| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
An important signal parameter estimation problem is time-delay estimation. Here the unknown is the time origin of the signal: . The duration of the signal (the domain over which the signal is defined) is assumed brief compared with theobservation interval . Although in continuous time the signal delay is a continuous-valued variable, in discrete time it is not.Consequently, the maximum likelihood estimate cannot be found by differentiation, and we must determine the maximum likelihood estimate of signal delayby the most fundamental expression of the maximization procedure. Assuming Gaussian noise, the maximum likelihoodestimate of delay is the solution of The term is usually assumed not to vary with the presumed time origin of the signal because of the signal's short duration. Ifthe noise is white, this term is constant except near the "edges" of the observation interval. If not white, the kernelof this quadratic form is equivalent to a whitening filter. As discussed later , this filter may be time varying. For noise spectra that are rational and haveonly poles, the whitening filter's unit-sample response varies only near the edges (see the example ). Thus, near the edges, this quadratic form varies with presumed delay and the maximizationis analytically difficult. Taking the "easy way out" by ignoring edge effects, the estimate is the solution of Thus, the delay estimate is the signal time origin that maximizes the matched filter's output.
In addition to the complexity of finding the maximum likelihood estimate, the discrete-valued nature of the parameter also callsinto question the use of the Cramér-Rao bound. One of the fundamental assumptions of the bound's derivation is the differentiability of the likelihood function with respect to theparameter. Mathematically, a sequence cannot be differentiated with respect to the integers. A sequence can be differentiatedwith respect to its argument if we consider the variable to be continuous valued. This approximation can be used only if thesampling interval, unity for the integers, is dense with respect to variations of the sequence. This condition means that thesignal must be oversampled to apply the Cramér-Rao bound in a meaningful way. Under these conditions, the mean-squaredestimation error for unbiased estimators can be no smaller than the Cramér-Rao bound, which is given by which, in the white-noise case, becomes
Assume that the noise is white. Because of this assumption, we determine the time delay by maximizing the match-filteredobservations. The number of terms in the sum equals the signal duration. [link] illustrates the match-filtered output in two separate situations; in one thesignal has a relatively low-frequency spectrum as compared with the second.
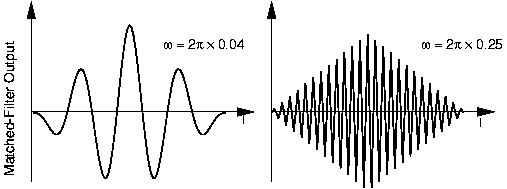
Because of the symmetry of the autocorrelation function, the estimate should be unbiased so long as the autocorrelation function is completely contained withinthe observation interval. Direct proof of this claim is left to the masochistic reader. For sinusoidal signals of energy and frequency , the Cramér-Rao bound is given by . This bound on the error is accurate only if the measured maximum frequently occurs in the dominant peak of thesignal's autocorrelation function. Otherwise, the maximum likelihood estimate "skips" a cycle and produces valuesconcentrated near one of the smaller peaks. The interval between zero crossings of the dominant peak is ; the signal-to-noise ratio must exceed (about 0.5). Remember that this result implicitly assumed a low-frequency sinusoid. Thesecond example demonstrates that cycle skipping occurs more frequently thanthis guideline suggests when a high-frequency sinusoid is used.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Statistical signal processing' conversation and receive update notifications?