| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Types of Adaptation
There are different types of adaptation. In this learning unit we shall be looking at adaptations that have to do with ways of feeding and protection by means of colour.
A. Adaptations with regard to Food
B. Adaptations with regard to colour
A. Food-related Adaptation
All animals require food to remain alive. This food must firstly be found and the animals’ bodies must, be adapted to ingest and digest the food.
FEEDING comprises both ingestion and digestion.
Activity: TO USE PRIOR KNOWLEDGE TO GAIN NEW KNOWLEDGE
The most common adaptations related to feeding are:( Complete from prior knowledge)
HERBIVORES
CARNIVORES
OMNIVORES
HERBIVORES
Name two examples of herbivores from each of the following categories:
1. mammals
2. birds
3. insects
CARNIVORES:
Name two examples of carnivores from each of the following categories:
1. mammals
2. birds
3. insects
OMNIVORES:
Name two examples of omnivores from each of the following categories:
1. mammals
2. birds
3. insects
The most common adaptation in this regard is related to the TEETH in the skull of the animal.
Supply the function of each kind of tooth with the different ways of feeding of herbivores, carnivores and omnivores.
HERBIVORES: have to cut, gnaw and grind and therefore need strong incisors and molars.
CARNIVORES: have to bite and tear and therefore need strong incisors and canines. Molars are shaped like canines and not like grinders.
OMNIVORES: all teeth work equally well and are equally developed
[LO 2.1; 2.4]
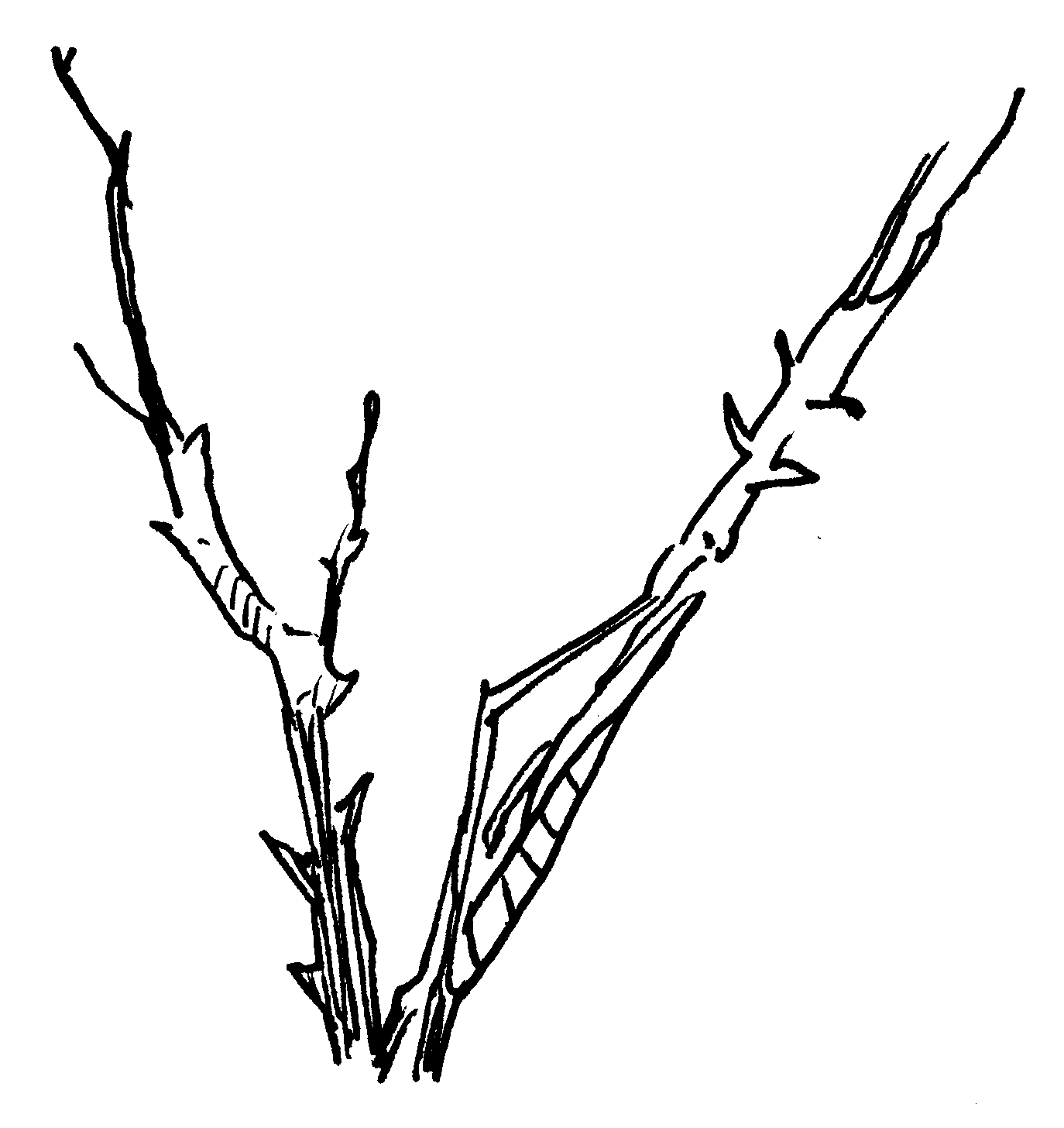
Teeth
Study the illustrations and answer the questions that follow:
