| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Differential equations can be used to represent the size of a population as it varies over time. We saw this in an earlier chapter in the section on exponential growth and decay, which is the simplest model. A more realistic model includes other factors that affect the growth of the population. In this section, we study the logistic differential equation and see how it applies to the study of population dynamics in the context of biology.
To model population growth using a differential equation, we first need to introduce some variables and relevant terms. The variable will represent time. The units of time can be hours, days, weeks, months, or even years. Any given problem must specify the units used in that particular problem. The variable will represent population. Since the population varies over time, it is understood to be a function of time. Therefore we use the notation for the population as a function of time. If is a differentiable function, then the first derivative represents the instantaneous rate of change of the population as a function of time.
In Exponential Growth and Decay , we studied the exponential growth and decay of populations and radioactive substances. An example of an exponential growth function is In this function, represents the population at time represents the initial population (population at time and the constant is called the growth rate . [link] shows a graph of Here and
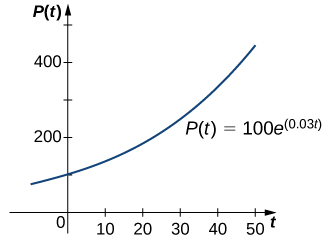
We can verify that the function satisfies the initial-value problem
This differential equation has an interesting interpretation. The left-hand side represents the rate at which the population increases (or decreases). The right-hand side is equal to a positive constant multiplied by the current population. Therefore the differential equation states that the rate at which the population increases is proportional to the population at that point in time. Furthermore, it states that the constant of proportionality never changes.
One problem with this function is its prediction that as time goes on, the population grows without bound. This is unrealistic in a real-world setting. Various factors limit the rate of growth of a particular population, including birth rate, death rate, food supply, predators, and so on. The growth constant usually takes into consideration the birth and death rates but none of the other factors, and it can be interpreted as a net (birth minus death) percent growth rate per unit time. A natural question to ask is whether the population growth rate stays constant, or whether it changes over time. Biologists have found that in many biological systems, the population grows until a certain steady-state population is reached. This possibility is not taken into account with exponential growth. However, the concept of carrying capacity allows for the possibility that in a given area, only a certain number of a given organism or animal can thrive without running into resource issues.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?