| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
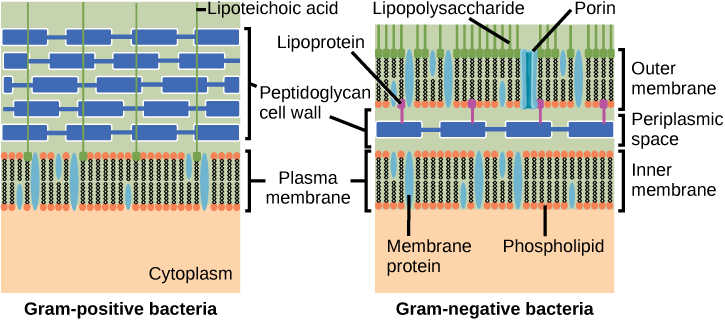
Which of the following statements is true?
Archaean cell walls do not have peptidoglycan. There are four different types of Archaean cell walls. One type is composed of pseudopeptidoglycan , which is similar to peptidoglycan in morphology but contains different sugars in the polysaccharide chain. The other three types of cell walls are composed of polysaccharides, glycoproteins, or pure protein.
| Structural Differences and Similarities between Bacteria and Archaea | ||
|---|---|---|
| Structural Characteristic | Bacteria | Archaea |
| Cell type | Prokaryotic | Prokaryotic |
| Cell morphology | Variable | Variable |
| Cell wall | Contains peptidoglycan | Does not contain peptidoglycan |
| Cell membrane type | Lipid bilayer | Lipid bilayer or lipid monolayer |
| Plasma membrane lipids | Fatty acids | Phytanyl groups |
Reproduction in prokaryotes is asexual and usually takes place by binary fission. Recall that the DNA of a prokaryote exists as a single, circular chromosome. Prokaryotes do not undergo mitosis. Rather the chromosome is replicated and the two resulting copies separate from one another, due to the growth of the cell. The prokaryote, now enlarged, is pinched inward at its equator and the two resulting cells, which are clones, separate. Binary fission does not provide an opportunity for genetic recombination or genetic diversity, but prokaryotes can share genes by three other mechanisms.
In transformation , the prokaryote takes in DNA found in its environment that is shed by other prokaryotes. If a nonpathogenic bacterium takes up DNA for a toxin gene from a pathogen and incorporates the new DNA into its own chromosome, it too may become pathogenic. In transduction , bacteriophages, the viruses that infect bacteria, sometimes also move short pieces of chromosomal DNA from one bacterium to another. Transduction results in a recombinant organism. Archaea are not affected by bacteriophages but instead have their own viruses that translocate genetic material from one individual to another. In conjugation , DNA is transferred from one prokaryote to another by means of a pilus, which brings the organisms into contact with one another. The DNA transferred can be in the form of a plasmid or as a hybrid, containing both plasmid and chromosomal DNA. These three processes of DNA exchange are shown in [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology 1308 bonus credit chapters--from openstax "biology"' conversation and receive update notifications?