| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
THE ATMOSPHERE
A layer of air called atmosphere envelops the earth. This layer usually contains two gases, namely oxygen (78%) and nitrogen (20%). The atmosphere consists of a number of layers, of which each has its own characteristics.
LAYERS IN THE ATMOSPHERE
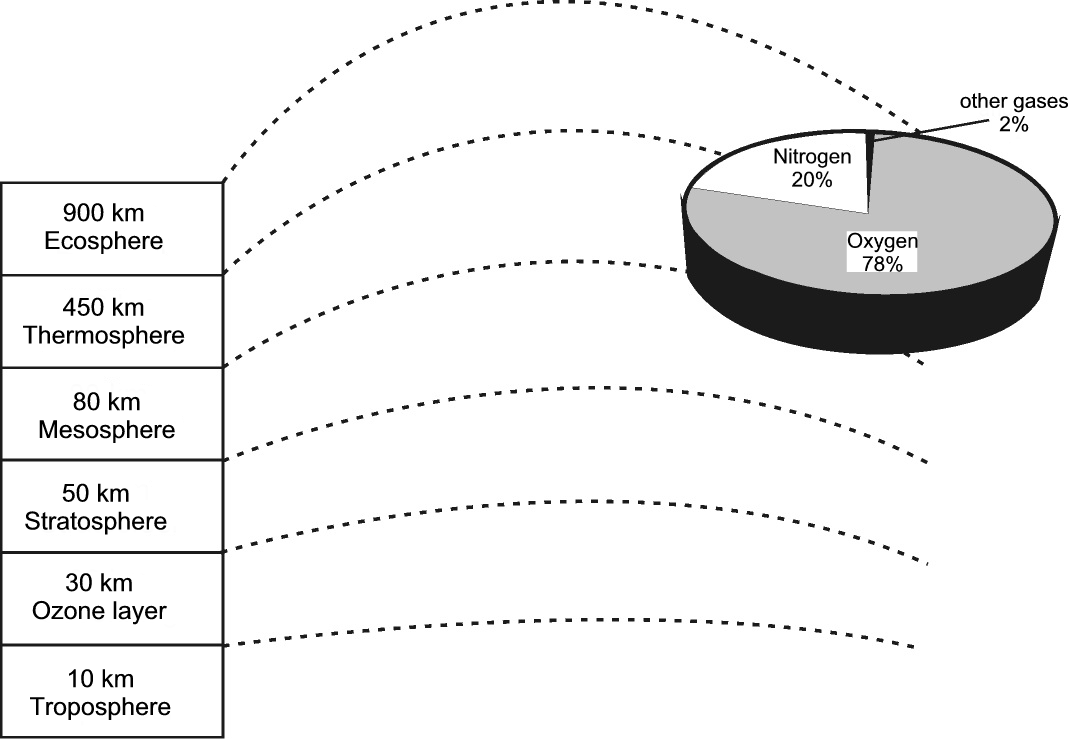
This is the layer closest to Earth. Here we find all the weather patterns and clouds, and this is also where aeroplanes and birds fly.
The harmful ultra-violet rays of the sun are absorbed in this layer.
It is here that modern jets fly. Oxygen supply is insufficient for man to breathe.
Most small meteors burn out in this layer.
Most of the sun’s heat is absorbed here; temperatures rise to 1 000 degrees Celsius.
There is almost no air in this layer. Only the lightest of gases are found here, as well as some weather satellites.
The above-mentioned layers do not have fixed limits and we can therefore say that they intermingle. The density decreases the higher the layer is until almost no air is present. Compared to the cross-section of the earth, the atmosphere is not really a very thick layer.
TASK 8:
Group work
| Educator Assessment: Diagrammatical Rrepresentation | 1. | 2. | 3. | 4. |
| 1. Aim: The message is carried over clearly | ||||
| 2. Detail: Detail is accurate and clear | ||||
| 3. Sketches and illustrations: Functional and purposeful | ||||
| 4. Creativity: Representation is creative and original | ||||
| 5. Presentation: neat and orderly | ||||
| DOMINANT CODE: ........MARK: ......./ 20 ..............%Educator:.................................................. |
Commentary:
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
Learner: _____________________________________________________________
Learning Outcome 2: The learner will know and be able to interpret and apply scientific, technological and environmental knowledge.
Assessment Standard 2.3: We know this when the learner interprets information: interprets information by identifying key ideas in text, finding patterns in recorded data, and making inferences from information in various forms (e.g. pictures, diagrams, text).
Learning Outcome 3: The learner will be able to demonstrate an understanding of the interrelationships between science and technology, society and the environment.
Assessment Standard 3.1: We know this when the learner understands science as a human endeavour: compares differing interpretations of events.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Natural sciences grade 7' conversation and receive update notifications?