| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
3. Volume of stone:
Take a first reading of the water in the measuring-cylinder. Then bind thread around the stone and lower it into the water-filled cylinder. Wait for all the air bubbles to escape and take the second reading. Subtract the first reading from the second to determine the volume of the stone.
The examples that follow will help you to understand how volumes of solid bodies are measured.
(We use objects that can be fitted into the measuring cylinder):
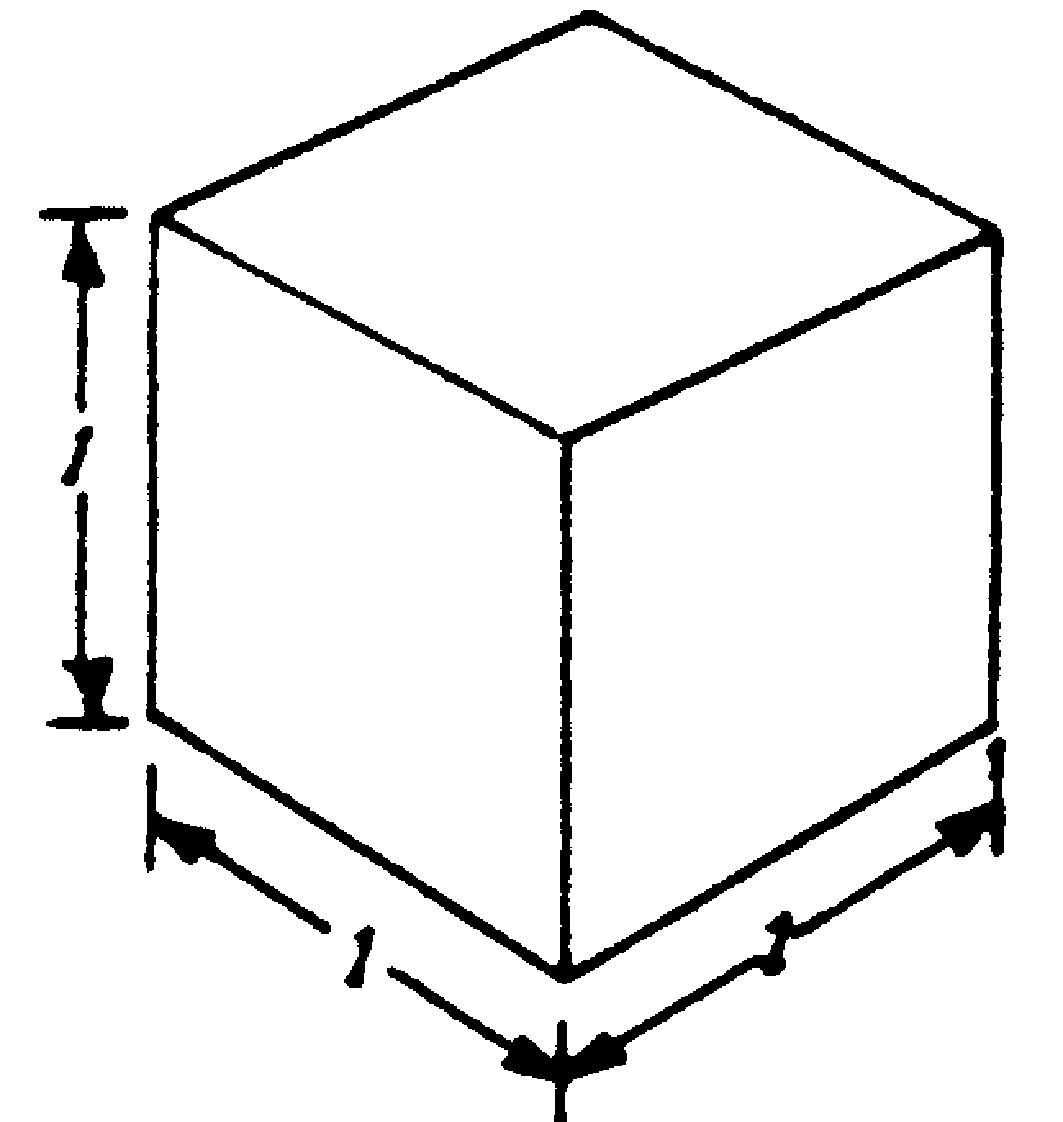
A cube is a solid that has six square plane faces. The angle between two adjacent angles is a right angle. V = ℓ3
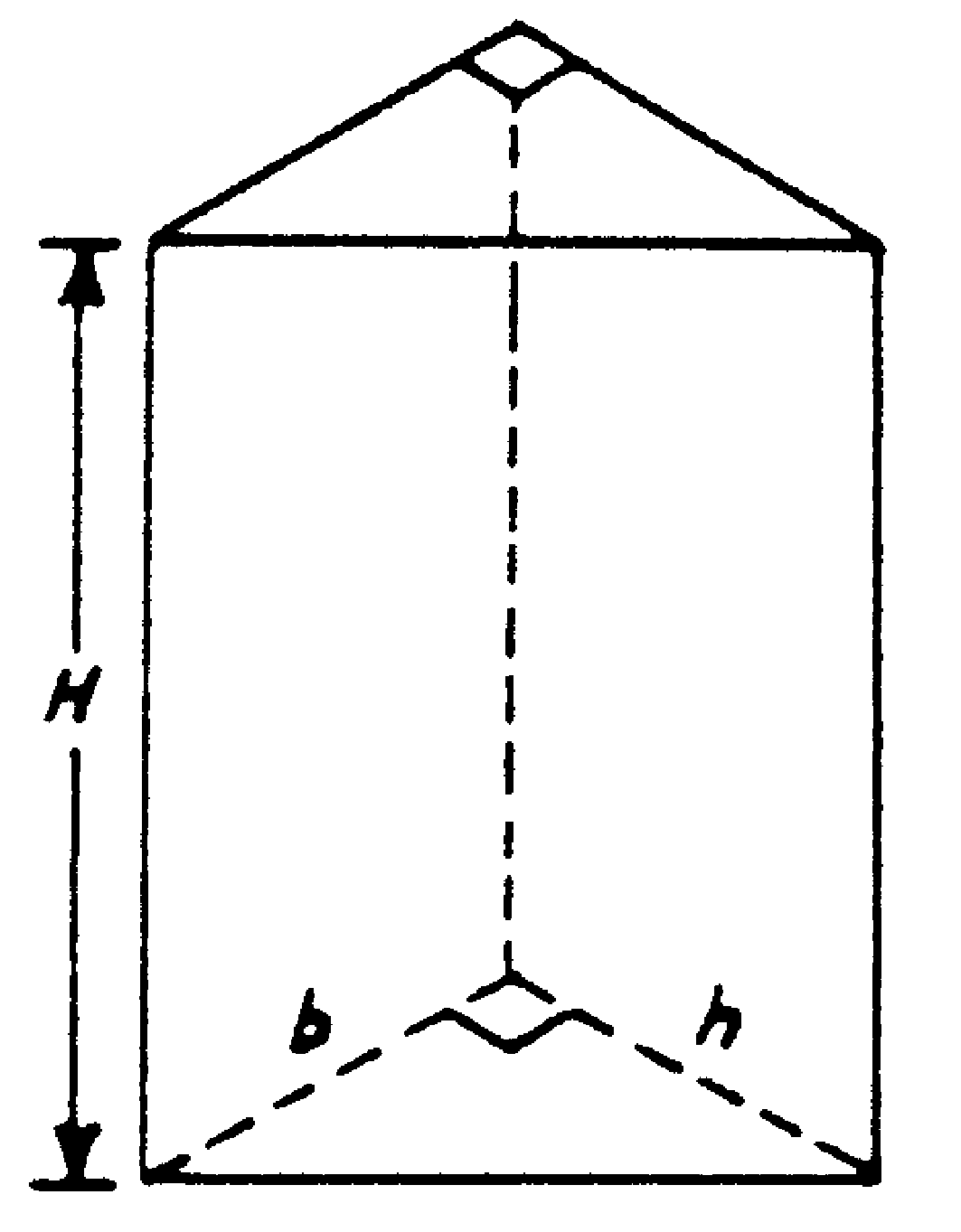
A triangular prism is a five-sided (polygonal) solid with identical triangular end planes and three rectangular plane faces perpendicular to the end planes.
