| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
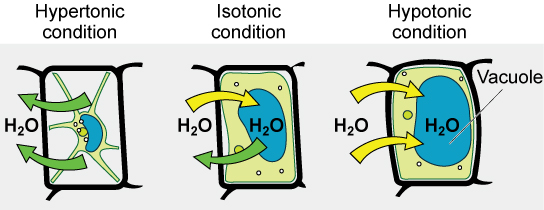

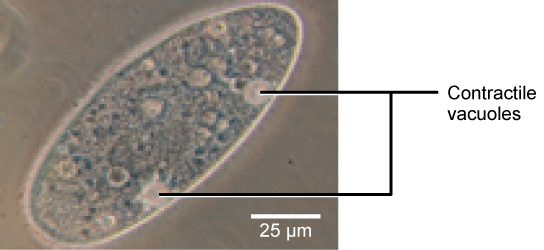
Tonicity is a concern for all living things. For example, paramecia and amoebas, which are protists that lack cell walls, have contractile vacuoles. This vesicle collects excess water from the cell and pumps it out, keeping the cell from lysing as it takes on water from its environment ( [link] ).
Many marine invertebrates have internal salt levels matched to their environments, making them isotonic with the water in which they live. Fish, however, must spend approximately five percent of their metabolic energy maintaining osmotic homeostasis. Freshwater fish live in an environment that is hypotonic to their cells. These fish actively take in salt through their gills and excrete diluted urine to rid themselves of excess water. Saltwater fish live in the reverse environment, which is hypertonic to their cells, and they secrete salt through their gills and excrete highly concentrated urine.
In vertebrates, the kidneys regulate the amount of water in the body. Osmoreceptors are specialized cells in the brain that monitor the concentration of solutes in the blood. If the levels of solutes increase beyond a certain range, a hormone is released that retards water loss through the kidney and dilutes the blood to safer levels. Animals also have high concentrations of albumin, which is produced by the liver, in their blood. This protein is too large to pass easily through plasma membranes and is a major factor in controlling the osmotic pressures applied to tissues.
The passive forms of transport, diffusion and osmosis, move materials of small molecular weight across membranes. Substances diffuse from areas of high concentration to areas of lower concentration, and this process continues until the substance is evenly distributed in a system. In solutions containing more than one substance, each type of molecule diffuses according to its own concentration gradient, independent of the diffusion of other substances. Many factors can affect the rate of diffusion, including concentration gradient, size of the particles that are diffusing, temperature of the system, and so on.
In living systems, diffusion of substances into and out of cells is mediated by the plasma membrane. Some materials diffuse readily through the membrane, but others are hindered, and their passage is made possible by specialized proteins, such as channels and transporters. The chemistry of living things occurs in aqueous solutions, and balancing the concentrations of those solutions is an ongoing problem. In living systems, diffusion of some substances would be slow or difficult without membrane proteins that facilitate transport.
[link] A doctor injects a patient with what the doctor thinks is an isotonic saline solution. The patient dies, and an autopsy reveals that many red blood cells have been destroyed. Do you think the solution the doctor injected was really isotonic?
[link] No, it must have been hypotonic as a hypotonic solution would cause water to enter the cells, thereby making them burst.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Cell biology' conversation and receive update notifications?