| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Write the Lewis symbols for each of the following ions:
(a) As 3–
(b) I –
(c) Be 2+
(d) O 2–
(e) Ga 3+
(f) Li +
(g) N 3–
(a) eight electrons:
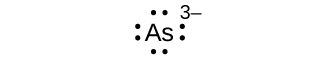 ;
;
(b) eight electrons:
 ;
;
(c) no electrons
Be
2+ ;
(d) eight electrons:
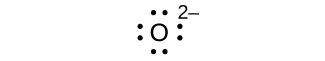 ;
;
(e) no electrons
Ga
3+ ;
(f) no electrons
Li
+ ;
(g) eight electrons:
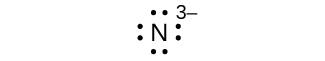
Many monatomic ions are found in seawater, including the ions formed from the following list of elements. Write the Lewis symbols for the monatomic ions formed from the following elements:
(a) Cl
(b) Na
(c) Mg
(d) Ca
(e) K
(f) Br
(g) Sr
(h) F
Write the Lewis symbols of the ions in each of the following ionic compounds and the Lewis symbols of the atom from which they are formed:
(a) MgS
(b) Al 2 O 3
(c) GaCl 3
(d) K 2 O
(e) Li 3 N
(f) KF
(a)
 ;
;
(b)
 ;
;
(c)
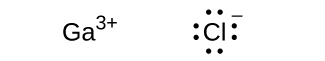 ;
;
(d)
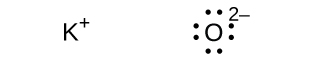 ;
;
(e)
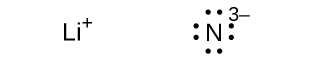 ;
;
(f)
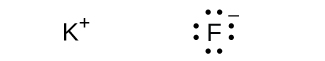
In the Lewis structures listed here, M and X represent various elements in the third period of the periodic table. Write the formula of each compound using the chemical symbols of each element:
(a)
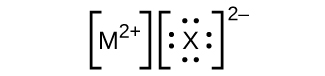
(b)
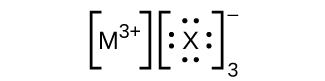
(c)
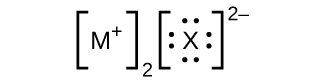
(d)
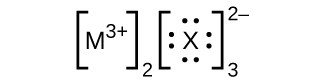
Write the Lewis structure for the diatomic molecule P 2 , an unstable form of phosphorus found in high-temperature phosphorus vapor.

Write Lewis structures for the following:
(a) H 2
(b) HBr
(c) PCl 3
(d) SF 2
(e) H 2 CCH 2
(f) HNNH
(g) H 2 CNH
(h) NO –
(i) N 2
(j) CO
(k) CN –
Write Lewis structures for the following:
(a) O 2
(b) H 2 CO
(c) AsF 3
(d) ClNO
(e) SiCl 4
(f) H 3 O +
(g)
(h)
(i) HCCH
(j) ClCN
(k)
(a)
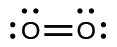
In this case, the Lewis structure is inadequate to depict the fact that experimental studies have shown two unpaired electrons in each oxygen molecule
.