V = ½bhH
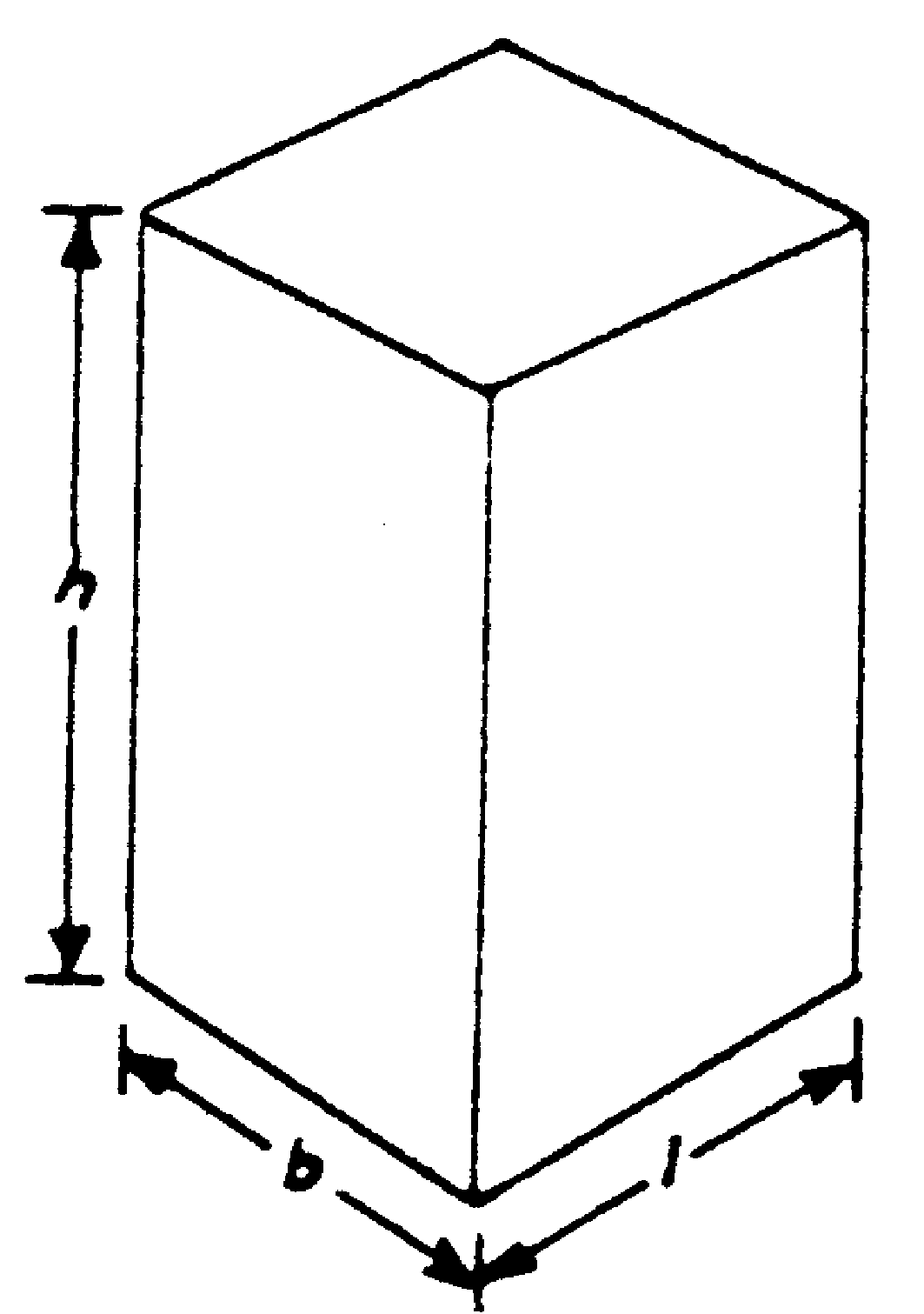
A rectangular prism is a six-sided (hexagonal) solid that has two identical rectangular end planes and four side planes perpendicular to the end planes.
V = ℓbh
A cube is a solid that has six square plane faces. The angle between two adjacent angles is a right angle.V = ℓ3 A triangular prism is a five-sided (polygonal) solid with identical triangular end planes and three rectangular plane faces perpendicular to the end planes.V = ½bhH A rectangular prism is a six-sided (hexagonal) solid that has two identical rectangular end planes and four side planes perpendicular to the end planes.V = ℓbh
There are two methods for measuring the volume of the above objects:
The water displacement technique operates as follows:
The measuring cylinder is filled with water to the halfway mark. This halfway mark is your first reading of the water level. Now carefully lower the object of which the volume must be measured into the measuring cylinder.
Tap the side of the measuring cylinder to ensure that all air bubbles escape.

1. Now use both these methods to determine the volumes of the given objects:
| Object | Volume as calculated | Volume: Water displacement |
| Metal cube | ||
| Rectangular glass brick | ||
| Prism |
6 x ½ = (3)
2. Was there any difference between the results obtained by the different methods?
_____________________________________________________________________
(1)
How do you explain the difference, if any, that you observe?
