| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In about one-third of men who are past puberty, mumps also causes testicular inflammation, typically affecting only one testis and rarely resulting in sterility. With the increasing use and effectiveness of mumps vaccines, the incidence of mumps has decreased dramatically. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the number of mumps cases dropped from more than 150,000 in 1968 to fewer than 1700 in 1993 to only 11 reported cases in 2011.
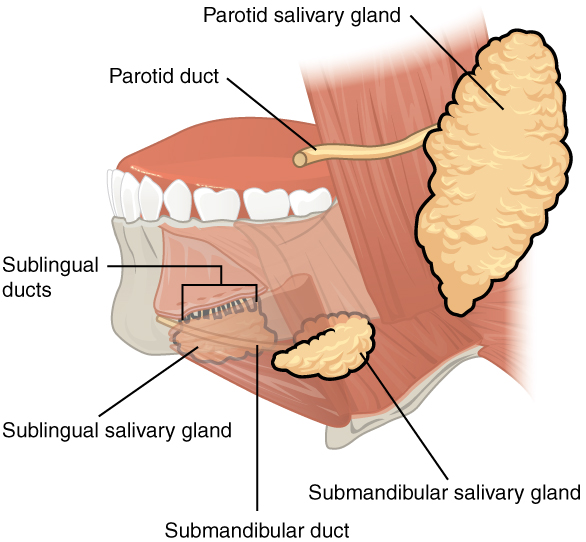
The autonomic nervous system regulates salivation (the secretion of saliva). In the absence of food, parasympathetic stimulation keeps saliva flowing at just the right level for comfort as you speak, swallow, sleep, and generally go about life. Over-salivation can occur, for example, if you are stimulated by the smell of food, but that food is not available for you to eat. Drooling is an extreme instance of the overproduction of saliva. During times of stress, such as before speaking in public, sympathetic stimulation takes over, reducing salivation and producing the symptom of dry mouth often associated with anxiety. When you are dehydrated, salivation is reduced, causing the mouth to feel dry and prompting you to take action to quench your thirst.
Salivation can be stimulated by the sight, smell, and taste of food. It can even be stimulated by thinking about food. You might notice whether reading about food and salivation right now has had any effect on your production of saliva.
How does the salivation process work while you are eating? Food contains chemicals that stimulate taste receptors on the tongue, which send impulses to the superior and inferior salivatory nuclei in the brain stem. These two nuclei then send back parasympathetic impulses through fibers in the glossopharyngeal and facial nerves, which stimulate salivation. Even after you swallow food, salivation is increased to cleanse the mouth and to water down and neutralize any irritating chemical remnants, such as that hot sauce in your burrito. Most saliva is swallowed along with food and is reabsorbed, so that fluid is not lost.
The teeth, or dentes (singular = dens), are organs similar to bones that you use to tear, grind, and otherwise mechanically break down food.
During the course of your lifetime, you have two sets of teeth (one set of teeth is a dentition ). Your 20 deciduous teeth , or baby teeth, first begin to appear at about 6 months of age. Between approximately age 6 and 12, these teeth are replaced by 32 permanent teeth . Moving from the center of the mouth toward the side, these are as follows ( [link] ):

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the '101-321-va - vertebrate form and function ii' conversation and receive update notifications?