| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Any force or combination of forces can cause a centripetal or radial acceleration. Just a few examples are the tension in the rope on a tether ball, the force of Earth’s gravity on the Moon, friction between roller skates and a rink floor, a banked roadway’s force on a car, and forces on the tube of a spinning centrifuge.
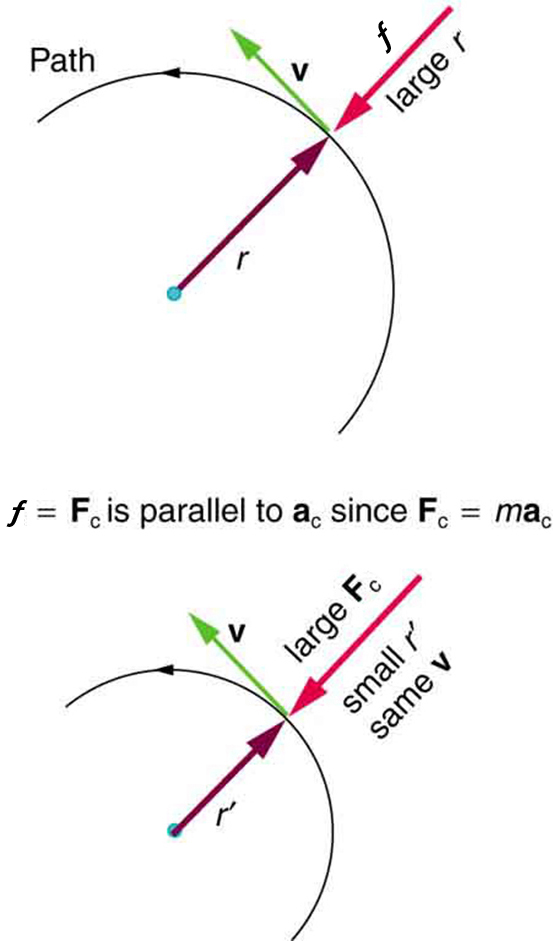
Any net force causing uniform circular motion is called a centripetal force . The direction of a centripetal force is toward the center of curvature, the same as the direction of centripetal acceleration. According to Newton’s second law of motion, net force is mass times acceleration: net . For uniform circular motion, the acceleration is the centripetal acceleration— . Thus, the magnitude of centripetal force is
By using the expressions for centripetal acceleration from , we get two expressions for the centripetal force in terms of mass, velocity, angular velocity, and radius of curvature:
You may use whichever expression for centripetal force is more convenient. Centripetal force is always perpendicular to the path and pointing to the center of curvature, because is perpendicular to the velocity and pointing to the center of curvature.
Note that if you solve the first expression for , you get
This implies that for a given mass and velocity, a large centripetal force causes a small radius of curvature—that is, a tight curve.
(a) Calculate the centripetal force exerted on a 900 kg car that negotiates a 500 m radius curve at 25.0 m/s.
(b) Assuming an unbanked curve, find the minimum static coefficient of friction, between the tires and the road, static friction being the reason that keeps the car from slipping (see [link] ).
Strategy and Solution for (a)
We know that . Thus,
Strategy for (b)
[link] shows the forces acting on the car on an unbanked (level ground) curve. Friction is to the left, keeping the car from slipping, and because it is the only horizontal force acting on the car, the friction is the centripetal force in this case. We know that the maximum static friction (at which the tires roll but do not slip) is , where is the static coefficient of friction and N is the normal force. The normal force equals the car’s weight on level ground, so that . Thus the centripetal force in this situation is
Now we have a relationship between centripetal force and the coefficient of friction. Using the first expression for from the equation

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics subject knowledge enhancement course (ske)' conversation and receive update notifications?