(b)
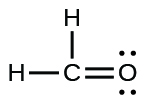 ;
;
(c)
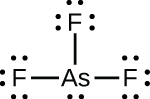 ;
;
(d)
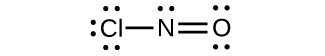 ;
;
(e)
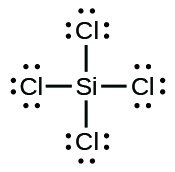 ;
;
(f)
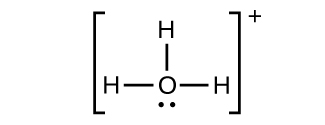 ;
;
(g)
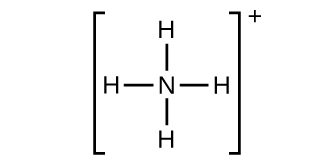 ;
;
(h)
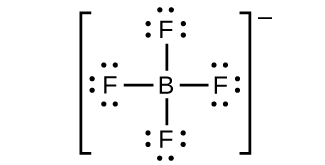 ;
;
(i)
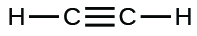 ;
;
(j)
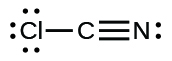 ;
;
(k)
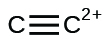
Write Lewis structures for the following:
(a) ClF 3
(b) PCl 5
(c) BF 3
(d)
Write Lewis structures for the following:
(a) SeF 6
(b) XeF 4
(c)
(d) Cl 2 BBCl 2 (contains a B–B bond)
(a) SeF
6 :
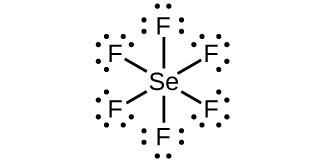 ;
;
(b) XeF
4 :
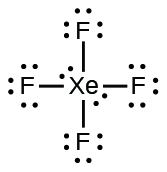 ;
;
(c)
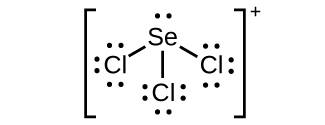 ;
;
(d) Cl
2 BBCl
2 :
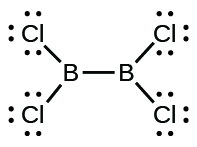
Write Lewis structures for:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) HONO
Correct the following statement: “The bonds in solid PbCl 2 are ionic; the bond in a HCl molecule is covalent. Thus, all of the valence electrons in PbCl 2 are located on the Cl – ions, and all of the valence electrons in a HCl molecule are shared between the H and Cl atoms.”
Two valence electrons per Pb atom are transferred to Cl atoms; the resulting Pb 2+ ion has a 6 s 2 valence shell configuration. Two of the valence electrons in the HCl molecule are shared, and the other six are located on the Cl atom as lone pairs of electrons.
Write Lewis structures for the following molecules or ions:
(a) SbH 3
(b) XeF 2
(c) Se 8 (a cyclic molecule with a ring of eight Se atoms)
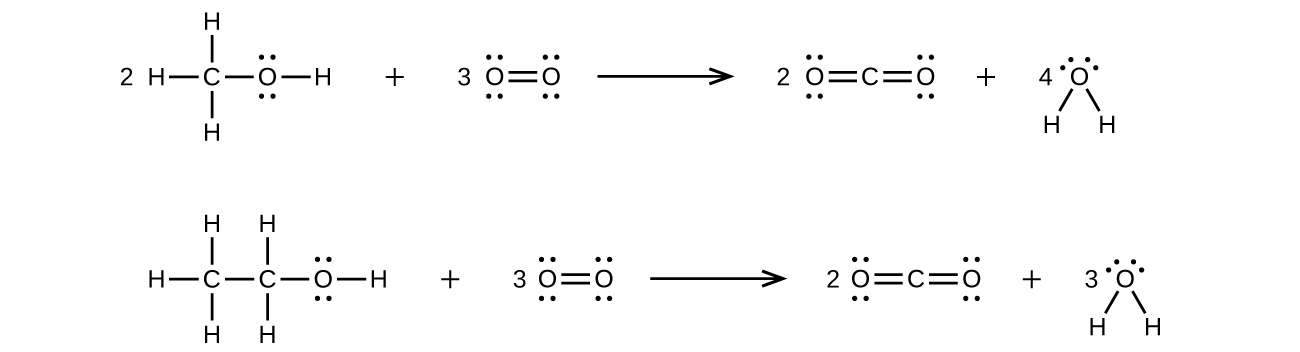
Methanol, H 3 COH, is used as the fuel in some race cars. Ethanol, C 2 H 5 OH, is used extensively as motor fuel in Brazil. Both methanol and ethanol produce CO 2 and H 2 O when they burn. Write the chemical equations for these combustion reactions using Lewis structures instead of chemical formulas.
Many planets in our solar system contain organic chemicals including methane (CH 4 ) and traces of ethylene (C 2 H 4 ), ethane (C 2 H 6 ), propyne (H 3 CCCH), and diacetylene (HCCCCH). Write the Lewis structures for each of these molecules.
