| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We can use hybrid orbitals, which are mathematical combinations of some or all of the valence atomic orbitals, to describe the electron density around covalently bonded atoms. These hybrid orbitals either form sigma (σ) bonds directed toward other atoms of the molecule or contain lone pairs of electrons. We can determine the type of hybridization around a central atom from the geometry of the regions of electron density about it. Two such regions imply sp hybridization; three, sp 2 hybridization; four, sp 3 hybridization; five, sp 3 d hybridization; and six, sp 3 d 2 hybridization. Pi (π) bonds are formed from unhybridized atomic orbitals ( p or d orbitals).
Why is the concept of hybridization required in valence bond theory?
Hybridization is introduced to explain the geometry of bonding orbitals in valance bond theory.
Give the shape that describes each hybrid orbital set:
(a) sp 2
(b) sp 3 d
(c) sp
(d) sp 3 d 2
Explain why a carbon atom cannot form five bonds using sp 3 d hybrid orbitals.
There are no d orbitals in the valence shell of carbon.
What is the hybridization of the central atom in each of the following?
(a) BeH 2
(b) SF 6
(c)
(d) PCl 5
A molecule with the formula AB 3 could have one of four different shapes. Give the shape and the hybridization of the central A atom for each.
trigonal planar, sp 2 ; trigonal pyramidal (one lone pair on A) sp 3 ; T-shaped (two lone pairs on A sp 3 d , or (three lone pairs on A) sp 3 d 2
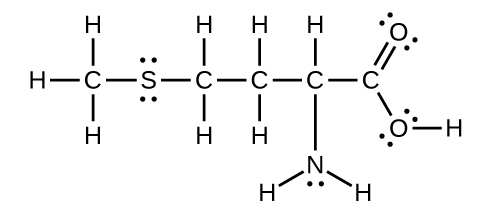
Methionine, CH 3 SCH 2 CH 2 CH(NH 2 )CO 2 H, is an amino acid found in proteins. Draw a Lewis structure of this compound. What is the hybridization type of each carbon, oxygen, the nitrogen, and the sulfur?
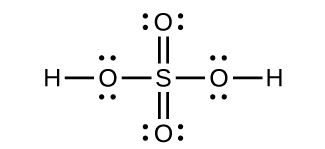
Sulfuric acid is manufactured by a series of reactions represented by the following equations:
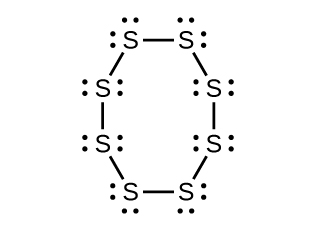
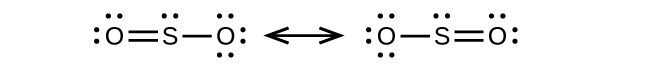
Draw a Lewis structure, predict the molecular geometry by VSEPR, and determine the hybridization of sulfur for the following:
(a) circular S 8 molecule
(b) SO 2 molecule
(c) SO 3 molecule
(d) H 2 SO 4 molecule (the hydrogen atoms are bonded to oxygen atoms)
(a) Each S has a bent (109°) geometry,
sp
3
(b) Bent (120°),
sp
2
(c) Trigonal planar,
sp
2
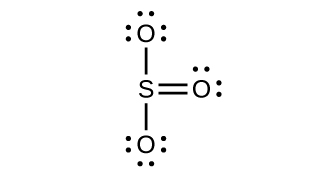
(d) Tetrahedral,
sp
3
Two important industrial chemicals, ethene, C
2 H
4 , and propene, C
3 H
6 , are produced by the steam (or thermal) cracking process:
For each of the four carbon compounds, do the following:
(a) Draw a Lewis structure.
(b) Predict the geometry about the carbon atom.
(c) Determine the hybridization of each type of carbon atom.
