| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
1. 4
2.
2.1 19
2.2 8
1. Take a good look at this sketch of a cube.
How many squares are not visible when you view it from the front?
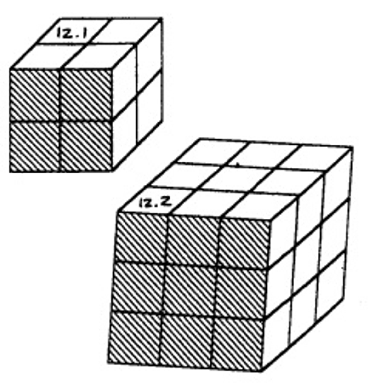
2. View the cube from the side.
2.1 How many cubes do you see?
_____________________________________________________________________
2.2 How many cubes are invisible?
_____________________________________________________________________
3. Now draw any one of these cubes from above.
CHALLENGE!
Ask your educator for the sheet of paper that you will need.
Time for self-assessment
Read the criteria. How do you feel about the work that we have just completed? Colour the face that is true for you.

DID YOU KNOW?
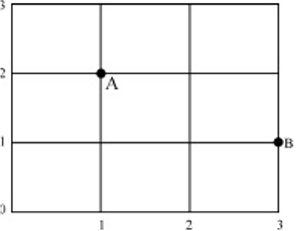
We can make use of co-ordinates when we need to read a map or directions. It is
important to know that we always have to read the horizontal axis first.
In this example, point A reads as
paired numbers (1,2).
If you read the pair (3,1), you will
arrive at B.
Sometimes direction is also given, and then it is: (1E, 2N) or (3E, 1N).
Learning Outcome 3: The learner will be able to describe and represent characteristics and relationships between two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional objects in a variety of orientations and positions.
Assessment Standard 3.7: We know this when the learner draws and interprets sketches of simple three-dimensional objects from different positions (perspectives).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 6' conversation and receive update notifications?