| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Explore how a capacitor works! Change the size of the plates and add a dielectric to see the effect on capacitance. Change the voltage and see charges built up on the plates. Observe the electric field in the capacitor. Measure the voltage and the electric field.

Does the capacitance of a device depend on the applied voltage? What about the charge stored in it?
Use the characteristics of the Coulomb force to explain why capacitance should be proportional to the plate area of a capacitor. Similarly, explain why capacitance should be inversely proportional to the separation between plates.
Give the reason why a dielectric material increases capacitance compared with what it would be with air between the plates of a capacitor. What is the independent reason that a dielectric material also allows a greater voltage to be applied to a capacitor? (The dielectric thus increases and permits a greater .)
How does the polar character of water molecules help to explain water’s relatively large dielectric constant? ( [link] )
Sparks will occur between the plates of an air-filled capacitor at lower voltage when the air is humid than when dry. Explain why, considering the polar character of water molecules.
Water has a large dielectric constant, but it is rarely used in capacitors. Explain why.
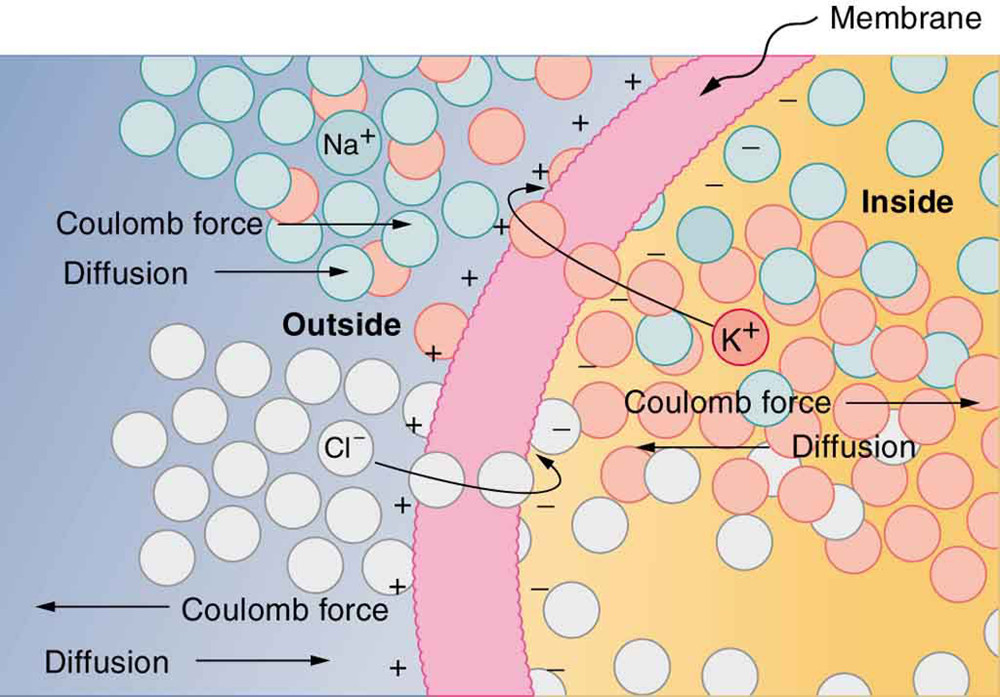
Membranes in living cells, including those in humans, are characterized by a separation of charge across the membrane. Effectively, the membranes are thus charged capacitors with important functions related to the potential difference across the membrane. Is energy required to separate these charges in living membranes and, if so, is its source the metabolization of food energy or some other source?
What charge is stored in a capacitor when 120 V is applied to it?
Find the charge stored when 5.50 V is applied to an 8.00 pF capacitor.
What charge is stored in the capacitor in [link] ?
Calculate the voltage applied to a capacitor when it holds of charge.
What voltage must be applied to an 8.00 nF capacitor to store 0.160 mC of charge?
20.0 kV
What capacitance is needed to store of charge at a voltage of 120 V?
What is the capacitance of a large Van de Graaff generator’s terminal, given that it stores 8.00 mC of charge at a voltage of 12.0 MV?
Find the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor having plates of area that are separated by 0.100 mm of Teflon.
(a)What is the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor having plates of area that are separated by 0.0200 mm of neoprene rubber? (b) What charge does it hold when 9.00 V is applied to it?
(a)
(b)
Integrated Concepts
A prankster applies 450 V to an capacitor and then tosses it to an unsuspecting victim. The victim’s finger is burned by the discharge of the capacitor through 0.200 g of flesh. What is the temperature increase of the flesh? Is it reasonable to assume no phase change?
Unreasonable Results
(a) A certain parallel plate capacitor has plates of area , separated by 0.0100 mm of nylon, and stores 0.170 C of charge. What is the applied voltage? (b) What is unreasonable about this result? (c) Which assumptions are responsible or inconsistent?
(a) 14.2 kV
(b) The voltage is unreasonably large, more than 100 times the breakdown voltage of nylon.
(c) The assumed charge is unreasonably large and cannot be stored in a capacitor of these dimensions.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'General physics ii phy2202ca' conversation and receive update notifications?