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
(2)
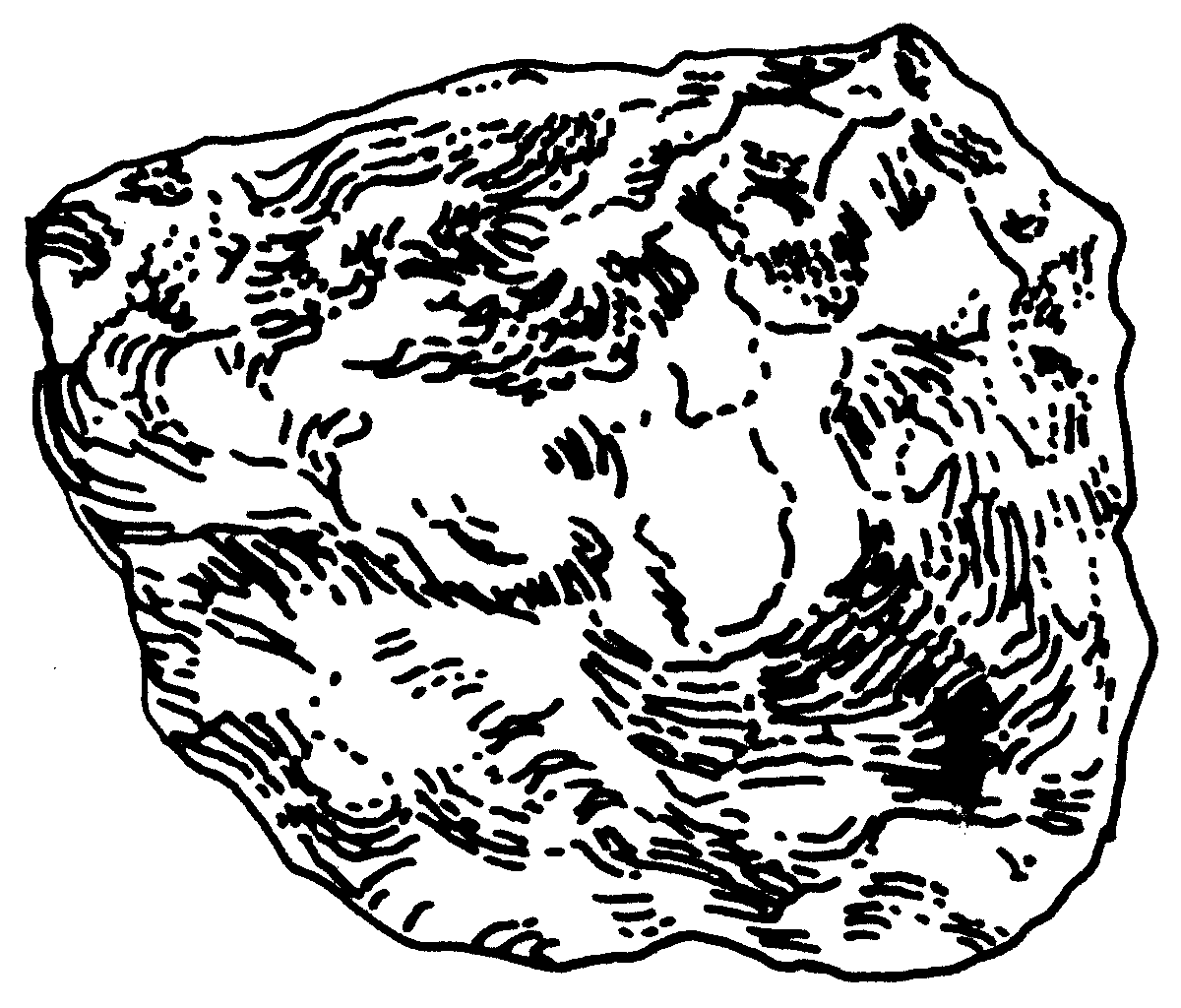
3. Explain how you would determine the volume of a stone such as the one illustrated below?
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
(2)
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
(2)
Learning Outcome 1: The learner will be able to act confidently on curiosity about natural phenomena, and to investigate relationships and solve problems in scientific, technological and environmental contexts.
Assessment Standard 1.2: We know this when the learner conducts investigations and collects data: organises and uses apparatus/equipment or sources to gain and record information.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Natural sciences grade 7' conversation and receive update notifications?