| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The kidneys lie on either side of the spine in the retroperitoneal space between the parietal peritoneum and the posterior abdominal wall, well protected by muscle, fat, and ribs. They are roughly the size of your fist, and the male kidney is typically a bit larger than the female kidney. The kidneys are well vascularized, receiving about 25 percent of the cardiac output at rest.
There have never been sufficient kidney donations to provide a kidney to each person needing one. Watch this video to learn about the TED (Technology, Entertainment, Design) Conference held in March 2011. In this video, Dr. Anthony Atala discusses a cutting-edge technique in which a new kidney is “printed.” The successful utilization of this technology is still several years in the future, but imagine a time when you can print a replacement organ or tissue on demand.
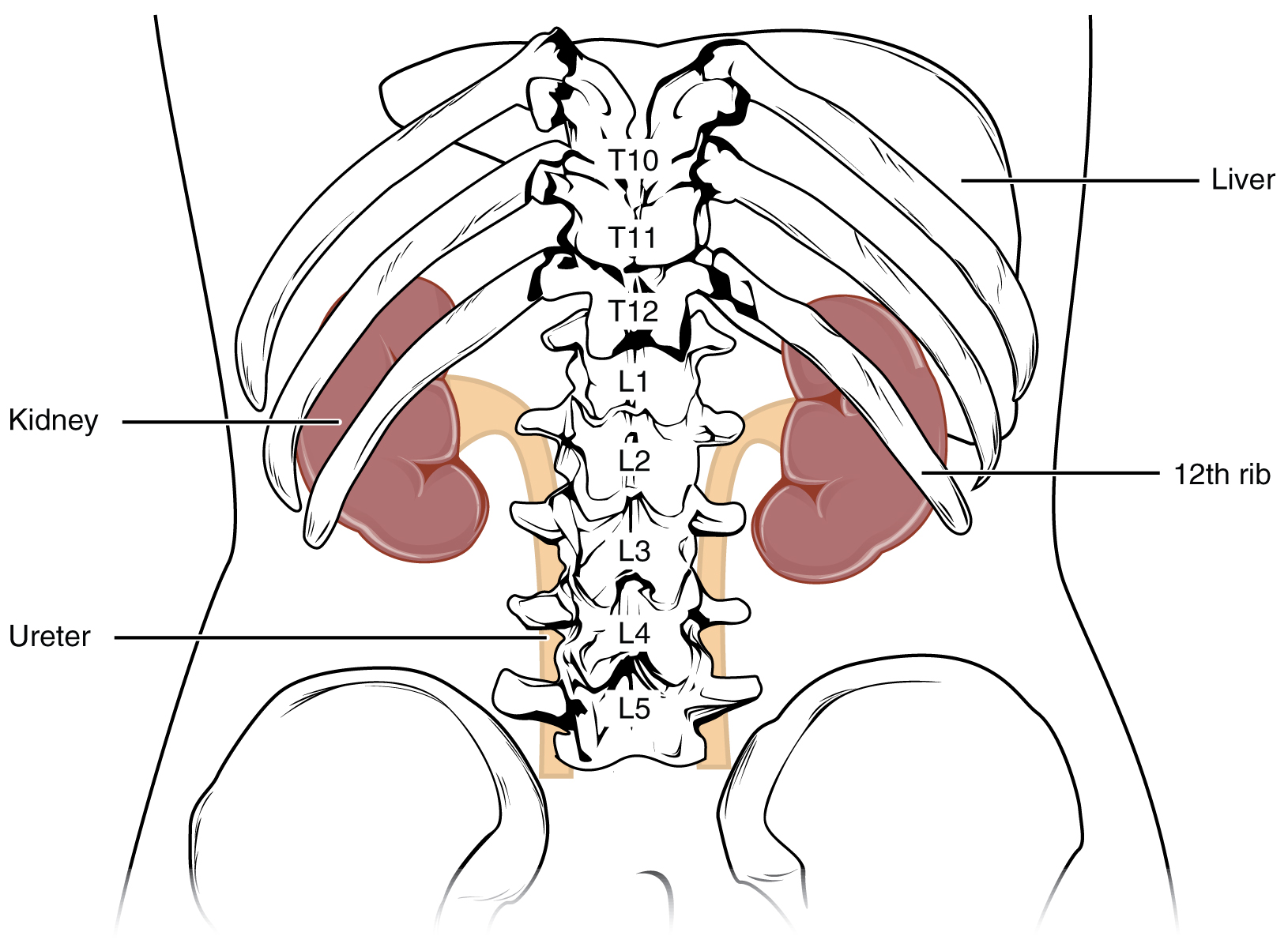
The left kidney is located at about the T12 to L3 vertebrae, whereas the right is lower due to slight displacement by the liver. Upper portions of the kidneys are somewhat protected by the eleventh and twelfth ribs ( [link] ). Each kidney weighs about 125–175 g in males and 115–155 g in females. They are about 11–14 cm in length, 6 cm wide, and 4 cm thick, and are directly covered by a fibrous capsule composed of dense, irregular connective tissue that helps to hold their shape and protect them. This capsule is covered by a shock-absorbing layer of adipose tissue called the renal fat pad , which in turn is encompassed by a tough renal fascia. The fascia and, to a lesser extent, the overlying peritoneum serve to firmly anchor the kidneys to the posterior abdominal wall in a retroperitoneal position.
On the superior aspect of each kidney is the adrenal gland. The adrenal cortex directly influences renal function through the production of the hormone aldosterone to stimulate sodium reabsorption.
A frontal section through the kidney reveals an outer region called the renal cortex and an inner region called the medulla ( [link] ). The renal columns are connective tissue extensions that radiate downward from the cortex through the medulla to separate the most characteristic features of the medulla, the renal pyramids and renal papillae . The papillae are bundles of collecting ducts that transport urine made by nephrons to the calyces of the kidney for excretion. The renal columns also serve to divide the kidney into 6–8 lobes and provide a supportive framework for vessels that enter and exit the cortex. The pyramids and renal columns taken together constitute the kidney lobes.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology: energy, maintenance and environmental exchange' conversation and receive update notifications?