| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Electric currents in the vastly complex system of billions of nerves in our body allow us to sense the world, control parts of our body, and think. These are representative of the three major functions of nerves. First, nerves carry messages from our sensory organs and others to the central nervous system, consisting of the brain and spinal cord. Second, nerves carry messages from the central nervous system to muscles and other organs. Third, nerves transmit and process signals within the central nervous system. The sheer number of nerve cells and the incredibly greater number of connections between them makes this system the subtle wonder that it is. Nerve conduction is a general term for electrical signals carried by nerve cells. It is one aspect of bioelectricity , or electrical effects in and created by biological systems.
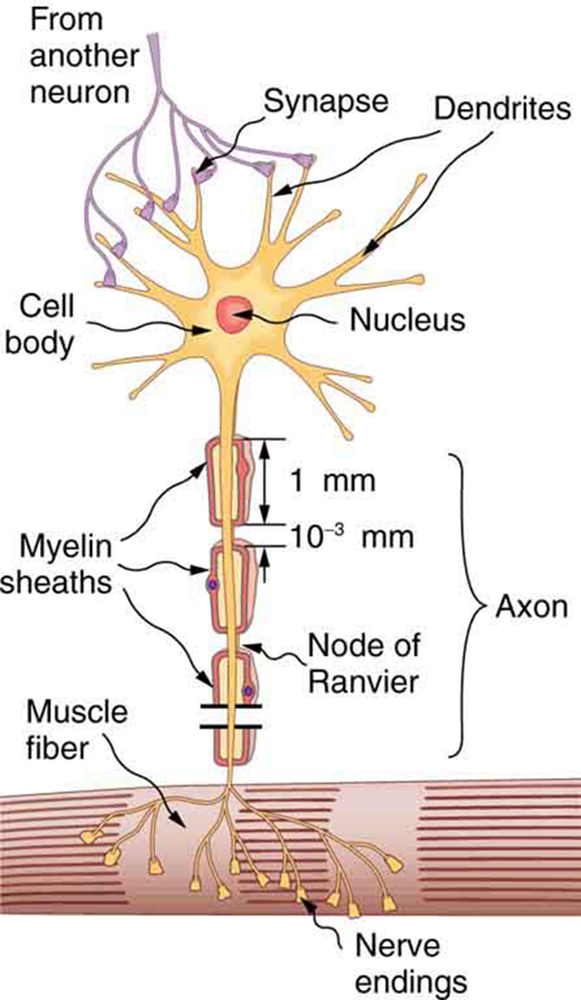
Nerve cells, properly called neurons , look different from other cells—they have tendrils, some of them many centimeters long, connecting them with other cells. (See [link] .) Signals arrive at the cell body across synapses or through dendrites , stimulating the neuron to generate its own signal, sent along its long axon to other nerve or muscle cells. Signals may arrive from many other locations and be transmitted to yet others, conditioning the synapses by use, giving the system its complexity and its ability to learn.
The method by which these electric currents are generated and transmitted is more complex than the simple movement of free charges in a conductor, but it can be understood with principles already discussed in this text. The most important of these are the Coulomb force and diffusion.
[link] illustrates how a voltage (potential difference) is created across the cell membrane of a neuron in its resting state. This thin membrane separates electrically neutral fluids having differing concentrations of ions, the most important varieties being , , and (these are sodium, potassium, and chlorine ions with single plus or minus charges as indicated). As discussed in Molecular Transport Phenomena: Diffusion, Osmosis, and Related Processes , free ions will diffuse from a region of high concentration to one of low concentration. But the cell membrane is semipermeable , meaning that some ions may cross it while others cannot. In its resting state, the cell membrane is permeable to and , and impermeable to . Diffusion of and thus creates the layers of positive and negative charge on the outside and inside of the membrane. The Coulomb force prevents the ions from diffusing across in their entirety. Once the charge layer has built up, the repulsion of like charges prevents more from moving across, and the attraction of unlike charges prevents more from leaving either side. The result is two layers of charge right on the membrane, with diffusion being balanced by the Coulomb force. A tiny fraction of the charges move across and the fluids remain neutral (other ions are present), while a separation of charge and a voltage have been created across the membrane.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'General physics ii phy2202ca' conversation and receive update notifications?