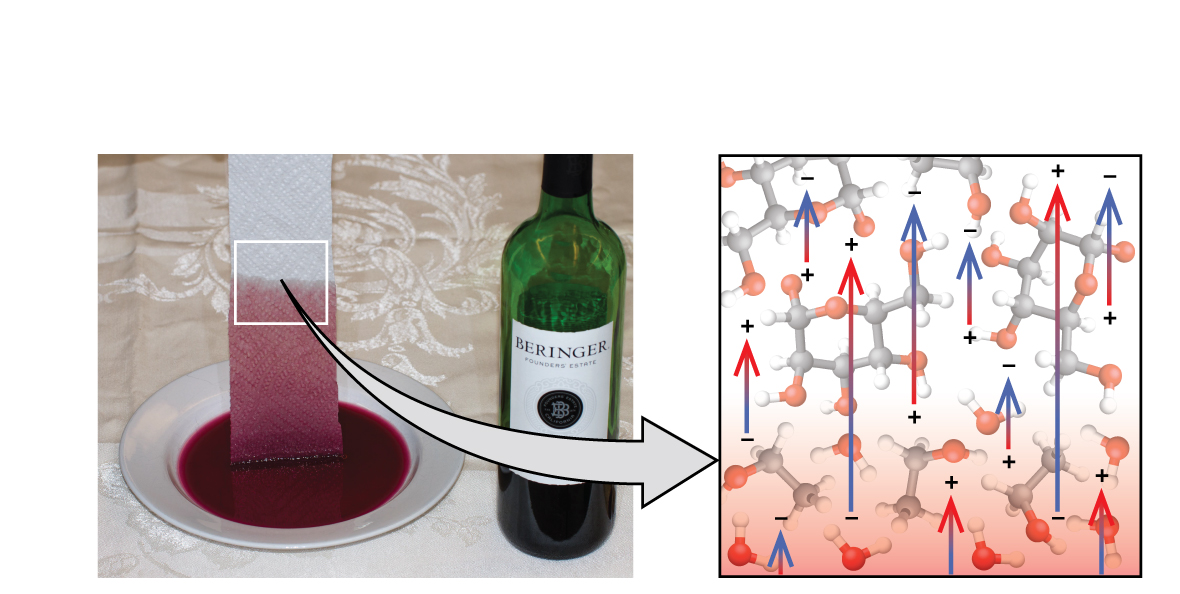
Towels soak up liquids like water because the fibers of a towel are made of molecules that are attracted to water molecules. Most cloth towels are made of cotton, and paper towels are generally made from paper pulp. Both consist of long molecules of cellulose that contain many −OH groups. Water molecules are attracted to these −OH groups and form hydrogen bonds with them, which draws the H 2 O molecules up the cellulose molecules. The water molecules are also attracted to each other, so large amounts of water are drawn up the cellulose fibers.
Capillary action can also occur when one end of a small diameter tube is immersed in a liquid, as illustrated in [link] . If the liquid molecules are strongly attracted to the tube molecules, the liquid creeps up the inside of the tube until the weight of the liquid and the adhesive forces are in balance. The smaller the diameter of the tube is, the higher the liquid climbs. It is partly by capillary action occurring in plant cells called xylem that water and dissolved nutrients are brought from the soil up through the roots and into a plant. Capillary action is the basis for thin layer chromatography, a laboratory technique commonly used to separate small quantities of mixtures. You depend on a constant supply of tears to keep your eyes lubricated and on capillary action to pump tear fluid away.
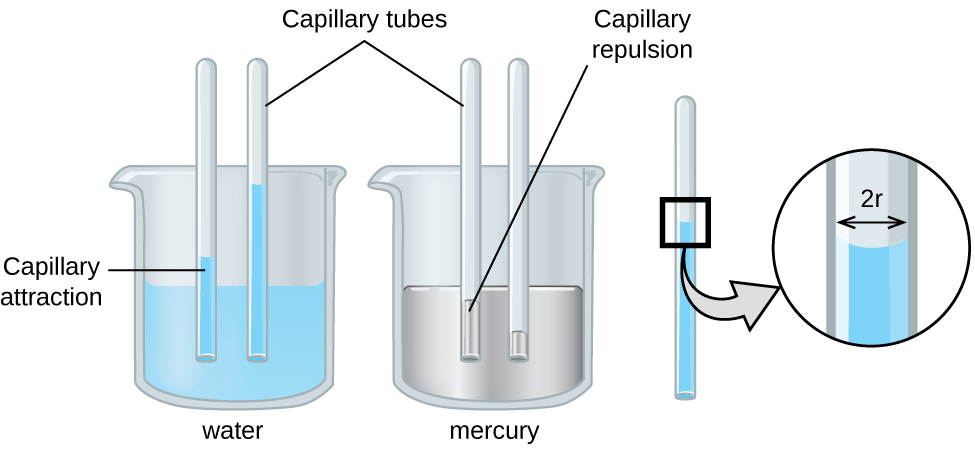
The height to which a liquid will rise in a capillary tube is determined by several factors as shown in the following equation:
In this equation, h is the height of the liquid inside the capillary tube relative to the surface of the liquid outside the tube, T is the surface tension of the liquid, θ is the contact angle between the liquid and the tube, r is the radius of the tube, ρ is the density of the liquid, and g is the acceleration due to gravity, 9.8 m/s 2 . When the tube is made of a material to which the liquid molecules are strongly attracted, they will spread out completely on the surface, which corresponds to a contact angle of 0°. This is the situation for water rising in a glass tube.
For water, T = 71.99 mN/m and ρ = 1.0 g/cm 3 .
The Newton is defined as a kg m/s 2 , and so the provided surface tension is equivalent to 0.07199 kg/s 2 . The provided density must be converted into units that will cancel appropriately: ρ = 1000 kg/m 3 . The diameter of the tube in meters is 0.00025 m, so the radius is 0.000125 m. For a glass tube immersed in water, the contact angle is θ = 0°, so cos θ = 1. Finally, acceleration due to gravity on the earth is g = 9.8 m/s 2 . Substituting these values into the equation, and cancelling units, we have:
diameter = 0.36 mm

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ut austin - principles of chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?