| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
During the seventeenth and especially eighteenth centuries, driven both by a desire to understand nature and a quest to make balloons in which they could fly ( [link] ), a number of scientists established the relationships between the macroscopic physical properties of gases, that is, pressure, volume, temperature, and amount of gas. Although their measurements were not precise by today’s standards, they were able to determine the mathematical relationships between pairs of these variables (e.g., pressure and temperature, pressure and volume) that hold for an ideal gas—a hypothetical construct that real gases approximate under certain conditions. Eventually, these individual laws were combined into a single equation—the ideal gas law —that relates gas quantities for gases and is quite accurate for low pressures and moderate temperatures. We will consider the key developments in individual relationships (for pedagogical reasons not quite in historical order), then put them together in the ideal gas law.
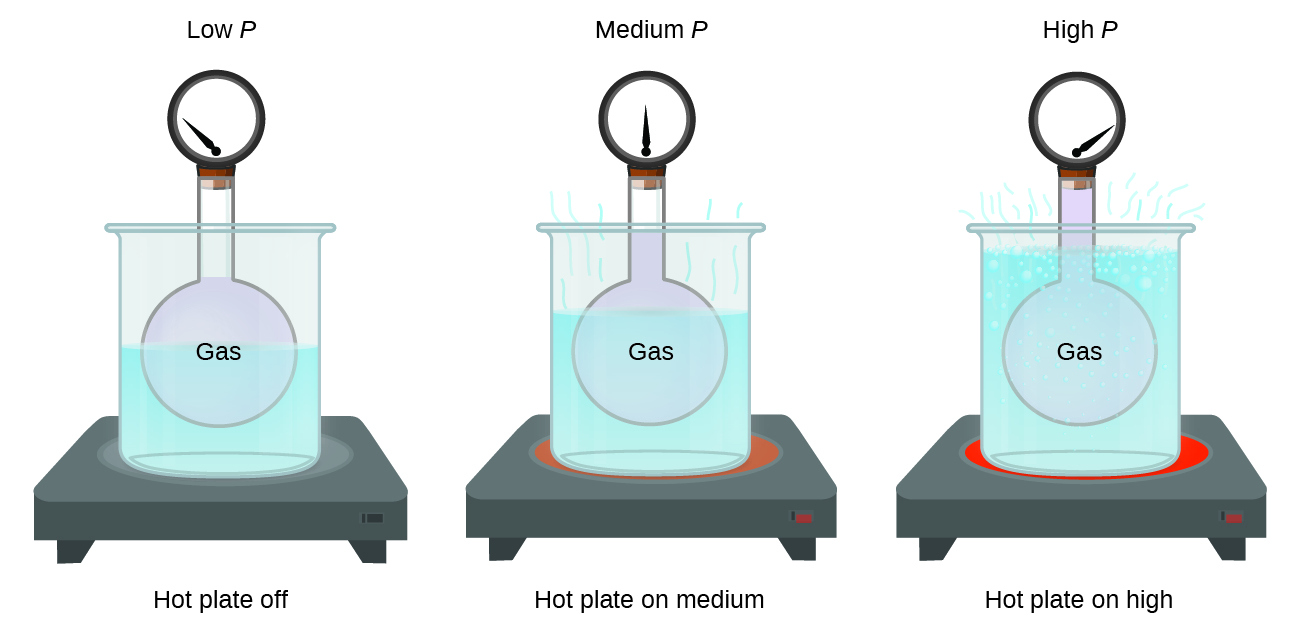
Imagine filling a rigid container attached to a pressure gauge with gas and then sealing the container so that no gas may escape. If the container is cooled, the gas inside likewise gets colder and its pressure is observed to decrease. Since the container is rigid and tightly sealed, both the volume and number of moles of gas remain constant. If we heat the sphere, the gas inside gets hotter ( [link] ) and the pressure increases.
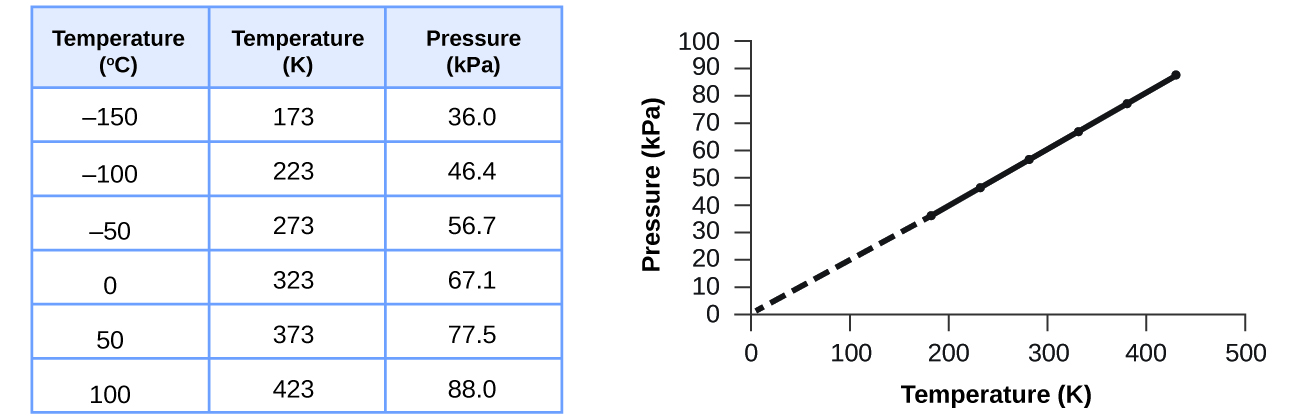
This relationship between temperature and pressure is observed for any sample of gas confined to a constant volume. An example of experimental pressure-temperature data is shown for a sample of air under these conditions in [link] . We find that temperature and pressure are linearly related, and if the temperature is on the kelvin scale, then P and T are directly proportional (again, when volume and moles of gas are held constant ); if the temperature on the kelvin scale increases by a certain factor, the gas pressure increases by the same factor.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ut austin - principles of chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?