| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The scientific definition of work differs in some ways from its everyday meaning. Certain things we think of as hard work, such as writing an exam or carrying a heavy load on level ground, are not work as defined by a scientist. The scientific definition of work reveals its relationship to energy—whenever work is done, energy is transferred.
For work, in the scientific sense, to be done, a force must be exerted and there must be motion or displacement in the direction of the force.
Formally, the work done on a system by a constant force is defined to be the product of the component of the force in the direction of motion times the distance through which the force acts . For one-way motion in one dimension, this is expressed in equation form as
as long as one keeps in mind that the force is in the same direction as the distance.
To find the work done on a system that undergoes motion that is not one-way or that is in two or three dimensions, we would divide the motion into one-way one-dimensional segments and add up the work done over each segment.
The work done on a system by a constant force is the product of the component of the force in the direction of motion times the distance through which the force acts . For one-way motion in one dimension, this is expressed in equation form as
Where is work, is the distance the force acts, is the force parallel to the direction of motion.
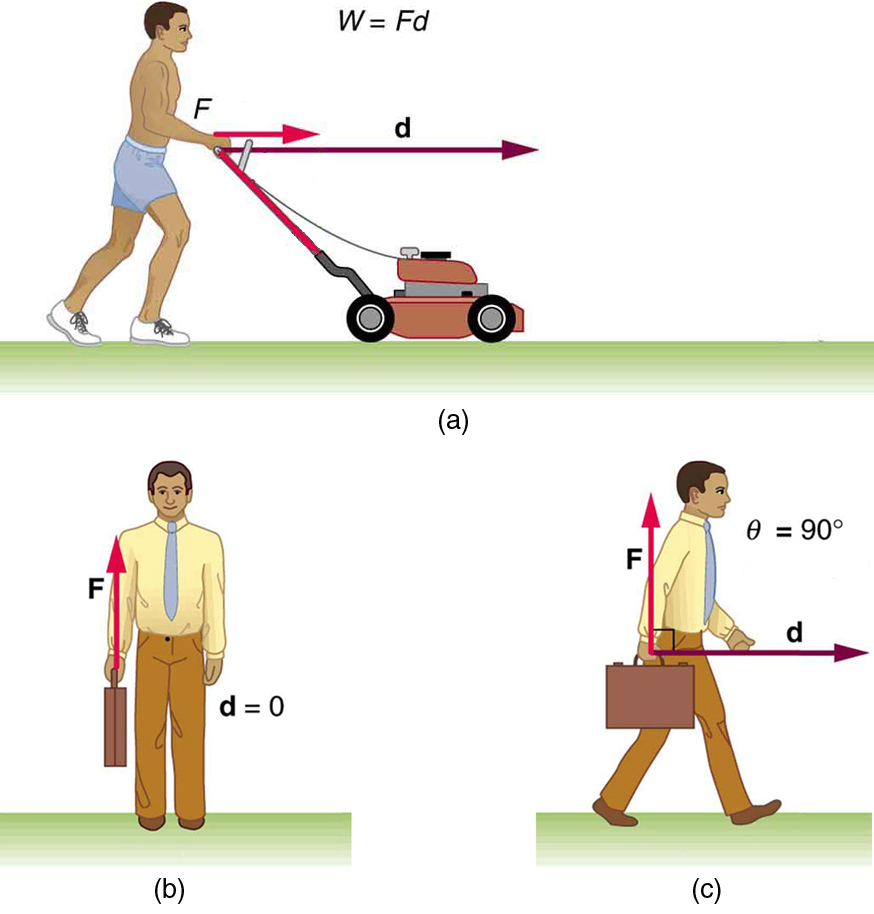
To examine what the definition of work means, let us consider the other situations shown in [link] . The person holding the briefcase in [link] (b) does no work, for example. Here , so . Why is it you get tired just holding a load? The answer is that your muscles are doing work against one another, but they are doing no work on the system of interest (the “briefcase-Earth system”). There must be motion for work to be done, and there must be a component of the force in the direction of the motion. For example, the person carrying the briefcase on level ground in [link] (c) does no work on it, because the force is perpendicular to the motion.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of physics' conversation and receive update notifications?