For many years after they were discovered, it was believed that the noble gases could not form compounds. Now we know that belief to be incorrect. A mixture of xenon and fluorine gases, confined in a quartz bulb and placed on a windowsill, is found to slowly produce a white solid. Analysis of the compound indicates that it contains 77.55% Xe and 22.45% F by mass.
(a) What is the formula of the compound?
(b) Write a Lewis structure for the compound.
(c) Predict the shape of the molecules of the compound.
(d) What hybridization is consistent with the shape you predicted?
(a) XeF
2
(b)
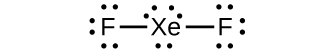
(c) linear (d)
sp
3
d
Consider nitrous acid, HNO 2 (HONO).
(a) Write a Lewis structure.
(b) What are the electron pair and molecular geometries of the internal oxygen and nitrogen atoms in the HNO 2 molecule?
(c) What is the hybridization on the internal oxygen and nitrogen atoms in HNO 2 ?
Strike-anywhere matches contain a layer of KClO 3 and a layer of P 4 S 3 . The heat produced by the friction of striking the match causes these two compounds to react vigorously, which sets fire to the wooden stem of the match. KClO 3 contains the ion. P 4 S 3 is an unusual molecule with the skeletal structure.
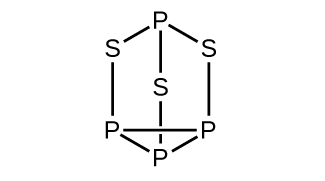
(a) Write Lewis structures for P 4 S 3 and the ion.
(b) Describe the geometry about the P atoms, the S atom, and the Cl atom in these species.
(c) Assign a hybridization to the P atoms, the S atom, and the Cl atom in these species.
(d) Determine the oxidation states and formal charge of the atoms in P 4 S 3 and the ion.
(a)
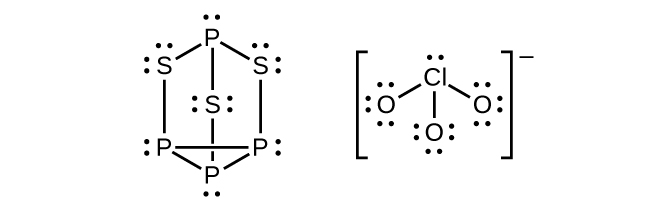
(b) P atoms, trigonal pyramidal; S atoms, bent, with two lone pairs; Cl atoms, trigonal pyramidal; (c) Hybridization about P, S, and Cl is, in all cases,
sp
3 ; (d) Oxidation states P +1, S
Cl +5, O –2. Formal charges: P 0; S 0; Cl +2: O –1
Identify the hybridization of each carbon atom in the following molecule. (The arrangement of atoms is given; you need to determine how many bonds connect each pair of atoms.)

Write Lewis structures for NF 3 and PF 5 . On the basis of hybrid orbitals, explain the fact that NF 3 , PF 3 , and PF 5 are stable molecules, but NF 5 does not exist.
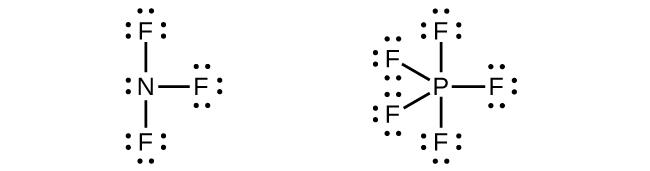
Phosphorus and nitrogen can form sp 3 hybrids to form three bonds and hold one lone pair in PF 3 and NF 3 , respectively. However, nitrogen has no valence d orbitals, so it cannot form a set of sp 3 d hybrid orbitals to bind five fluorine atoms in NF 5 . Phosphorus has d orbitals and can bind five fluorine atoms with sp 3 d hybrid orbitals in PF 5 .
In addition to NF 3 , two other fluoro derivatives of nitrogen are known: N 2 F 4 and N 2 F 2 . What shapes do you predict for these two molecules? What is the hybridization for the nitrogen in each molecule?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ut austin - principles of chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?