| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
1. Density = mass per volume. Therefore
(a) = 1,6 g/cm 3
(b) = 2,5 g/cm 3
(c) 8,7 g/cm 3
(d) = 7,7 g/cm 3
(e) 0,8 g/cm 3
2. Use two liquids that do not mix. Pour them in a glass jug. The liquid with the lower density will float on the other, e.g. oil on water.
Drop a 50-cent coin and a wooden block into a glass dish that is half full of water. The coin will sink and the wooden block will float.

_____________________________________________________________________
The block weighs more than the coin, but floats because it has less density. When we combine the mass and the volume of a substance, we are dealing with the density of the particular substance.
The five blocks below are of equal size, but are made of different substances. The volume of each is exactly 10 cubic centimetres (10 cm3). The approximate mass of each is given.
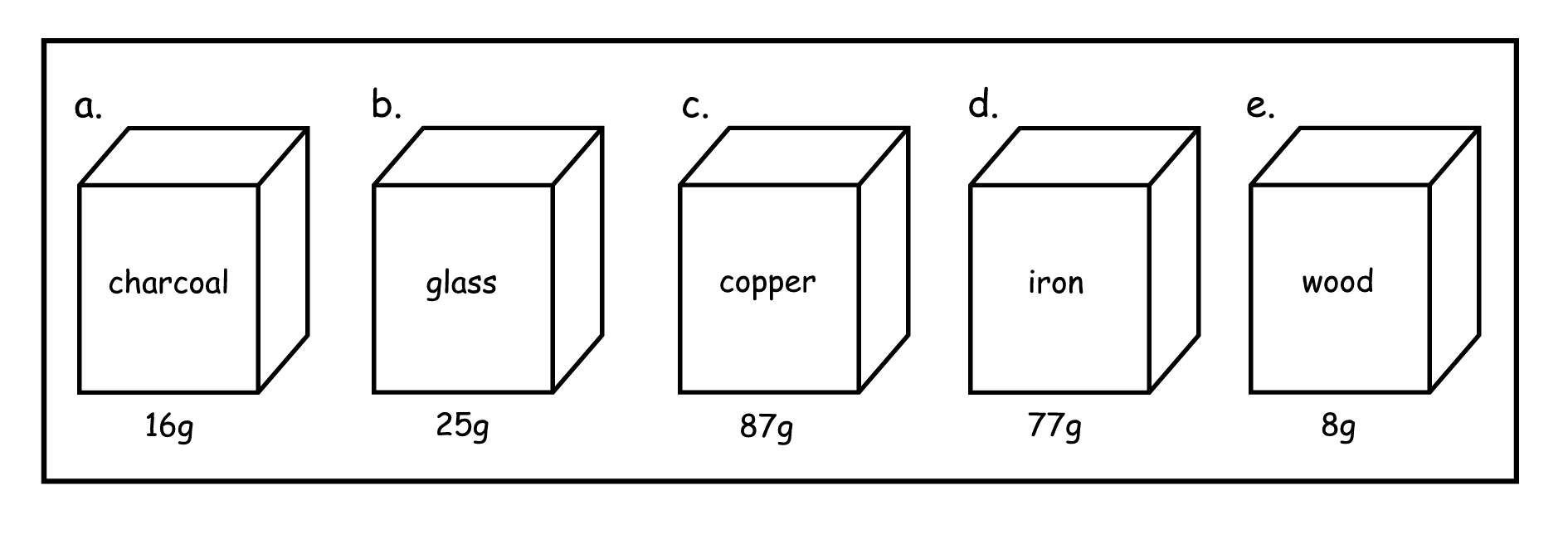
We can compare the mass of the five substances because they have the same volume.
The mass in gram of 1 cmз of a substance is known as its density.
1. Indicate the density of each of the blocks.
(a) __________________________________________________________________
(b) __________________________________________________________________
(c) __________________________________________________________________
(d) __________________________________________________________________
(e) __________________________________________________________________
2. Describe what you would do (with the help of a glass beaker and two liquid substances) to illustrate that the density of different liquid substances also varies. (Suggestion: First decide which liquids you would use).
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
Learning Outcome 1: The learner will be able to act confidently on curiosity about natural phenomena, and to investigate relationships and solve problems in scientific, technological and environmental contexts.
Assessment Standard 1.1: We know this when the learner plans investigations: plans simple tests and comparisons and considers how to conduct these properly.
Learning Outcome 2: The learner will know and be able to interpret and apply scientific, technological and environmental knowledge.
Assessment Standard 2.4: We know this when the learner application of knowledge: applies knowledge appropriately by connecting the learnt concept to a variation of the known situation.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Natural sciences grade 7' conversation and receive update notifications?