| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A. NORTH-EAST AFRICA
Design a catching tourist brochure that explains the historical value of an Empire/place of your choice. Tourists must be encouraged to visit the area.
The Egyptian civilisation (3000 B.C. – 6 00 A.D.) was one of the greatest and best-known civilisations of ancient times. But we shall be focusing on smaller kingdoms like those that developed in Nubia (Meroë), Cush and Axum.
Gold, ivory, slaves, copper, iron, jewellery, spices and pelts (animal skins) lured traders and sailing vessels from the Moslem world, India and China to East Africa. The rulers of large cities like Mogadishu, Malindi and Kilwa became fabulously rich through the taxes that were levied when traders travelled through these cities.
The Nubian Kingdom (750 B.C. – 500 A.D)
The kingdoms of Cush developed along the southern parts of the Nile. Commerce involved trading in ivory, gold, pelts, ostrich feathers and slaves.
The Nubian Kingdom , situated further south than Egypt and nowadays known as the Sudan, was also established. Although the country largely consisted of desert, the soil around the Nile was extremely fertile due to the annual flooding. By 600 B.C., Meroë was made the capital city. There was a constant flow of trade in gold, ivory, exotic animals, elephant tusks, wood, iron, pelts and fruit with Egypt and the countries of the Mediterranean region. Nubian art, architecture and religion were influenced by the Egyptians, but the Nubians developed their own alphabet. They kept cattle, cultivated cotton and used water wheels operated by oxen to get water to irrigate their fields.
Their kingdom was subjected and taken over by the Kingdom of Axum round about 500 A.D.
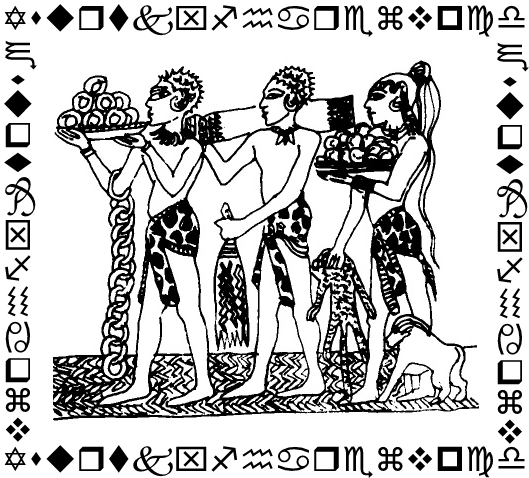
A mural from an Egyptian tomb showing Nubians delivering gifts of fruit, jewels, clothing and monkeys to the pharaoh.
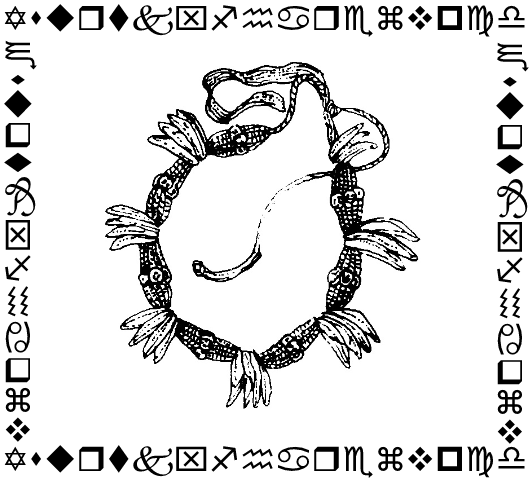
Egyptian murals depicting Nubian men and women wearing necklaces of animal teeth.
The Kingdom of Axum (500 B.C. – 600 A.D.)
This Kingdom near the southern reaches of the Red Sea, in the mountains of the present Ethiopia, developed to the southeast of Cush. Its advantageous position favoured trade in ivory, spices, exotic animals, gold, precious stones, wine and slaves and the wealth of the kingdom increased. Most of the inhabitants were farmers, builders and wood carvers. Axum was one of the first African kingdoms to embrace Christianity. A new style of government was practised, with powerful rulers governing specific areas and paying taxes as well as contributing in other ways to the kingdom. With sailors developing better ways of using the winds, trade with the Mediterranean countries and countries around the Red Sea, as well as the Persian Gulf and the Indian Ocean was extended. They even engaged in trade with the Greeks and the Romans.
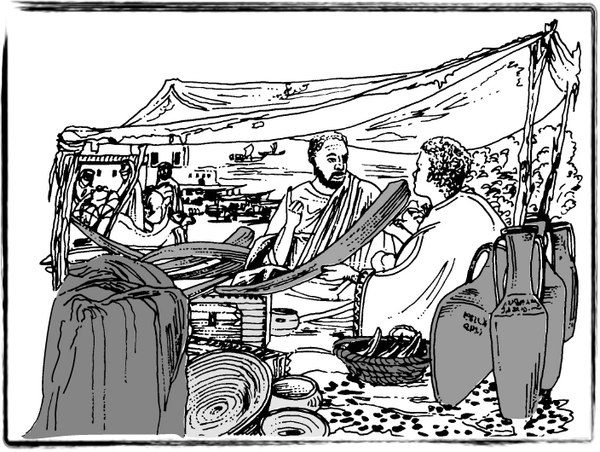

A variety of goods were used for trading
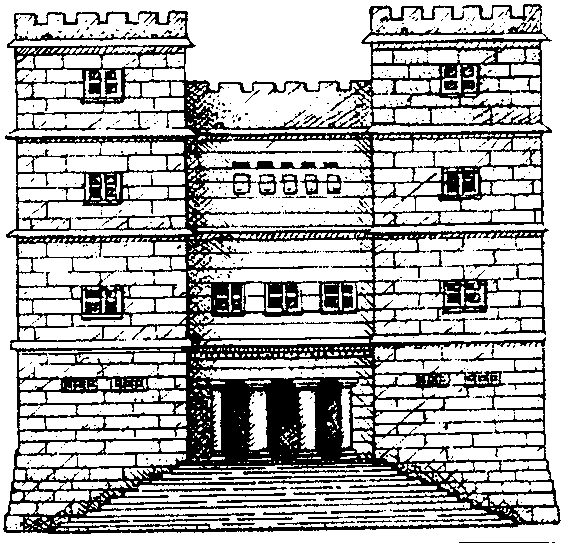
A typical palace in which a king might have lived
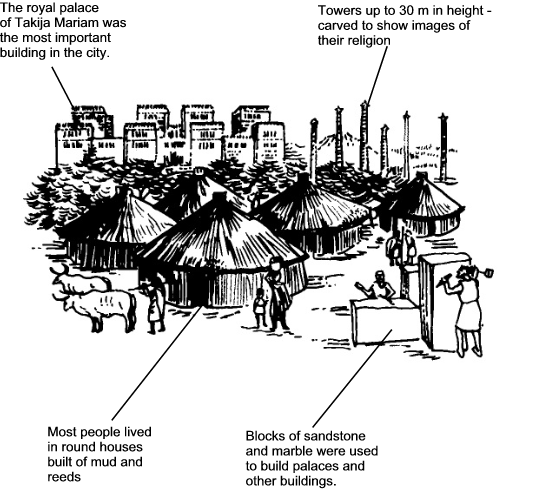
B . WEST AFRICA

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'History grade 6' conversation and receive update notifications?