| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Freeze drying is a process in which substances, such as foods, are dried by placing them in a vacuum chamber and lowering the atmospheric pressure around them. How does the lowered atmospheric pressure speed the drying process, and why does it cause the temperature of the food to drop?
Decreased the atmospheric pressure results in decreased partial pressure of water, hence a lower humidity. So evaporation of water from food, for example, will be enhanced. The molecules of water most likely to break away from the food will be those with the greatest velocities. Those remaining thus have a lower average velocity and a lower temperature. This can (and does) result in the freezing and drying of the food; hence the process is aptly named freeze drying.
Watch different types of molecules form a solid, liquid, or gas. Add or remove heat and watch the phase change. Change the temperature or volume of a container and see a pressure-temperature diagram respond in real time. Relate the interaction potential to the forces between molecules.

Because humidity depends only on water’s vapor pressure and temperature, are the saturation vapor densities listed in [link] valid in an atmosphere of helium at a pressure of , rather than air? Are those values affected by altitude on Earth?
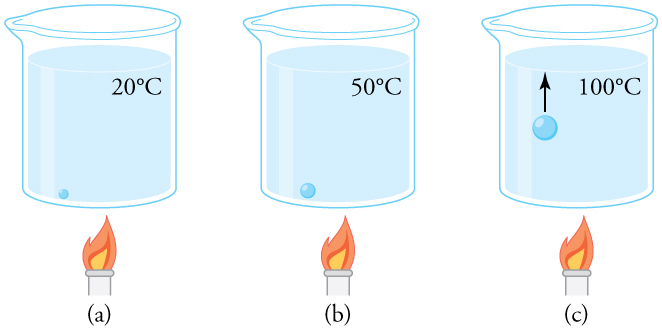
Why does a beaker of water placed in a vacuum chamber start to boil as the chamber is evacuated (air is pumped out of the chamber)? At what pressure does the boiling begin? Would food cook any faster in such a beaker?
Why does rubbing alcohol evaporate much more rapidly than water at STP (standard temperature and pressure)?
Dry air is 78.1% nitrogen. What is the partial pressure of nitrogen when the atmospheric pressure is ?
(a) What is the vapor pressure of water at ? (b) What percentage of atmospheric pressure does this correspond to? (c) What percent of air is water vapor if it has 100% relative humidity? (The density of dry air at is .)
Pressure cookers increase cooking speed by raising the boiling temperature of water above its value at atmospheric pressure. (a) What pressure is necessary to raise the boiling point to ? (b) What gauge pressure does this correspond to?
(a)
(b) 0.97 atm

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics (engineering physics 2, tuas)' conversation and receive update notifications?