| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Located on the medial wall of the petrous ridge in the posterior cranial fossa is the internal acoustic meatus (see [link] ). This opening provides for passage of the nerve from the hearing and equilibrium organs of the inner ear, and the nerve that supplies the muscles of the face. Located at the anterior-lateral margin of the foramen magnum is the hypoglossal canal . These emerge on the inferior aspect of the skull at the base of the occipital condyle and provide passage for an important nerve to the tongue.
Immediately inferior to the internal acoustic meatus is the large, irregularly shaped jugular foramen (see [link] a ). Several cranial nerves from the brain exit the skull via this opening. It is also the exit point through the base of the skull for all the venous return blood leaving the brain. The venous structures that carry blood inside the skull form large, curved grooves on the inner walls of the posterior cranial fossa, which terminate at each jugular foramen.
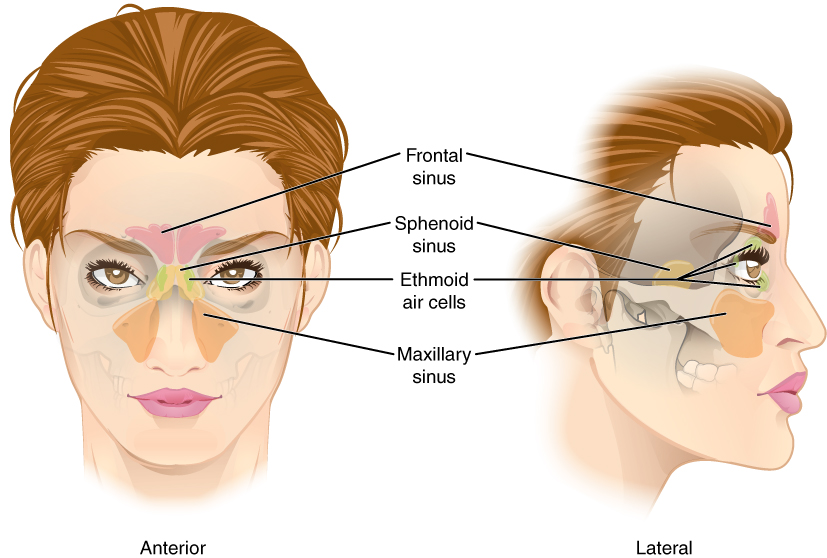
The paranasal sinuses are hollow, air-filled spaces located within certain bones of the skull ( [link] ). All of the sinuses communicate with the nasal cavity (paranasal = “next to nasal cavity”) and are lined with nasal mucosa. They serve to reduce bone mass and thus lighten the skull, and they also add resonance to the voice. This second feature is most obvious when you have a cold or sinus congestion. These produce swelling of the mucosa and excess mucus production, which can obstruct the narrow passageways between the sinuses and the nasal cavity, causing your voice to sound different to yourself and others. This blockage can also allow the sinuses to fill with fluid, with the resulting pressure producing pain and discomfort.
The paranasal sinuses are named for the skull bone that each occupies. The frontal sinus is located just above the eyebrows, within the frontal bone (see [link] ). This irregular space may be divided at the midline into bilateral spaces, or these may be fused into a single sinus space. The frontal sinus is the most anterior of the paranasal sinuses. The largest sinus is the maxillary sinus . These are paired and located within the right and left maxillary bones, where they occupy the area just below the orbits. The maxillary sinuses are most commonly involved during sinus infections. Because their connection to the nasal cavity is located high on their medial wall, they are difficult to drain. The sphenoid sinus is a single, midline sinus. It is located within the body of the sphenoid bone, just anterior and inferior to the sella turcica, thus making it the most posterior of the paranasal sinuses. The lateral aspects of the ethmoid bone contain multiple small spaces separated by very thin bony walls. Each of these spaces is called an ethmoid air cell . These are located on both sides of the ethmoid bone, between the upper nasal cavity and medial orbit, just behind the superior nasal conchae.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology: support and movement' conversation and receive update notifications?