| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
1.
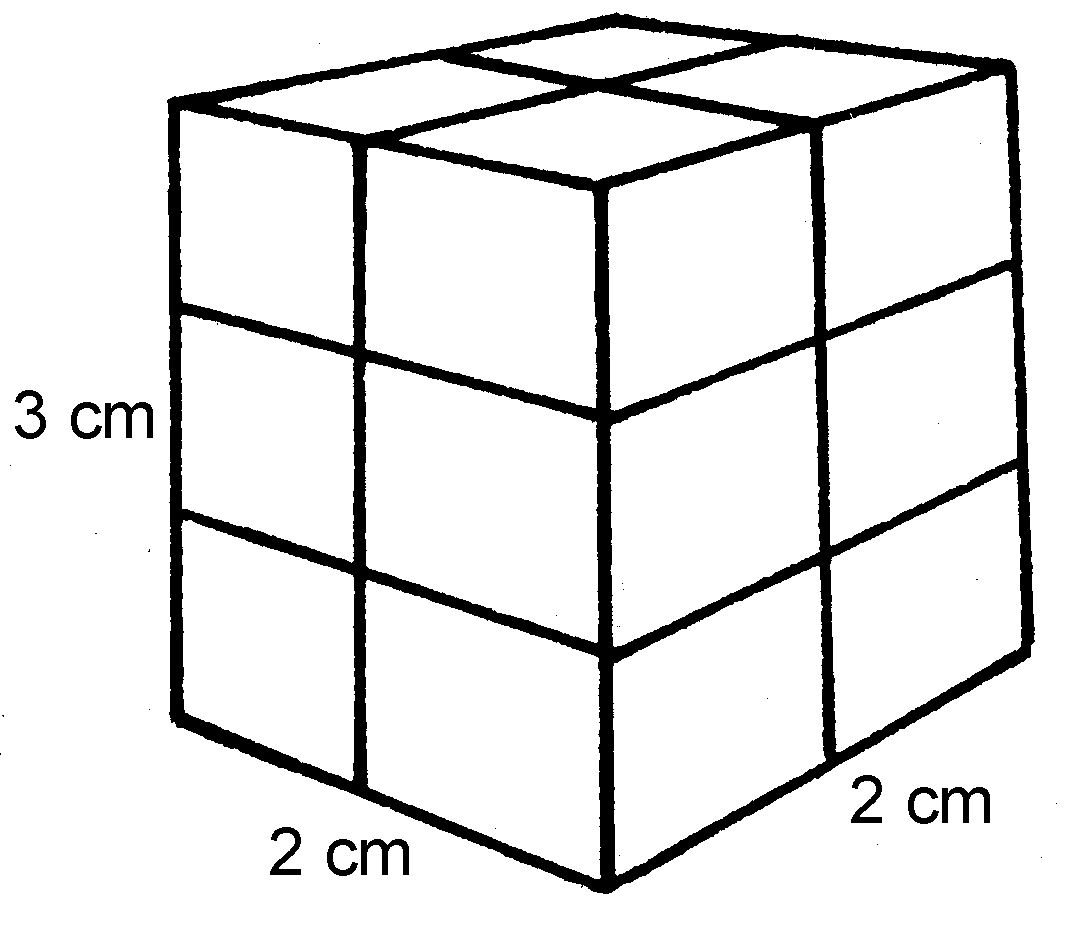
1.1 3 cm × 2 cm × 2 cm = 12 cm³
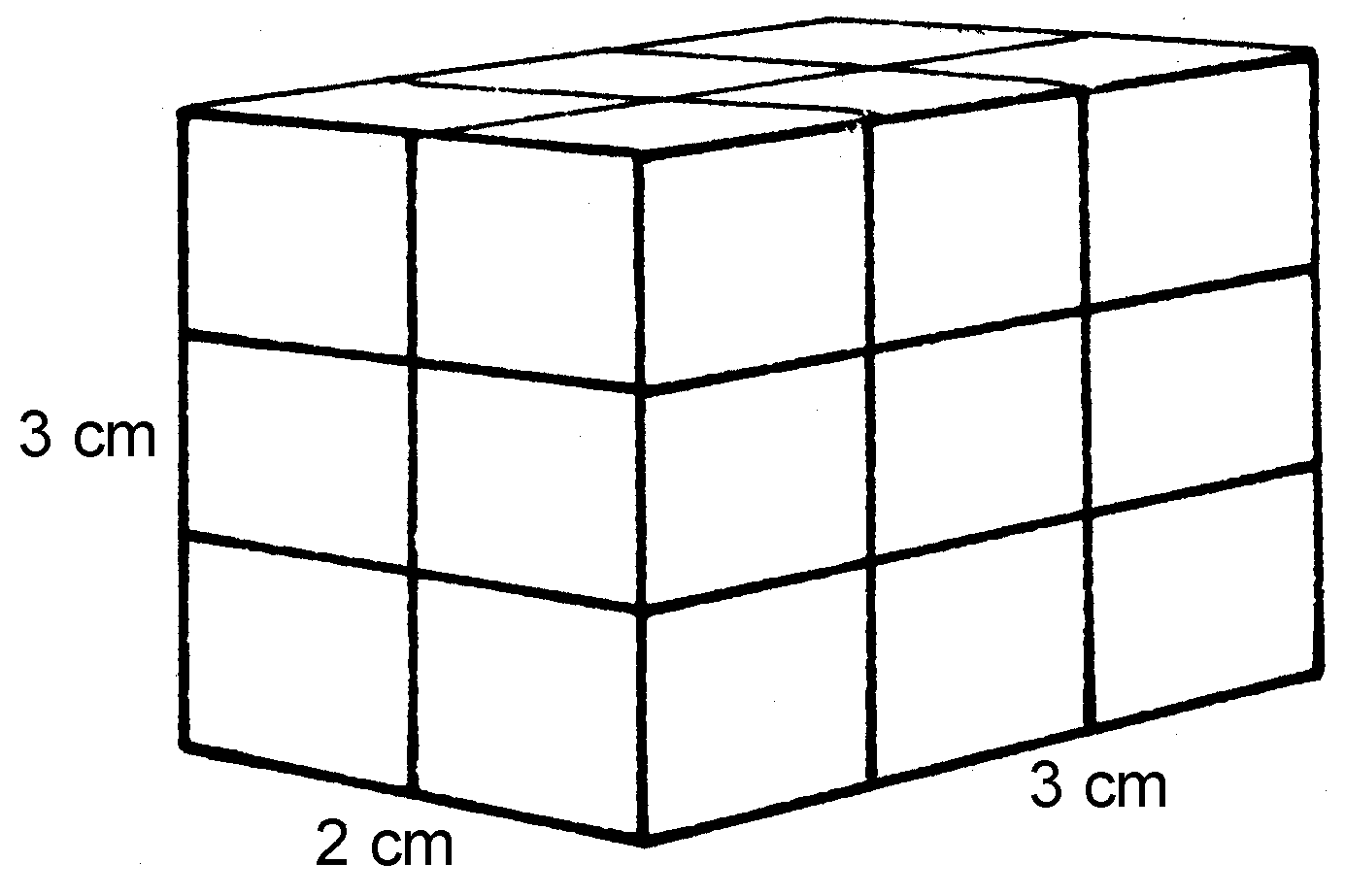
3 cm × 2 cm × 3 cm = 18 cm³
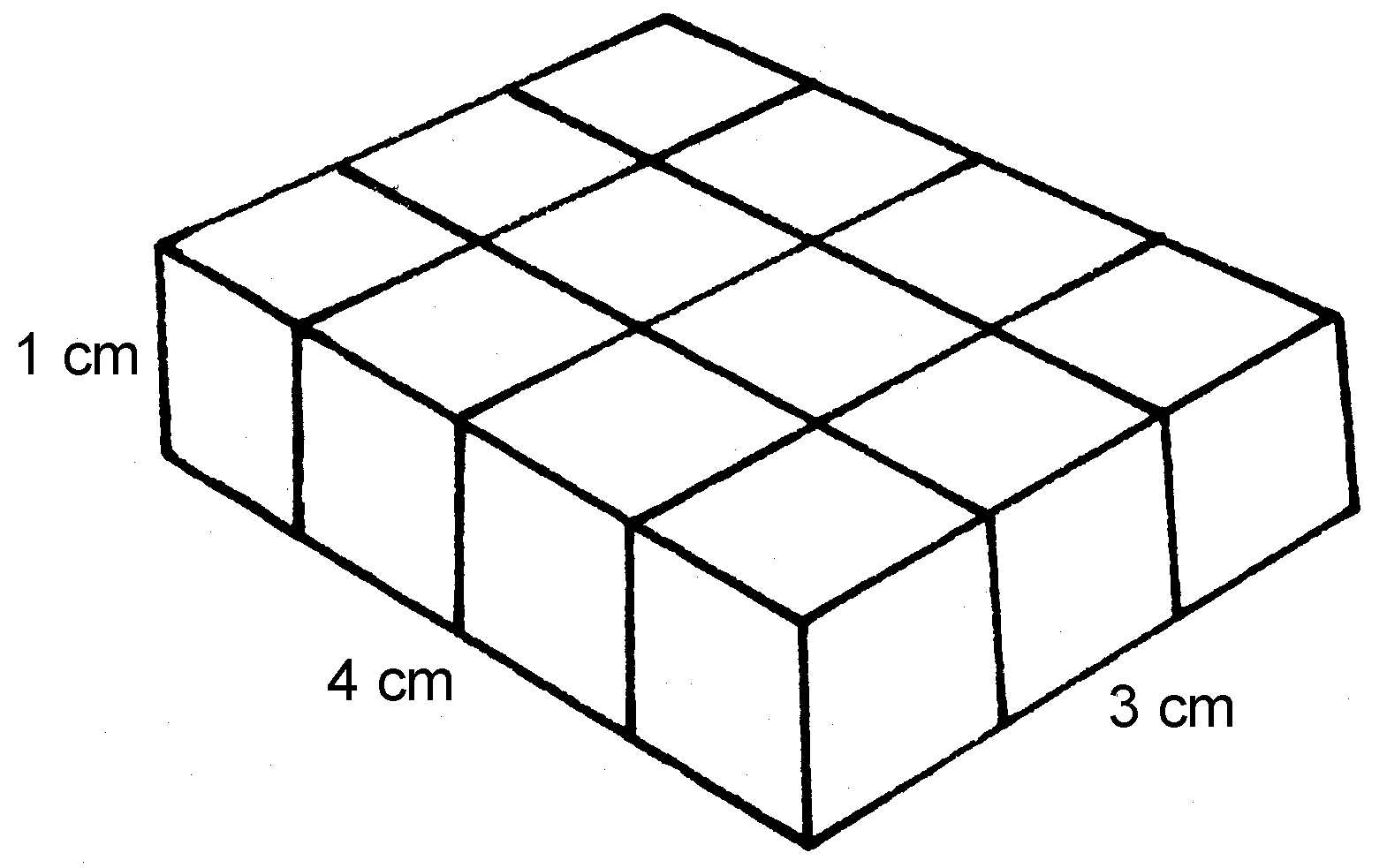
1 cm × 4 cm × 3 cm = 12 cm³
1.2 5 m × 3,5 m × 2 m = 35 m²
1.3 9 cm × 6 cm × 2 cm = 108 cm²
2. 2.1 577 912 cm²
2.1 583 296 cm²
3. (78 cm × 46 cm × 52 cm) ÷ (24 cm × 8 cm × 11 cm)
= 186 576 cm² ÷ 2 112 cm²
= 88,34
= 88 small boxes
1. Calculate the volume of the following:
1.1
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
1.2 A swimming pool 5 m long, 3,5 m wide and 2 m deep.
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
1.3 A tin of tuna: 9 cm by 6 cm by 2 cm.
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
2. Which container has the biggest volume:
2.1: 106 cm by 94 cm by 58 cm, or
_____________________________________________________________________
2.2: 93 cm by 98 cm by 64 cm?.
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
3. How many small boxes with the measurements 24 cm × 8 cm × 11 cm can you pack into a big box of 78 cm by 46 cm by 52 cm?
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
Learning Outcome 1: The learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent numbers and their relationships, and to count, estimate, calculate and check with competence and confidence in solving problems.
Assessment Standard 1.6: We know this when the learner solves problems in context including contexts that may be used to build awareness of other Learning Areas, as well as human rights, social, economic and environmental issues such as:
1.6.2: measurements in Natural Sciences and Technology contexts.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 6' conversation and receive update notifications?