| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The thoracic cage (rib cage) forms the thorax (chest) portion of the body. It consists of the 12 pairs of ribs with their costal cartilages and the sternum ( [link] ). The ribs are anchored posteriorly to the 12 thoracic vertebrae (T1–T12). The thoracic cage protects the heart and lungs.
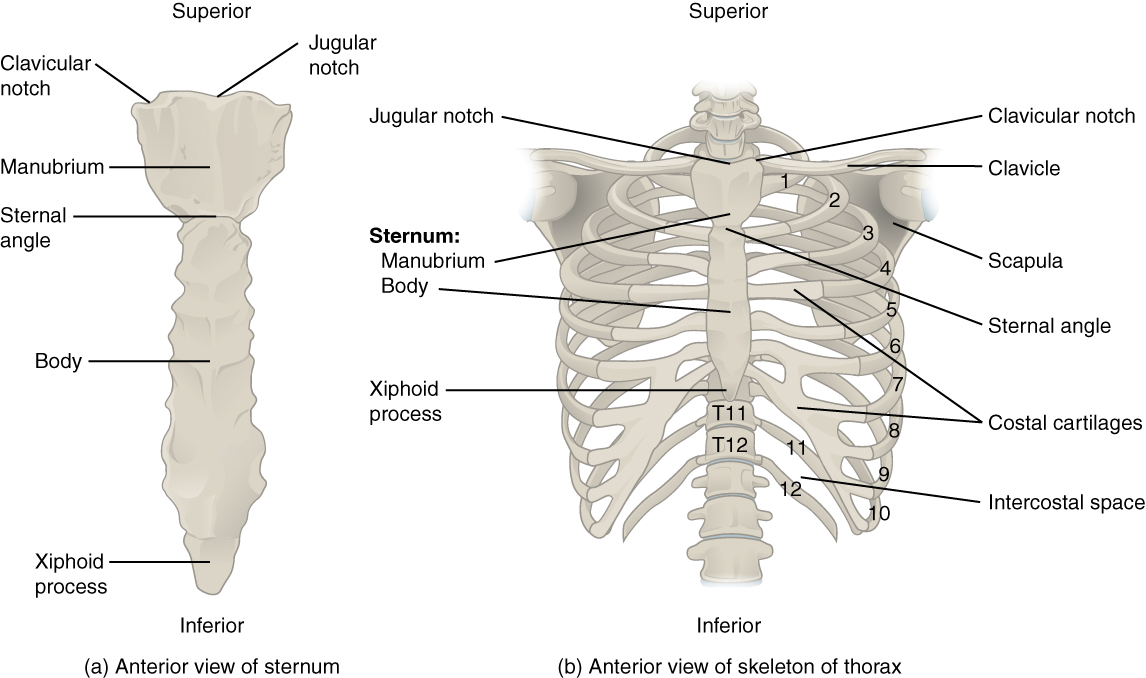
The sternum is the elongated bony structure that anchors the anterior thoracic cage. It consists of three parts: the manubrium, body, and xiphoid process. The manubrium is the wider, superior portion of the sternum. The top of the manubrium has a shallow, U-shaped border called the jugular (suprasternal) notch . This can be easily felt at the anterior base of the neck, between the medial ends of the clavicles. The clavicular notch is the shallow depression located on either side at the superior-lateral margins of the manubrium. This is the site of the sternoclavicular joint, between the sternum and clavicle. The first ribs also attach to the manubrium.
The elongated, central portion of the sternum is the body. The manubrium and body join together at the sternal angle , so called because the junction between these two components is not flat, but forms a slight bend. The second rib attaches to the sternum at the sternal angle. Since the first rib is hidden behind the clavicle, the second rib is the highest rib that can be identified by palpation. Thus, the sternal angle and second rib are important landmarks for the identification and counting of the lower ribs. Ribs 3–7 attach to the sternal body.
The inferior tip of the sternum is the xiphoid process . This small structure is cartilaginous early in life, but gradually becomes ossified starting during middle age.
Each rib is a curved, flattened bone that contributes to the wall of the thorax. The ribs articulate posteriorly with the T1–T12 thoracic vertebrae, and most attach anteriorly via their costal cartilages to the sternum. There are 12 pairs of ribs. The ribs are numbered 1–12 in accordance with the thoracic vertebrae.
The posterior end of a typical rib is called the head of the rib (see [link] ). This region articulates primarily with the costal facet located on the body of the same numbered thoracic vertebra and to a lesser degree, with the costal facet located on the body of the next higher vertebra. Lateral to the head is the narrowed neck of the rib . A small bump on the posterior rib surface is the tubercle of the rib , which articulates with the facet located on the transverse process of the same numbered vertebra. The remainder of the rib is the body of the rib (shaft). Just lateral to the tubercle is the angle of the rib , the point at which the rib has its greatest degree of curvature. The angles of the ribs form the most posterior extent of the thoracic cage. In the anatomical position, the angles align with the medial border of the scapula. A shallow costal groove for the passage of blood vessels and a nerve is found along the inferior margin of each rib.
The bony ribs do not extend anteriorly completely around to the sternum. Instead, each rib ends in a costal cartilage . These cartilages are made of hyaline cartilage and can extend for several inches. Most ribs are then attached, either directly or indirectly, to the sternum via their costal cartilage (see [link] ). The ribs are classified into three groups based on their relationship to the sternum.
Ribs 1–7 are classified as true ribs (vertebrosternal ribs). The costal cartilage from each of these ribs attaches directly to the sternum. Ribs 8–12 are called false ribs (vertebrochondral ribs). The costal cartilages from these ribs do not attach directly to the sternum. For ribs 8–10, the costal cartilages are attached to the cartilage of the next higher rib. Thus, the cartilage of rib 10 attaches to the cartilage of rib 9, rib 9 then attaches to rib 8, and rib 8 is attached to rib 7. The last two false ribs (11–12) are also called floating ribs (vertebral ribs). These are short ribs that do not attach to the sternum at all. Instead, their small costal cartilages terminate within the musculature of the lateral abdominal wall.
The thoracic cage protects the heart and lungs. It is composed of 12 pairs of ribs with their costal cartilages and the sternum. The ribs are anchored posteriorly to the 12 thoracic vertebrae. The sternum consists of the manubrium, body, and xiphoid process. The manubrium and body are joined at the sternal angle, which is also the site for attachment of the second ribs.
Ribs are flattened, curved bones and are numbered 1–12. Posteriorly, the head of the rib articulates with the costal facets located on the bodies of thoracic vertebrae and the rib tubercle articulates with the facet located on the vertebral transverse process. The angle of the ribs forms the most posterior portion of the thoracic cage. The costal groove in the inferior margin of each rib carries blood vessels and a nerve. Anteriorly, each rib ends in a costal cartilage. True ribs (1–7) attach directly to the sternum via their costal cartilage. The false ribs (8–12) either attach to the sternum indirectly or not at all. Ribs 8–10 have their costal cartilages attached to the cartilage of the next higher rib. The floating ribs (11–12) are short and do not attach to the sternum or to another rib.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology: support and movement' conversation and receive update notifications?