| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
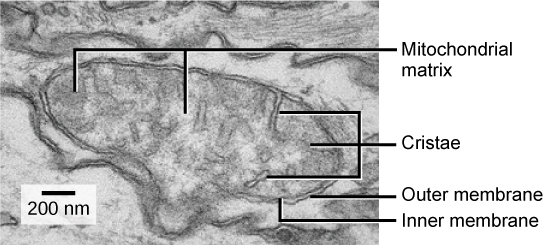
Mitochondria are oval-shaped, double membrane organelles ( [link] ) that have their own ribosomes and DNA. Each membrane is a phospholipid bilayer embedded with proteins. The inner layer has folds called cristae. The area surrounded by the folds is called the mitochondrial matrix. The cristae and the matrix have different roles in cellular respiration.
Peroxisomes are small, round organelles enclosed by single membranes. They carry out oxidation reactions that break down fatty acids and amino acids. They also detoxify many poisons that may enter the body. (Many of these oxidation reactions release hydrogen peroxide, H 2 O 2 , which would be damaging to cells; however, when these reactions are confined to peroxisomes, enzymes safely break down the H 2 O 2 into oxygen and water.) For example, alcohol is detoxified by peroxisomes in liver cells. Glyoxysomes, which are specialized peroxisomes in plants, are responsible for converting stored fats into sugars.
Vesicles and vacuoles are membrane-bound sacs that function in storage and transport. Other than the fact that vacuoles are somewhat larger than vesicles, there is a very subtle distinction between them: The membranes of vesicles can fuse with either the plasma membrane or other membrane systems within the cell. Additionally, some agents such as enzymes within plant vacuoles break down macromolecules. The membrane of a vacuole does not fuse with the membranes of other cellular components.
At this point, you know that each eukaryotic cell has a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, a nucleus, ribosomes, mitochondria, peroxisomes, and in some, vacuoles, but there are some striking differences between animal and plant cells. While both animal and plant cells have microtubule organizing centers (MTOCs), animal cells also have centrioles associated with the MTOC: a complex called the centrosome. Animal cells each have a centrosome and lysosomes, whereas plant cells do not. Plant cells have a cell wall, chloroplasts and other specialized plastids, and a large central vacuole, whereas animal cells do not.
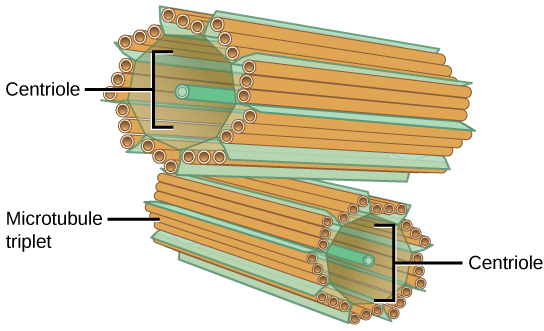
The centrosome is a microtubule-organizing center found near the nuclei of animal cells. It contains a pair of centrioles, two structures that lie perpendicular to each other ( [link] ). Each centriole is a cylinder of nine triplets of microtubules.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ap biology - part 1: the cell' conversation and receive update notifications?