| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The molecular shape simulator lets you build various molecules and practice naming their electron-pair geometries and molecular structures.
Build the molecule HCN in the simulator based on the following Lewis structure:
Click on each bond type or lone pair at right to add that group to the central atom. Once you have the complete molecule, rotate it to examine the predicted molecular structure. What molecular structure is this?
Answers will vary. For example, an atom with four single bonds, a double bond, and a lone pair has an octahedral electron-group geometry and a square pyramidal molecular structure. XeOF 4 is a molecule that adopts this structure.
As discussed previously, polar covalent bonds connect two atoms with differing electronegativities, leaving one atom with a partial positive charge (δ+) and the other atom with a partial negative charge (δ–), as the electrons are pulled toward the more electronegative atom. This separation of charge gives rise to a bond dipole moment . The magnitude of a bond dipole moment is represented by the Greek letter mu ( µ ) and is given by the formula shown here, where Q is the magnitude of the partial charges (determined by the electronegativity difference) and r is the distance between the charges:
This bond moment can be represented as a vector , a quantity having both direction and magnitude ( [link] ). Dipole vectors are shown as arrows pointing along the bond from the less electronegative atom toward the more electronegative atom. A small plus sign is drawn on the less electronegative end to indicate the partially positive end of the bond. The length of the arrow is proportional to the magnitude of the electronegativity difference between the two atoms.
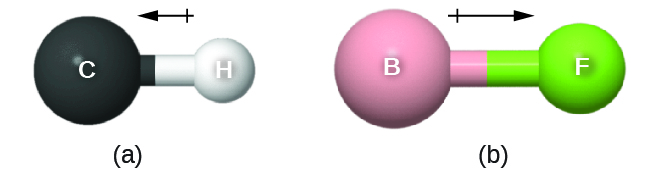
A whole molecule may also have a separation of charge, depending on its molecular structure and the polarity of each of its bonds. If such a charge separation exists, the molecule is said to be a polar molecule (or dipole); otherwise the molecule is said to be nonpolar. The dipole moment measures the extent of net charge separation in the molecule as a whole. We determine the dipole moment by adding the bond moments in three-dimensional space, taking into account the molecular structure.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ut austin - principles of chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?