| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Push the weft rows firmly against each other after every row – use a coarse comb for this – to make the weaving strong and firm.
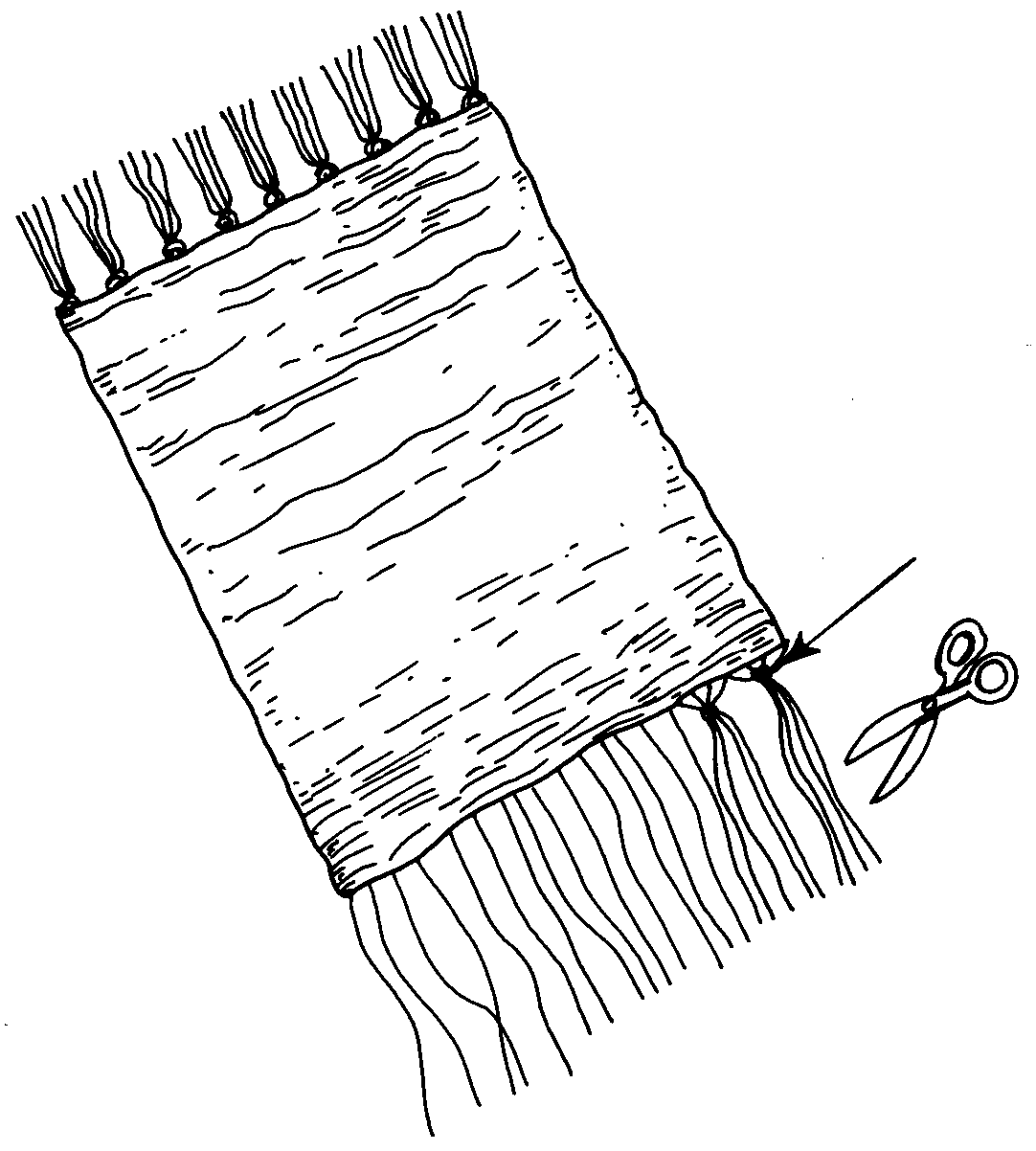
When you have covered all the visible warp threads on the top of the box, you may cut through the threads at the bottom of the box (so that the loose ends are equal in length) and knot these loose ends together in pairs right against the cardboard frame to finish off the woven mat. Cut the ends shorter to form a fringe and remove the mat from the frame.