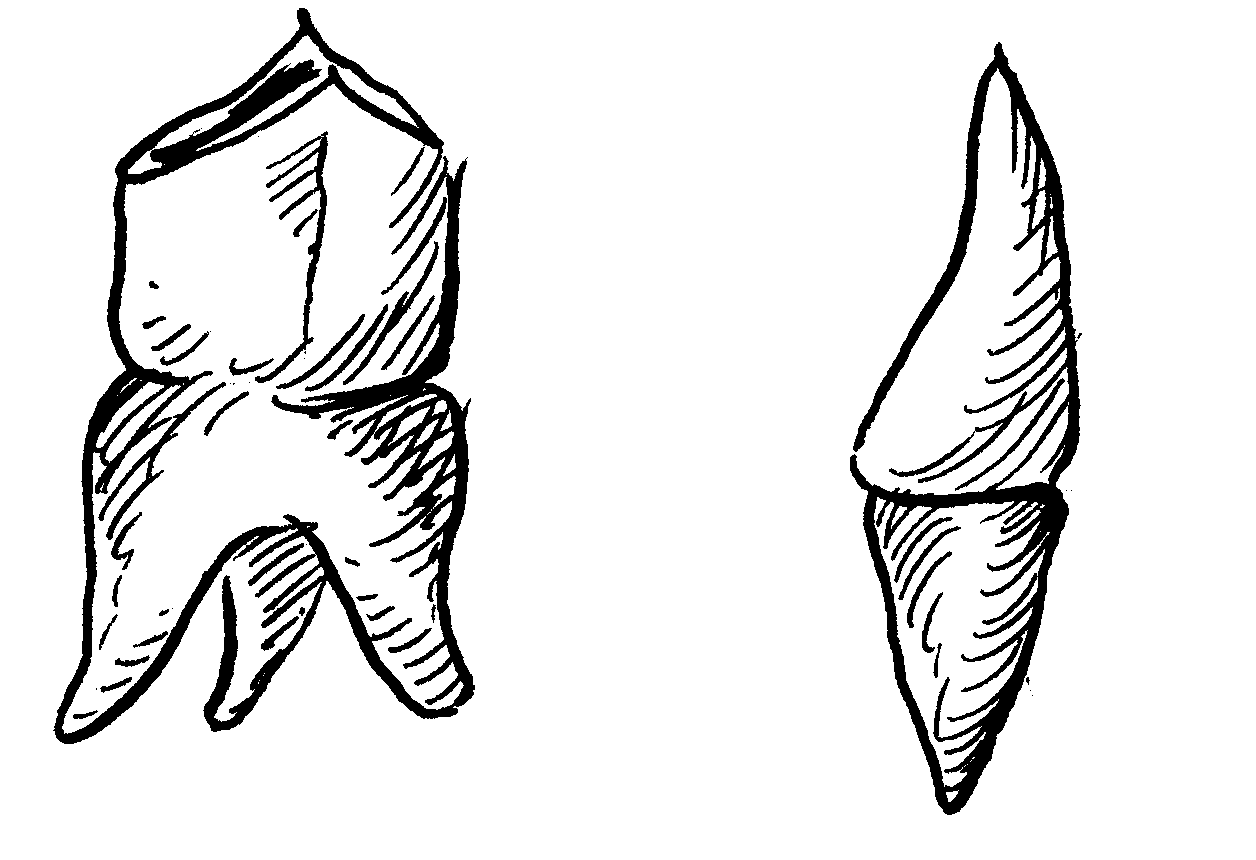
1. Which drawing represents a molar? Explain your choice:
2. To which kind of animal might the molar belong?
3. Identify the other tooth and explain your choice:
ASSIGNMENT:
We have examined the ways in which animal teeth are adapted to particular ways of feeding. Draw upon your own knowledge of cats, lions and leopards and describe the ways in which the bodies of carnivores are adapted to their manner of feeding.
[LO 2.4]
B. Colour Adaptations
