| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A view of the lateral skull is dominated by the large, rounded brain case above and the upper and lower jaws with their teeth below ( [link] ). Separating these areas is the bridge of bone called the zygomatic arch. The zygomatic arch is the bony arch on the side of skull that spans from the area of the cheek to just above the ear canal. It is formed by the junction of two bony processes: a short anterior component, the temporal process of the zygomatic bone (the cheekbone) and a longer posterior portion, the zygomatic process of the temporal bone , extending forward from the temporal bone. Thus the temporal process (anteriorly) and the zygomatic process (posteriorly) join together, like the two ends of a drawbridge, to form the zygomatic arch. One of the major muscles that pulls the mandible upward during biting and chewing arises from the zygomatic arch.
On the lateral side of the brain case, above the level of the zygomatic arch, is a shallow space called the temporal fossa . Below the level of the zygomatic arch and deep to the vertical portion of the mandible is another space called the infratemporal fossa . Both the temporal fossa and infratemporal fossa contain muscles that act on the mandible during chewing.
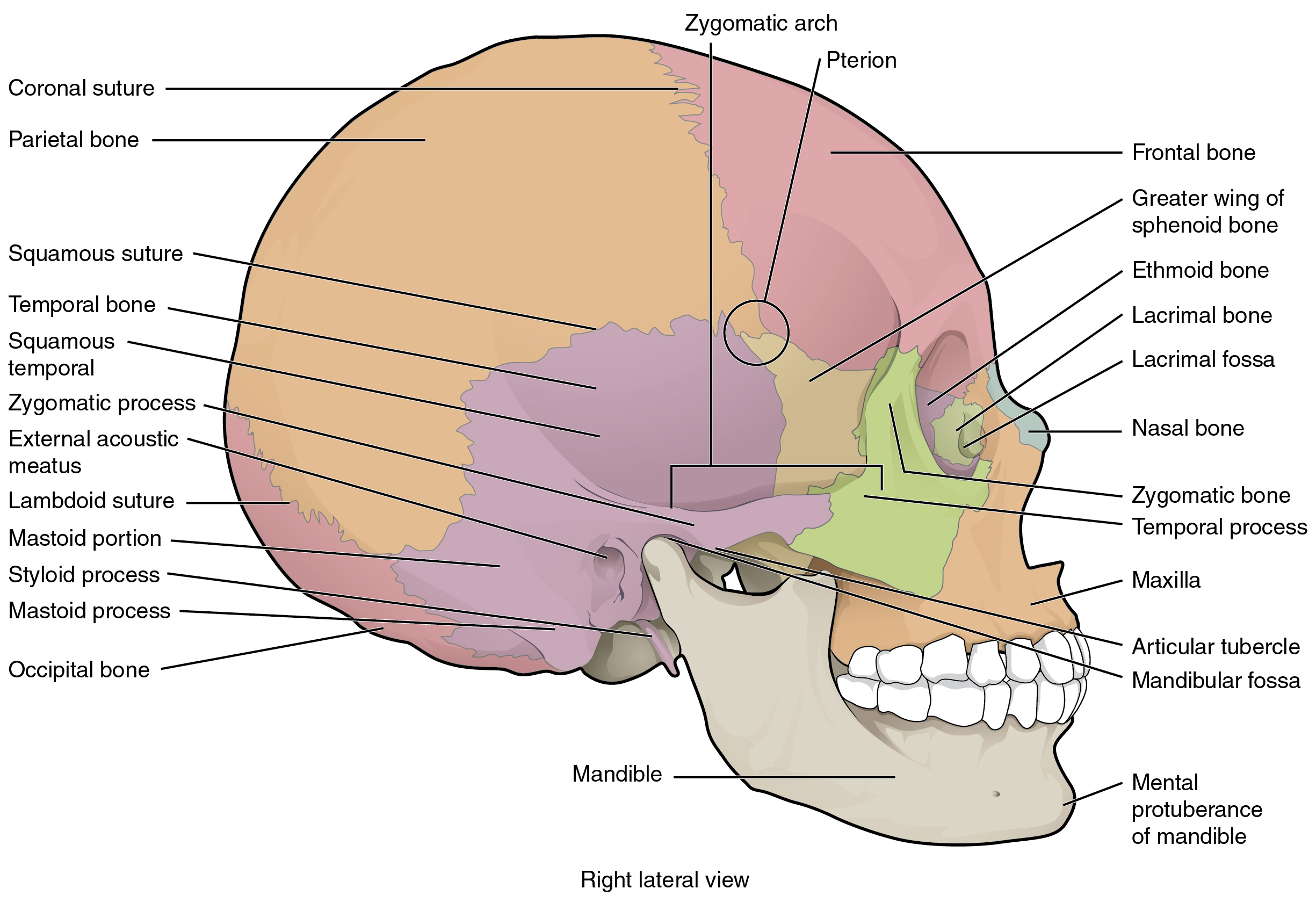
The brain case contains and protects the brain. The interior space that is almost completely occupied by the brain is called the cranial cavity . This cavity is bounded superiorly by the rounded top of the skull, which is called the calvaria (skullcap), and the lateral and posterior sides of the skull. The bones that form the top and sides of the brain case are usually referred to as the “flat” bones of the skull.
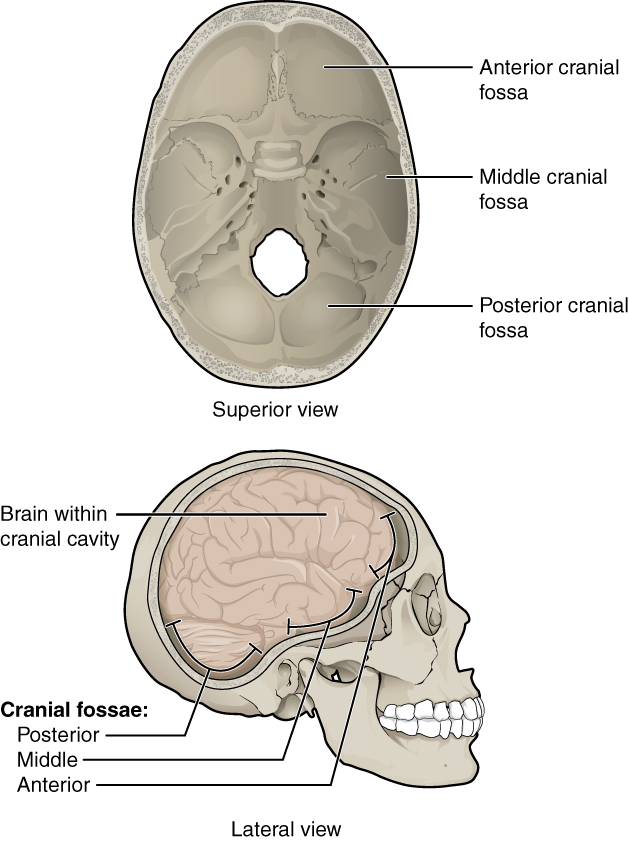
The floor of the brain case is referred to as the base of the skull. This is a complex area that varies in depth and has numerous openings for the passage of cranial nerves, blood vessels, and the spinal cord. Inside the skull, the base is subdivided into three large spaces, called the anterior cranial fossa , middle cranial fossa , and posterior cranial fossa (fossa = “trench or ditch”) ( [link] ). From anterior to posterior, the fossae increase in depth. The shape and depth of each fossa corresponds to the shape and size of the brain region that each houses. The boundaries and openings of the cranial fossae (singular = fossa) will be described in a later section.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology: support and movement' conversation and receive update notifications?