| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Additional ligaments are located inside the vertebral canal, next to the spinal cord, along the length of the vertebral column. The posterior longitudinal ligament is found anterior to the spinal cord, where it is attached to the posterior sides of the vertebral bodies. Posterior to the spinal cord is the ligamentum flavum (“yellow ligament”). This consists of a series of short, paired ligaments, each of which interconnects the lamina regions of adjacent vertebrae. The ligamentum flavum has large numbers of elastic fibers, which have a yellowish color, allowing it to stretch and then pull back. Both of these ligaments provide important support for the vertebral column when bending forward.
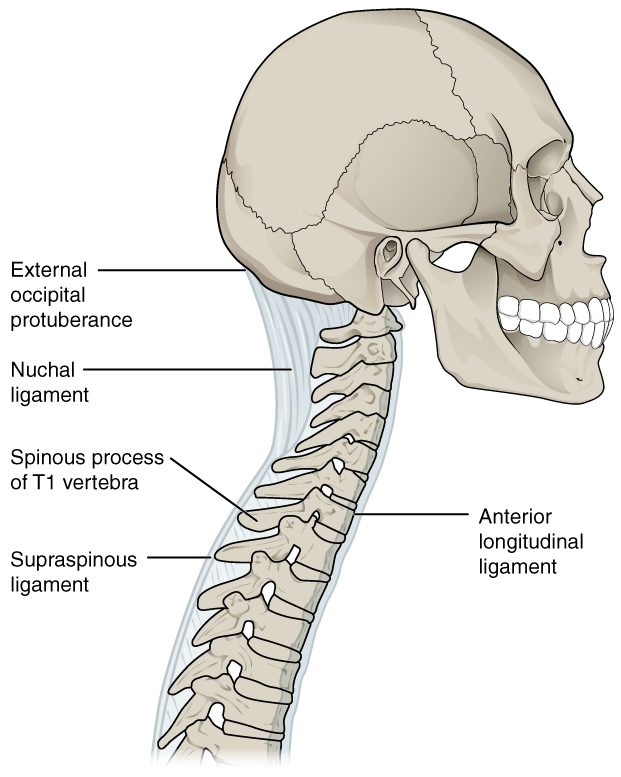
Use this tool to identify the bones, intervertebral discs, and ligaments of the vertebral column. The thickest portions of the anterior longitudinal ligament and the supraspinous ligament are found in which regions of the vertebral column?
Chiropractors use a drug-free, hands-on approach for patient diagnosis and treatment. They will perform a physical exam, assess the patient’s posture and spine, and may perform additional diagnostic tests, including taking X-ray images. They primarily use manual techniques, such as spinal manipulation, to adjust the patient’s spine or other joints. They can recommend therapeutic or rehabilitative exercises, and some also include acupuncture, massage therapy, or ultrasound as part of the treatment program. In addition to those in general practice, some chiropractors specialize in sport injuries, neurology, orthopaedics, pediatrics, nutrition, internal disorders, or diagnostic imaging.
To become a chiropractor, students must have 3–4 years of undergraduate education, attend an accredited, four-year Doctor of Chiropractic (D.C.) degree program, and pass a licensure examination to be licensed for practice in their state. With the aging of the baby-boom generation, employment for chiropractors is expected to increase.
The vertebral column forms the neck and back. The vertebral column originally develops as 33 vertebrae, but is eventually reduced to 24 vertebrae, plus the sacrum and coccyx. The vertebrae are divided into the cervical region (C1–C7 vertebrae), the thoracic region (T1–T12 vertebrae), and the lumbar region (L1–L5 vertebrae). The sacrum arises from the fusion of five sacral vertebrae and the coccyx from the fusion of four small coccygeal vertebrae. The vertebral column has four curvatures, the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacrococcygeal curves. The thoracic and sacrococcygeal curves are primary curves retained from the original fetal curvature. The cervical and lumbar curves develop after birth and thus are secondary curves. The cervical curve develops as the infant begins to hold up the head, and the lumbar curve appears with standing and walking.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology: support and movement' conversation and receive update notifications?