| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
While the chemistry of strontium, barium (and radium) is similar to that of calcium, magnesium and beryllium show marked differences. In both cases these differences are due to the small size of the ions.
Beryllium can be thought of as being even more covalent than magnesium. The small size ( ca. 0.3 Å) results in a very high charge density of Be 2+ . In addition, the ionization energy for beryllium is a large positive value (1 st ionization energy = 899.5 kJ/mol, 2 nd ionization energy = 14,848.7 kJ/mol). Both of these factors means that the free ion does not exist. Instead, beryllium forms covalent compounds in a similar manner to its diagonal analog aluminum. Both beryllium and aluminum form covalent compounds or strongly solvated cations, and both form polymeric hydrides, chlorides, and alkyls.
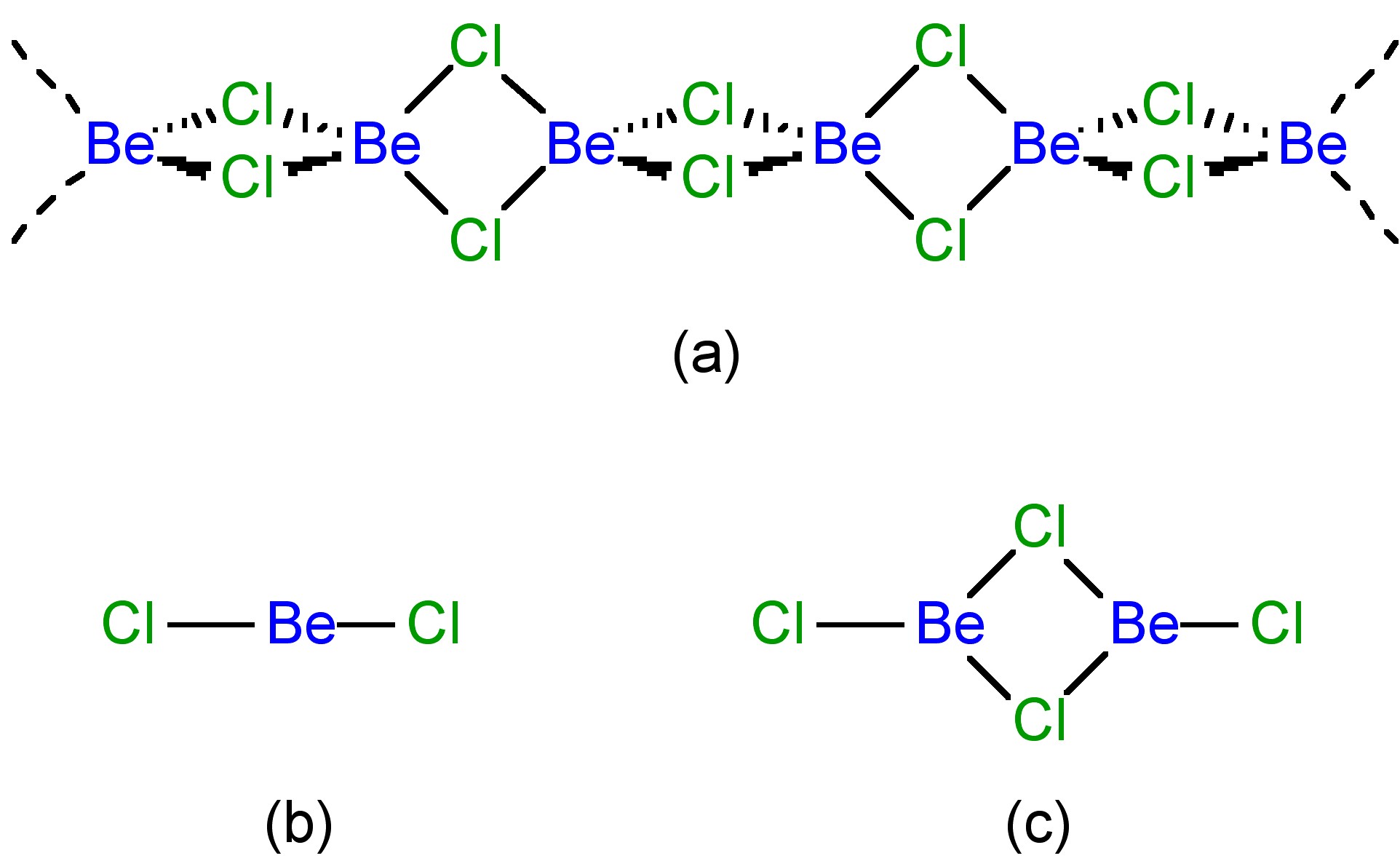
Beryllium chloride is not a lattice structure with a concomitantly high melting and boiling point as observed for the other Group 2 metals ( [link] ). Instead BeCl 2 is a polymer in the solid state ( [link] a), and an equilibrium between a monomer ( [link] b) and dimer ( [link] c) in the vapor phase.
| M | Structure |
| Be | Polymer (4-coordinate Be) |
| Mg | Cadmium chloride structure (6-coordinate Mg) |
| Ca | Deformed rutile structure (6-coordinate Ca) |
| Sr | Deformed rutile structure (6-coordinate Sr) |
| Ba | PbCl 2 structure (9-coordinate Ba) or fluorite structure (8-coordinate Ba) |
The ionic radius for the +2 cation of magnesium is fairly small (0.65 Å). As a consequence the charge density (z/r) is high, which results in a high polarizing power of the Mg 2+ ion. Thus, magnesium tends to form polar covalent bonds rather than ionic complexes. As with lithium there is a wide range of organometallic derivatives of magnesium, especially the Grignards (RMgX, where X = Cl, Br).
A further consequence of the covalent character of the bonding is that magnesium tends to form either 4-coordinate (tetrahedral) or 6-coordinate (octahedral) complexes with well-defined geometries.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry of the main group elements' conversation and receive update notifications?