| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In ionic compounds, electrons are transferred between atoms of different elements to form ions. But this is not the only way that compounds can be formed. Atoms can also make chemical bonds by sharing electrons equally between each other. Such bonds are called covalent bonds . Covalent bonds are formed between two atoms when both have similar tendencies to attract electrons to themselves (i.e., when both atoms have identical or fairly similar ionization energies and electron affinities). For example, two hydrogen atoms bond covalently to form an H 2 molecule; each hydrogen atom in the H 2 molecule has two electrons stabilizing it, giving each atom the same number of valence electrons as the noble gas He.
Compounds that contain covalent bonds exhibit different physical properties than ionic compounds. Because the attraction between molecules, which are electrically neutral, is weaker than that between electrically charged ions, covalent compounds generally have much lower melting and boiling points than ionic compounds. In fact, many covalent compounds are liquids or gases at room temperature, and, in their solid states, they are typically much softer than ionic solids. Furthermore, whereas ionic compounds are good conductors of electricity when dissolved in water, most covalent compounds are insoluble in water; since they are electrically neutral, they are poor conductors of electricity in any state.
Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. For example, the hydrogen molecule, H 2 , contains a covalent bond between its two hydrogen atoms. [link] illustrates why this bond is formed. Starting on the far right, we have two separate hydrogen atoms with a particular potential energy, indicated by the red line. Along the x -axis is the distance between the two atoms. As the two atoms approach each other (moving left along the x -axis), their valence orbitals (1 s ) begin to overlap. The single electrons on each hydrogen atom then interact with both atomic nuclei, occupying the space around both atoms. The strong attraction of each shared electron to both nuclei stabilizes the system, and the potential energy decreases as the bond distance decreases. If the atoms continue to approach each other, the positive charges in the two nuclei begin to repel each other, and the potential energy increases. The bond length is determined by the distance at which the lowest potential energy is achieved.
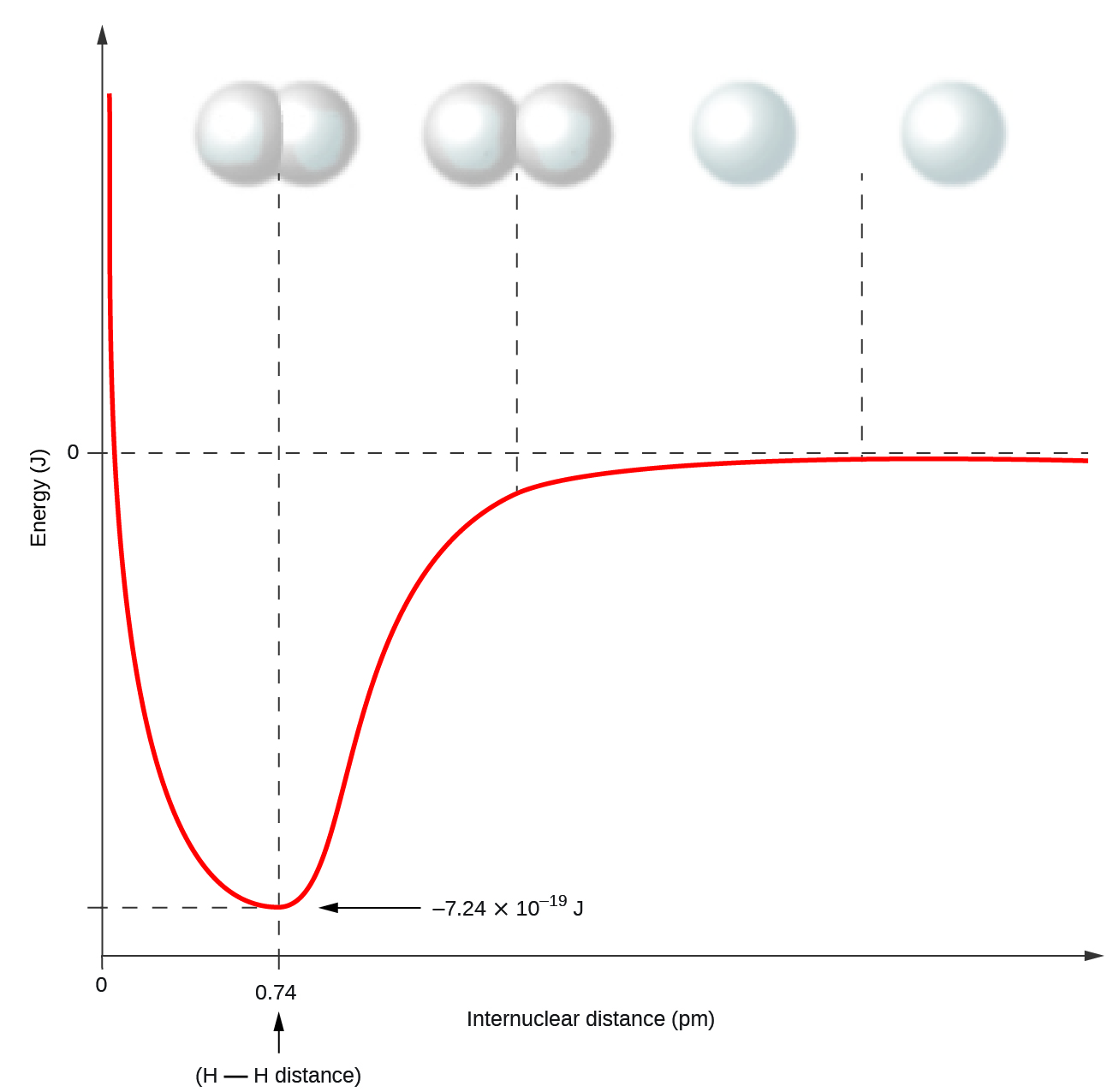
It is essential to remember that energy must be added to break chemical bonds (an endothermic process), whereas forming chemical bonds releases energy (an exothermic process). In the case of H 2 , the covalent bond is very strong; a large amount of energy, 436 kJ, must be added to break the bonds in one mole of hydrogen molecules and cause the atoms to separate:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ut austin - principles of chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?