Each animal in nature is a possible PREY to another organism. They need to protect themselves in any way possible for the sake of SURVIVAL.
We are going to look at COLOUR ADAPTATION to illustrate ways of fooling enemies:
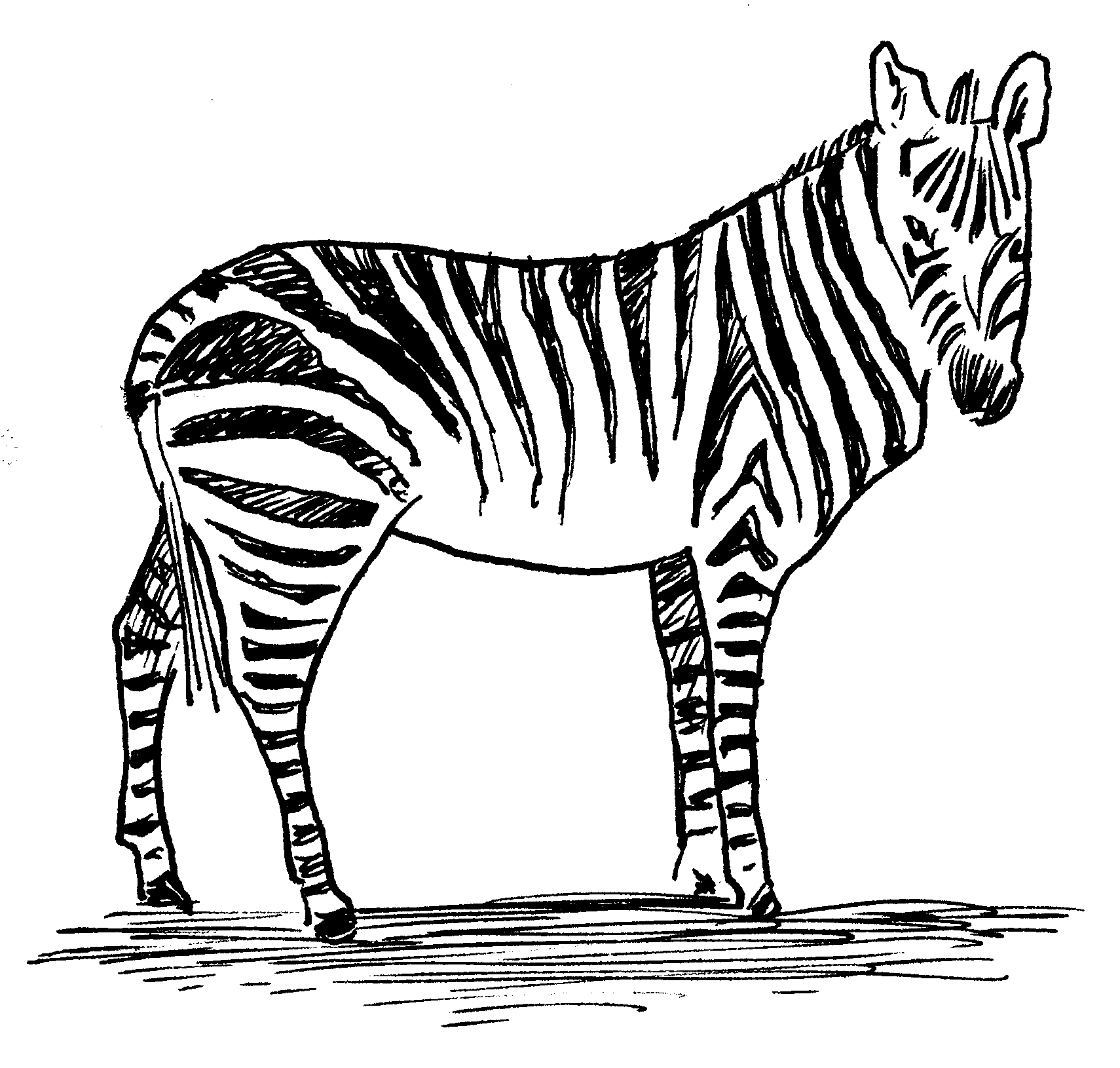
Camouflage
The animal seeks to blend into its natural environment by means of:
colour, e.g. green grasshoppers on grass
patterns, e.g. moth on the bark of a tree
stripes, e.g. some frogs among reeds
spots, e.g. the wings of a nightjar
colour changes, e.g. chameleons or fish
many marine animals have shiny white bellies and dark backs