Carbon tetrachloride was formerly used in fire extinguishers for electrical fires. It is no longer used for this purpose because of the formation of the toxic gas phosgene, Cl 2 CO. Write the Lewis structures for carbon tetrachloride and phosgene.
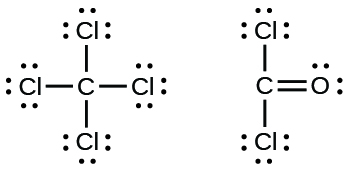
Identify the atoms that correspond to each of the following electron configurations. Then, write the Lewis symbol for the common ion formed from each atom:
(a) 1 s 2 2 s 2 2 p 5
(b) 1 s 2 2 s 2 2 p 6 3 s 2
(c) 1 s 2 2 s 2 2 p 6 3 s 2 3 p 6 4 s 2 3 d 10
(d) 1 s 2 2 s 2 2 p 6 3 s 2 3 p 6 4 s 2 3 d 10 4 p 4
(e) 1 s 2 2 s 2 2 p 6 3 s 2 3 p 6 4 s 2 3 d 10 4 p 1
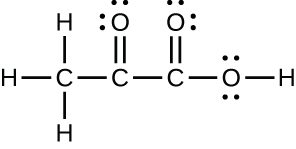
The arrangement of atoms in several biologically important molecules is given here. Complete the Lewis structures of these molecules by adding multiple bonds and lone pairs. Do not add any more atoms.
(a) the amino acid serine:
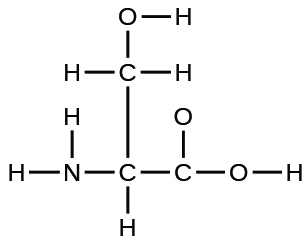
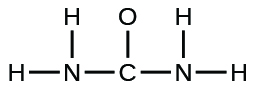
(b) urea:
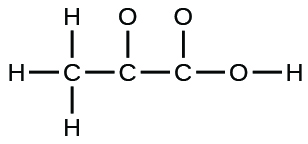
(c) pyruvic acid:
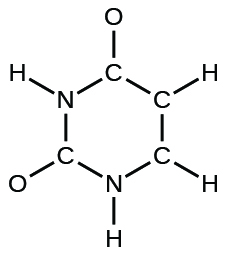
(d) uracil:
(e) carbonic acid:
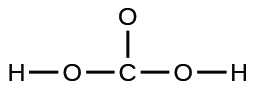
(a)
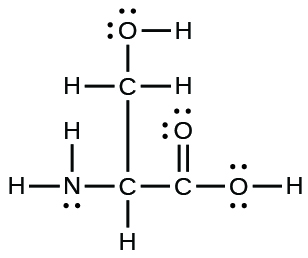 ;
;
(b)
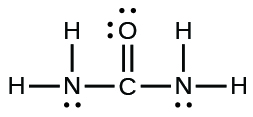 ;
;
(c)
 ;
;
(d)
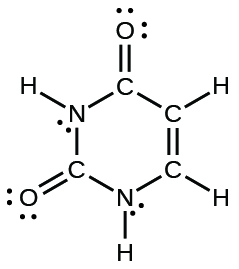 ;
;
(e)
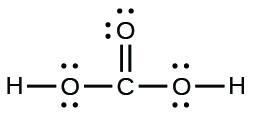
A compound with a molar mass of about 28 g/mol contains 85.7% carbon and 14.3% hydrogen by mass. Write the Lewis structure for a molecule of the compound.
A compound with a molar mass of about 42 g/mol contains 85.7% carbon and 14.3% hydrogen by mass. Write the Lewis structure for a molecule of the compound.
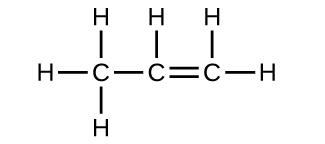
Two arrangements of atoms are possible for a compound with a molar mass of about 45 g/mol that contains 52.2% C, 13.1% H, and 34.7% O by mass. Write the Lewis structures for the two molecules.
How are single, double, and triple bonds similar? How do they differ?
Each bond includes a sharing of electrons between atoms. Two electrons are shared in a single bond; four electrons are shared in a double bond; and six electrons are shared in a triple bond.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ut austin - principles of chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?