If you have many similar bags, you may make a plain mat, but if you have a variety of colours, you may weave stripes of colour or experiment with weaving blocks of colour to form a repeat pattern.
Non-flexible materials as option
Should you like to use reeds or rubber strips as weft, cut it to the desired width and thread it through alternatively. Repeat until the entire width has been weaved.
As a matter of interest
Consult sources on methods of weaving and try to weave patterns into your doormat.
[LO 1.8]
Assignment 4
Make a three-dimensional drawing of the mat you have woven, in colour and with labels. Also indicate the exact size (length and width).
[LO 1.12]
Background and information
It is very difficult to get rid of plastic bags that have been allowed to pollute nature. They do not decay naturally and are not absorbed into the soil because they are manmade. This means that they do not form biodegradable waste, just like glass and metal, which also do not decompose readily. If you therefore recycle plastic bags (by using old products to make new products) you will be helping to reduce the amount of waste that litters the earth and you will be making a positive contribution to ensure the continued existence of the earth.
Assignment 5
Write down five examples of old plastic, metal or glass products used to make new products.
[LO 3.2]
Assignment 6
Evaluation
Does your doormat meet expectations? Motivate this with reasons.
Indicate two aspects of the assignment that you found difficult.
Indicate two aspects of the assignment that you found easy to do.
What were the problems that occurred and what did you do to solve them?
[LO 1.11]
Ask at least five adults to give their honest opinion of your mat and to say what they would be willing to pay for such a mat.
| NAME | OPINION | PRICE |
Provide at least three recommendations that you would follow to improve your design and product if you had to repeat the assignment.
Calculate the approximate cost of making the mat.
How much did you have to spend to weave the mat?
[LO 1.10]
CHALLENGE: How about weaving mats like these in your spare time and selling them?
Asssessment
LO 1
Technological Processes and Skills
The learner will be able to apply technological processes and skills ethically and responsibly using appropriate information and communication technologies.
We know this when the learner:
investigates:
1.2 finds out about existing products relevant to a problem, need or opportunity, and identifies some design aspects (e.g. who it is for, what it looks like, what it is for, what it is made of).
1.3 performs, where appropriate, scientific investigations about concepts relevant to a problem, need or opportunity using science process skills:
planning investigations;
conducting investigations;
processing and interpreting data;
evaluating and communicating findings.
designs:
1.4 writes or communicates, with assistance, a short and clear statement (design brief) related to a given problem, need or opportunity that demonstrates some understanding of the technological purposes of the solution;
1.5 suggests and records at least two alternative solutions to the problem, need or opportunity that link to the design brief and to given specifications and constraints (e.g. people, purpose, environment);
1.6 chooses one of these solutions, giving reasons for the choice, and develops the idea further.
makes:
1.8 uses suitable tools and materials to make products by measuring out, cutting or separating, shaping or forming, joining or combining, and finishing the chosen material.
evaluates:
1.10 evaluates, with assistance, the product according to the design brief and given spesifications and constraints (e.g. people, purpose, environment), and suggests improvements and modifications id necessary;
1.11 evaluates the plan of action followed and suggests improvements and modifications if necessary.
communicates:
1.12 produces labelled two-dimensional drawings enhanced with colour where appropriate.
LO 2
Technological Knowlede and Understanding
The learner will be able to understand and apply relevant technological knowledge ethically and responsibly.
We know this when the learner:
structures:
demonstrates knowledge and understanding of how materials can be processed to change or improve properties (e.g. strength, fire resistance, waterproofing, taste, volume, texture).
LO 3
Technology, Society and the Environment
The learner will be able to demonstrate an understanding of the interrelationships between science, technology, society and the environment.
We know this when the learner:
Indigenous Technology and Culture:
3.1 recognises how products and technologies have been adapted from other times and cultures.
Impact of Technology:
3.2 suggests ways to improve technological products or processes to minimise negative effects on people and/or the health of the environment.
Memorandum
Assignment 3
(a) originality own discretion
(b) originality/ creativity, own discretion
Assignment 4
Completeness, use of colour, proportion, labels, own discretion
Assignment 5
Perceptiveness, originality, creativity, own discretion
Assignment 6
Careful observation, honesty, thoroughness, own discretion

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Technology grade 5' conversation and receive update notifications?