| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
As you have learned, the process of mechanical digestion is relatively simple. It involves the physical breakdown of food but does not alter its chemical makeup. Chemical digestion, on the other hand, is a complex process that reduces food into its chemical building blocks, which are then absorbed to nourish the cells of the body ( [link] ). In this section, you will look more closely at the processes of chemical digestion and absorption.
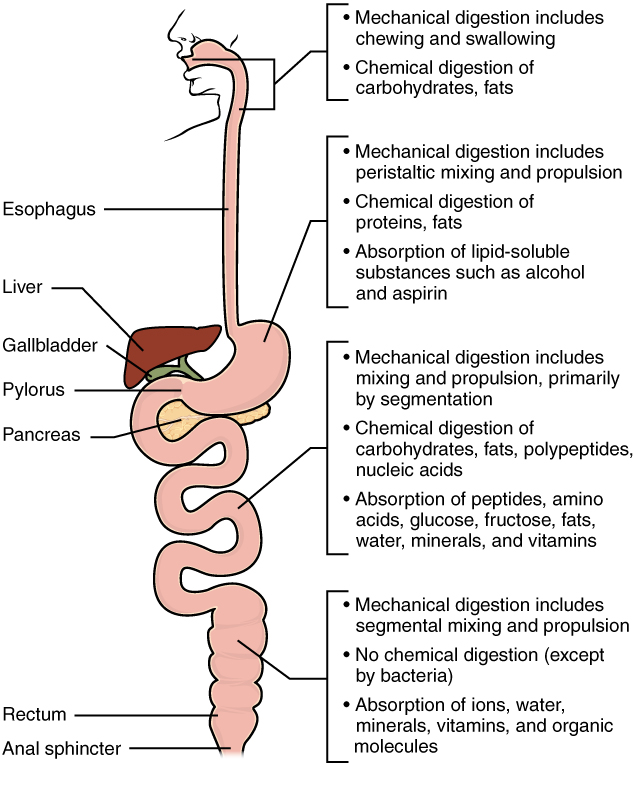
Large food molecules (for example, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and starches) must be broken down into subunits that are small enough to be absorbed by the lining of the alimentary canal. This is accomplished by enzymes through hydrolysis. The many enzymes involved in chemical digestion are summarized in [link] .
| The Digestive Enzymes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enzyme Category | Enzyme Name | Source | Substrate | Product |
| Salivary Enzymes | Lingual lipase | Lingual glands | Triglycerides | Free fatty acids, and mono- and diglycerides |
| Salivary Enzymes | Salivary amylase | Salivary glands | Polysaccharides | Disaccharides and trisaccharides |
| Gastric enzymes | Gastric lipase | Chief cells | Triglycerides | Fatty acids and monoacylglycerides |
| Gastric enzymes | Pepsin* | Chief cells | Proteins | Peptides |
| Brush border enzymes | α-Dextrinase | Small intestine | α-Dextrins | Glucose |
| Brush border enzymes | Enteropeptidase | Small intestine | Trypsinogen | Trypsin |
| Brush border enzymes | Lactase | Small intestine | Lactose | Glucose and galactose |
| Brush border enzymes | Maltase | Small intestine | Maltose | Glucose |
| Brush border enzymes | Nucleosidases and phosphatases | Small intestine | Nucleotides | Phosphates, nitrogenous bases, and pentoses |
| Brush border enzymes | Peptidases | Small intestine |
|
|
| Brush border enzymes | Sucrase | Small intestine | Sucrose | Glucose and fructose |
| Pancreatic enzymes | Carboxy-peptidase* | Pancreatic acinar cells | Amino acids at the carboxyl end of peptides | Amino acids and peptides |
| Pancreatic enzymes | Chymotrypsin* | Pancreatic acinar cells | Proteins | Peptides |
| Pancreatic enzymes | Elastase* | Pancreatic acinar cells | Proteins | Peptides |
| Pancreatic enzymes | Nucleases | Pancreatic acinar cells |
|
Nucleotides |
| Pancreatic enzymes | Pancreatic amylase | Pancreatic acinar cells | Polysaccharides (starches) | α-Dextrins, disaccharides (maltose), trisaccharides (maltotriose) |
| Pancreatic enzymes | Pancreatic lipase | Pancreatic acinar cells | Triglycerides that have been emulsified by bile salts | Fatty acids and monoacylglycerides |
| Pancreatic enzymes | Trypsin* | Pancreatic acinar cells | Proteins | Peptides |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the '101-321-va - vertebrate form and function ii' conversation and receive update notifications?