| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
All the forces discussed in this section are real forces, but there are a number of other real forces, such as lift and thrust, that are not discussed in this section. They are more specialized, and it is not necessary to discuss every type of force. It is natural, however, to ask where the basic simplicity we seek to find in physics is in the long list of forces. Are some more basic than others? Are some different manifestations of the same underlying force? The answer to both questions is yes, as will be seen in the next (extended) section and in the treatment of modern physics later in the text.
Explore the forces at work when you try to push a filing cabinet. Create an applied force and see the resulting friction force and total force acting on the cabinet. Charts show the forces, position, velocity, and acceleration vs. time. View a free-body diagram of all the forces (including gravitational and normal forces).

If a leg is suspended by a traction setup as shown in [link] , what is the tension in the rope?
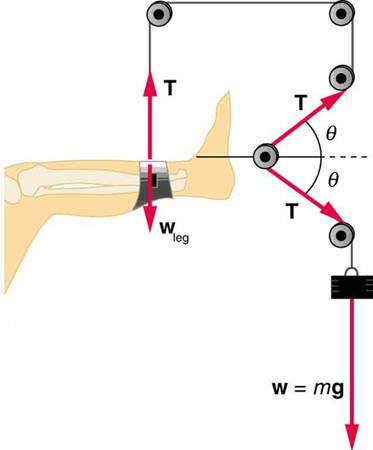
In a traction setup for a broken bone, with pulleys and rope available, how might we be able to increase the force along the femur using the same weight? (See [link] .) (Note that the femur is the shin bone shown in this image.)
Two teams of nine members each engage in a tug of war. Each of the first team’s members has an average mass of 68 kg and exerts an average force of 1350 N horizontally. Each of the second team’s members has an average mass of 73 kg and exerts an average force of 1365 N horizontally. (a) What is the acceleration of the two teams? (b) What is the tension in the section of rope between the teams?
What force does a trampoline have to apply to a 45.0-kg gymnast to accelerate her straight up at ? Note that the answer is independent of the velocity of the gymnast—she can be moving either up or down, or be stationary.
(a) Calculate the tension in a vertical strand of spider web if a spider of mass hangs motionless on it. (b) Calculate the tension in a horizontal strand of spider web if the same spider sits motionless in the middle of it much like the tightrope walker in [link] . The strand sags at an angle of below the horizontal. Compare this with the tension in the vertical strand (find their ratio).
(a)
(b) . This is 2.41 times the tension in the vertical strand.
Suppose a 60.0-kg gymnast climbs a rope. (a) What is the tension in the rope if he climbs at a constant speed? (b) What is the tension in the rope if he accelerates upward at a rate of ?
Show that, as stated in the text, a force exerted on a flexible medium at its center and perpendicular to its length (such as on the tightrope wire in [link] ) gives rise to a tension of magnitude .
Newton’s second law applied in vertical direction gives
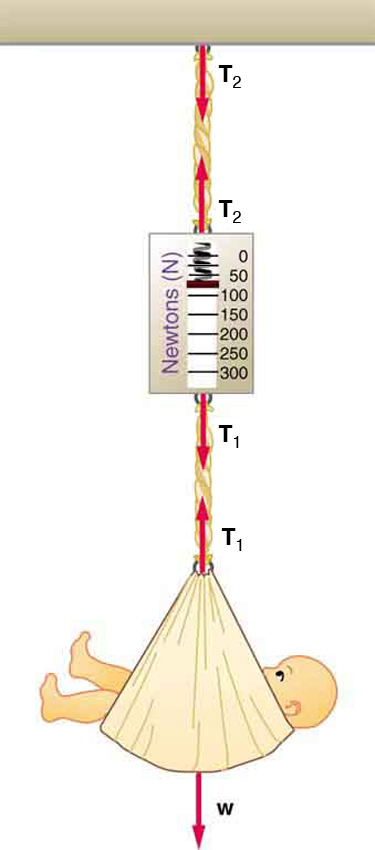
Consider the baby being weighed in [link] . (a) What is the mass of the child and basket if a scale reading of 55 N is observed? (b) What is the tension in the cord attaching the baby to the scale? (c) What is the tension in the cord attaching the scale to the ceiling, if the scale has a mass of 0.500 kg? (d) Draw a sketch of the situation indicating the system of interest used to solve each part. The masses of the cords are negligible.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introduction to applied math and physics' conversation and receive update notifications?