| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A periodic signal, such as the half-wave rectified sinusoid,consists of a sum of elemental sinusoids. A plot of the Fourier coefficients as a function of the frequency index, such as shownin [link] , displays the signal's spectrum . The word "spectrum" implies that the independent variable, here , corresponds somehow to frequency. Each coefficient is directly related to a sinusoidhaving a frequency of . Thus, if we half-wave rectified a 1 kHz sinusoid, corresponds to 1 kHz, to 2 kHz, etc.
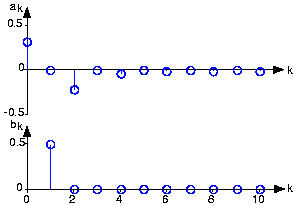
A subtle, but very important, aspect of the Fourier spectrum isits uniqueness : You can unambiguously find the spectrum from the signal( decomposition ) and the signal from the spectrum( composition ). Thus, any aspect of the signal can be found from the spectrumand vice versa. A signal's frequency domain expression is its spectrum . A periodic signal can be defined either in the time domain (as a function) or in thefrequency domain (as a spectrum).
A fundamental aspect of solving electrical engineering problems is whether the time or frequency domain provides themost understanding of a signal's properties and the simplest way of manipulatingit. The uniqueness property says that either domain can provide the right answer.As a simple example, suppose we want to know the (periodic) signal's maximum value. Clearly the time domain provides theanswer directly. To use a frequency domain approach would require us to find the spectrum, form the signal from thespectrum and calculate the maximum; we're back in the time domain!
Another feature of a signal is its average power . A signal's instantaneous power is defined to be its square. Theaverage power is the average of the instantaneous power over some time interval. For a periodic signal, the natural timeinterval is clearly its period; for nonperiodic signals, a better choice would be entire time or time from onset. For aperiodic signal, the average power is the square of its root-mean-squared (rms) value. We define the rms value of a periodic signal to be
What is the rms value of the half-wave rectified sinusoid?
The rms value of a sinusoid equals its amplitude divided by . As a half-wave rectified sine wave is zero during half ofthe period, its rms value is since the integral of the squared half-wave rectified sine wave equals half that of a squared sinusoid.
To find the average power in the frequency domain, we need to substitute the spectral representation of the signal into thisexpression. The square inside the integral will contain all possible pairwise products. However, the orthogonality properties say that most of these crossterms integrate to zero. Thesurvivors leave a rather simple expression for the power we seek.
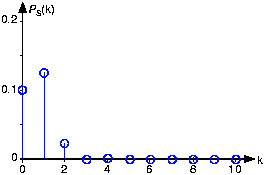
It could well be that computing this sum is easier than integrating the signal's square. Furthermore, the contributionof each term in the Fourier series toward representing the signal can be measured by its contribution to the signal'saverage power. Thus, the power contained in a signal at its th harmonic is . The power spectrum , , such as shown in [link] , plots each harmonic's contribution to the total power.
In high-end audio, deviation of a sine wave from theideal is measured by the total harmonic distortion , which equals the total power in the harmonics higher than thefirst compared to power in the fundamental. Find an expression for the total harmonic distortion for anyperiodic signal. Is this calculation most easily performed in the time or frequency domain?
Total harmonic distortion equals . Clearly, this quantity is most easily computed in thefrequency domain. However, the numerator equals the square of the signal's rms value minus the power in the average andthe power in the first harmonic.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Fundamentals of electrical engineering i' conversation and receive update notifications?