colour changes that are seasonal, e.g. the polar fox
colour adaptation that accompanies adaptation of shape, e.g. stick insects or inch-worms
Warning colouring
Elegant grasshopper
Striped mongoose
Ladybirds
Wasps
Mimicry
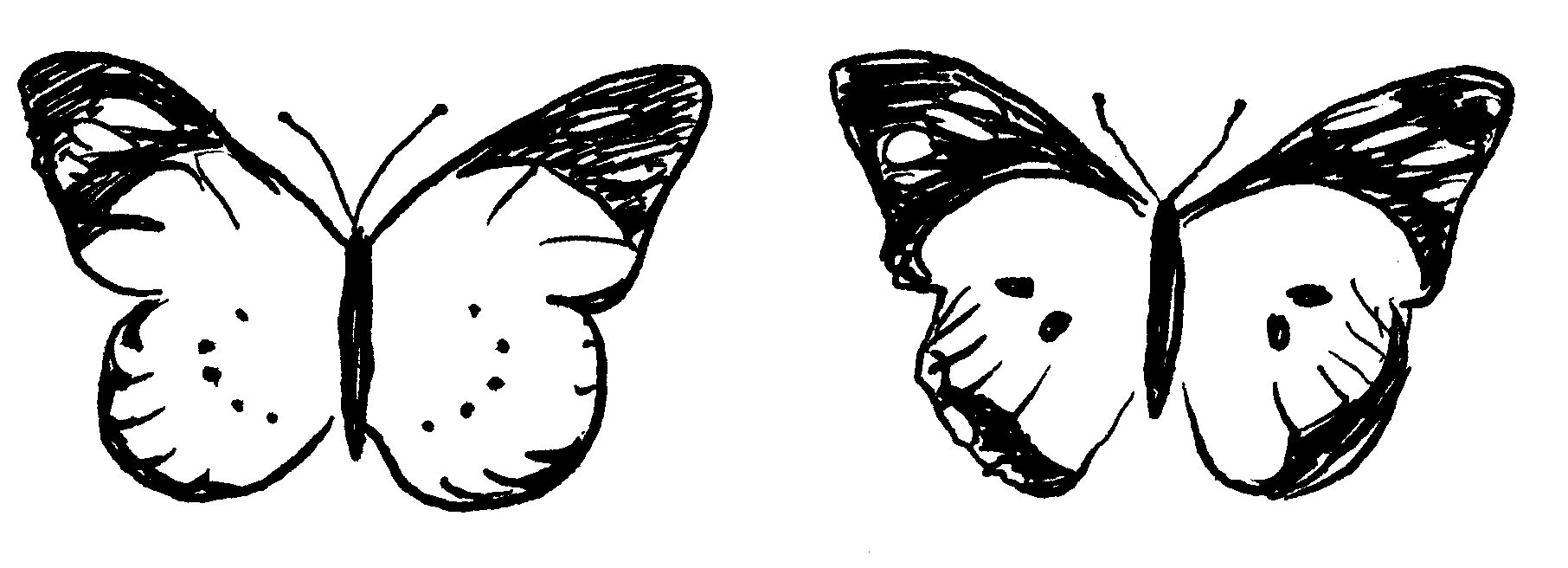

Activity: TO IDENTIFY EXAMPLES OF COLOUR ADAPTATION
Study the sketches and indicate the relevant type of adaptation
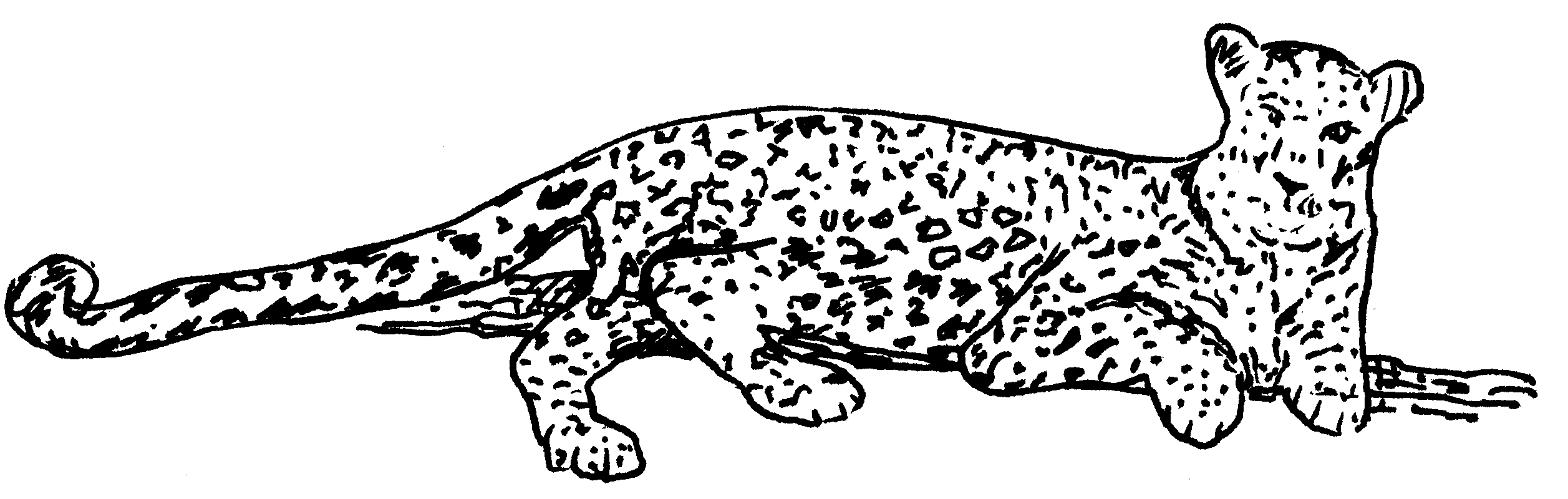


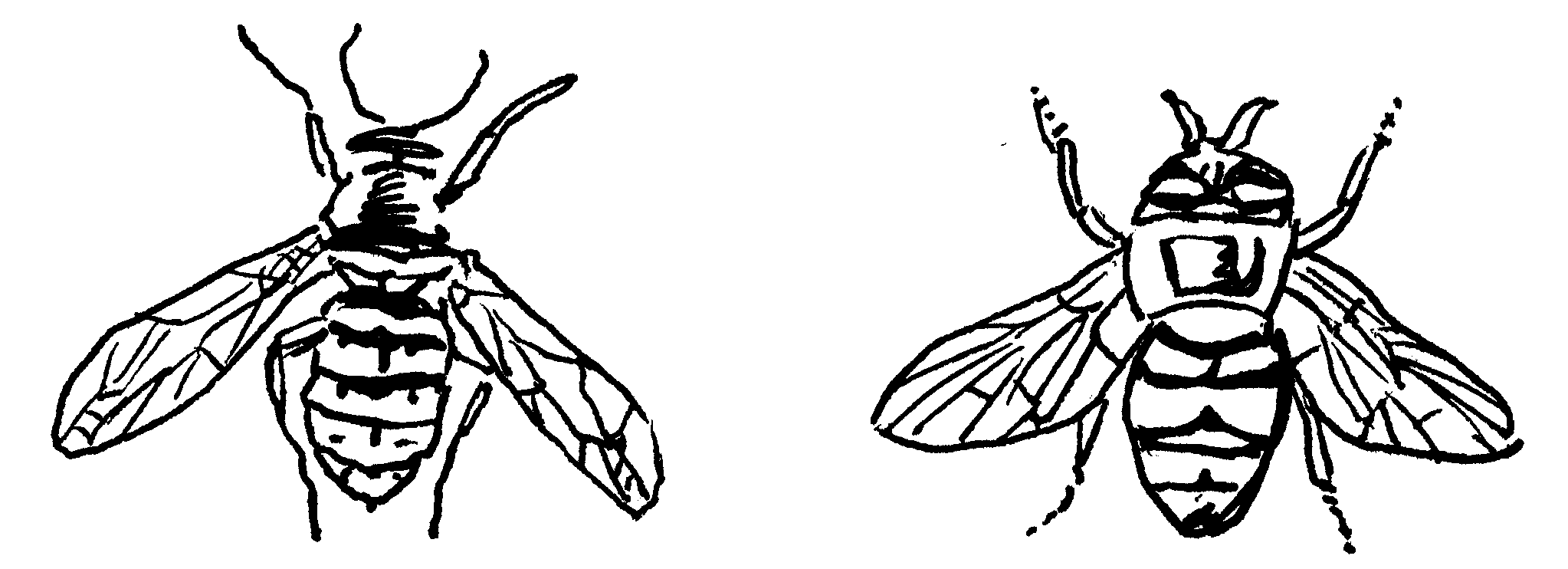
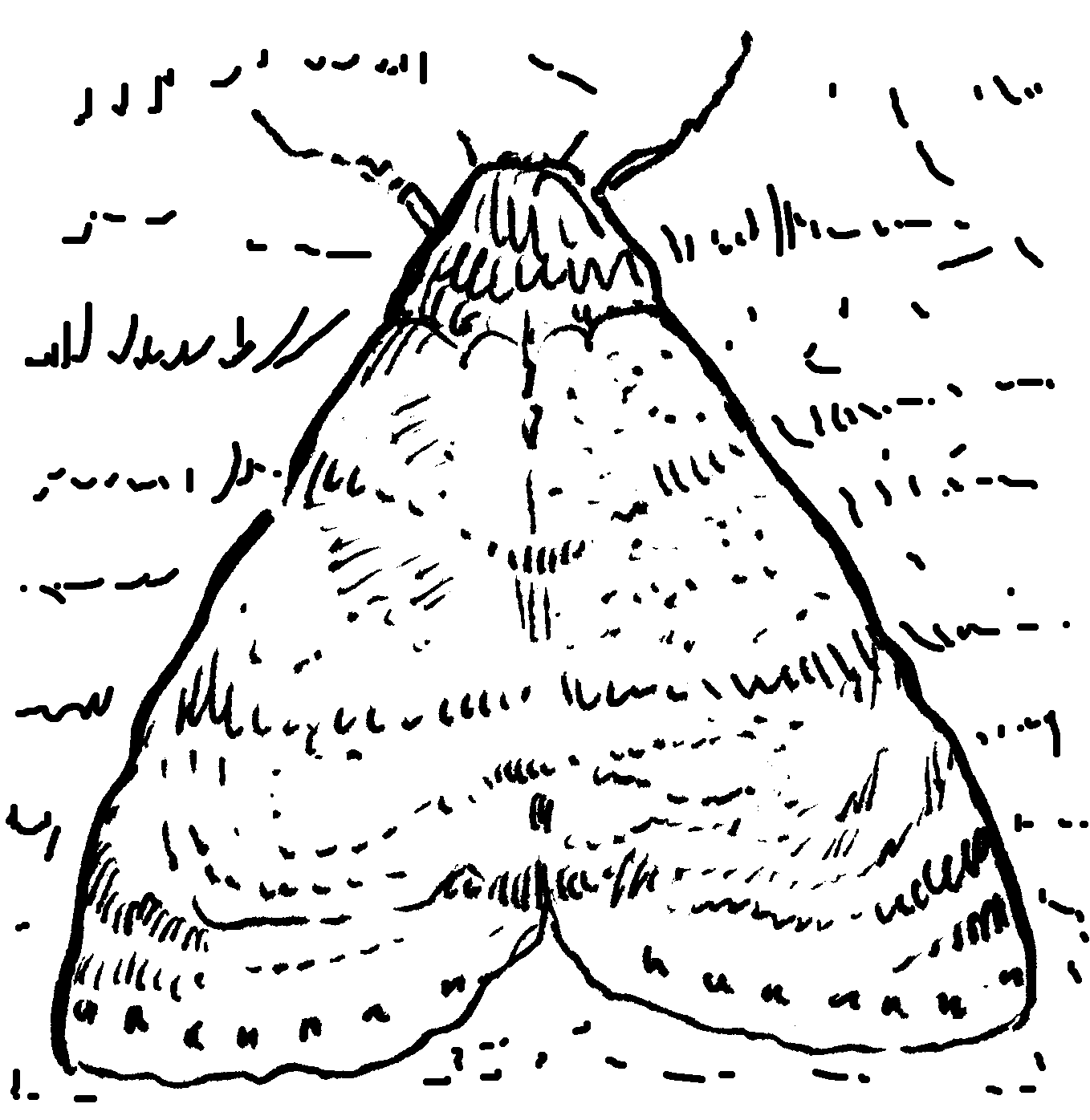
Assessment of APPLICATION:
Could you identify the adaptations correctly?
[LO 2.4]
Learning outcomes 2: Constructing Science Knowledge
The learner will know and be able to interpret and apply scientific, technological and environmental knowledge.
This is evident when the learner
2.1 is able to recall meaningful information;
2.4 is able to apply knowledge.
Activity: IDENTIFICATION – teeth and dentition
Activity: IDENTIFY - COLOUR ADAPTATION

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Natural sciences grade 8' conversation and receive update notifications?